How usually have you ever caught your self pondering, “Wouldn’t it’s simpler handy the mission over to AI as a substitute of paying a group of builders?” It’s a tempting thought, particularly within the age of AI — however the actuality is way extra complicated.
On this article, we’ll discover what AI can truly do in software program improvement, the place it nonetheless falls quick in comparison with people, and what conclusions firms ought to draw earlier than entrusting a mission to synthetic intelligence.
When AI Tried to Play Software program Engineer
Just lately, a shopper approached SCAND with a novel experiment in thoughts. They needed to check whether or not synthetic intelligence might independently develop a small internet software and determined to make use of Cursor for the duty. The applying’s goal was easy — fetch statistics from an exterior API and show them in a desk.
The preliminary end result appeared promising: AI created a functioning mission that included each client- and server-side parts, applied the fundamental logic for retrieving information, and even designed the interface. The desk accurately displayed the statistics, and the general code construction appeared respectable at first look.
Nevertheless, upon nearer inspection, it grew to become clear that the answer was overengineered. As an alternative of instantly connecting to the API and displaying the info within the browser, AI constructed a full backend server that proxied requests, saved intermediate information, and required separate deployment.
For such a easy job, this was pointless — it difficult the infrastructure, added additional setup steps, and lengthened the mixing course of.
Furthermore, AI didn’t account for error dealing with, request optimization, or integration with the shopper’s current techniques. This meant builders needed to step in and redo elements of the answer.
The Limits of Generative AI in Coding and Software program Improvement
Generative AI has already confirmed that it could possibly rapidly produce working code, however in follow, its capabilities in real-world software program improvement usually transform restricted. Listed below are the important thing points we often encounter when reviewing AI‑generated initiatives:
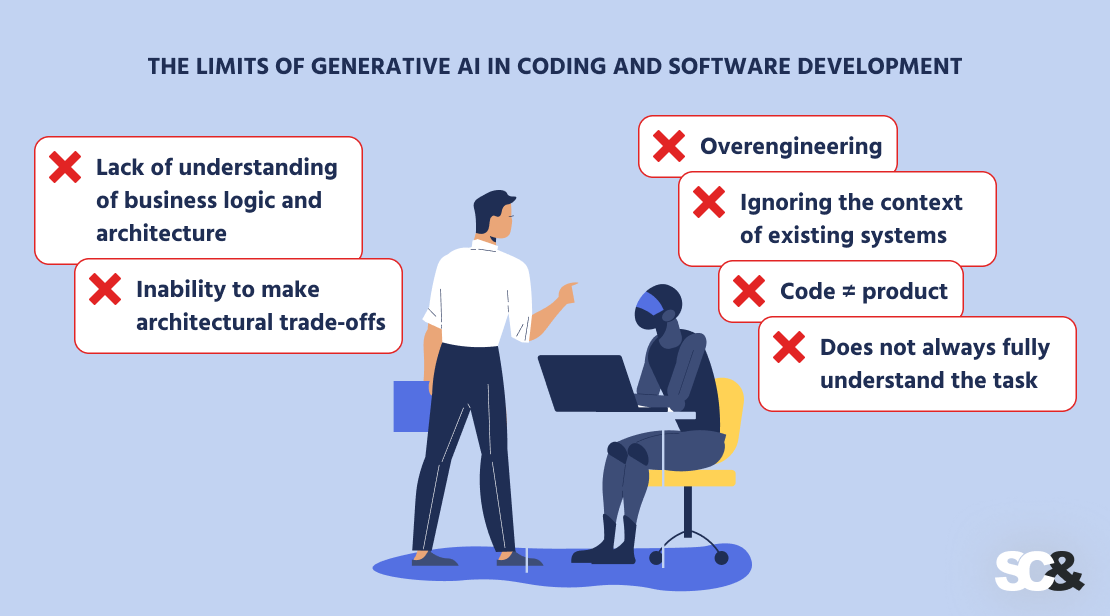
- Lack of know-how of enterprise logic and structure. AI can’t see the total image of a mission, its objectives, and its constraints. In consequence, the options it produces could also be technically appropriate however utterly misaligned with the precise enterprise wants.
- Incapability to make architectural commerce‑offs. An skilled software program engineer evaluates the steadiness between improvement pace, implementation price, and ease of upkeep. AI, alternatively, can’t weigh these components and tends to decide on an ordinary and even unnecessarily complicated strategy.
- Overengineering. Producing pointless layers, modules, and providers is a standard mistake. For instance, a easy software could find yourself with an additional backend that requires separate deployment and upkeep.
- Ignoring the context of current techniques. AI doesn’t have in mind how new code will combine with the present infrastructure, which might result in incompatibilities or extra prices for rework.
- Code ≠ product. Synthetic intelligence can write fragments of code, however it doesn’t ship full options that have in mind UX, safety, scalability, and long-term assist.
- Doesn’t at all times totally perceive the duty. To get the specified end result, prompts usually have to be clarified or rewritten in additional element — typically stretching to a full web page. This slows down the method and forces the developer to spend time refining the request as a substitute of transferring on to efficient implementation.
In the end, regardless of the rising position of AI in software program improvement, with out the involvement of skilled builders, such initiatives danger turning into a supply of technical debt and pointless prices.
Why Human Software program Builders Nonetheless Beat AI Brokers
Sure, generative AI and agentic AI can write code at this time — typically even pretty good code. However there are nonetheless some issues that synthetic intelligence can’t change in an expert software program developer’s workflow..
First, it’s understanding the enterprise context. A human doesn’t simply write a program — they know why and for whom it’s being created. AI sees a set of directions; a developer sees the true job and understands the way it matches into the corporate’s objectives.
Second comes the flexibility to make knowledgeable choices — whether or not to reuse current code or construct one thing from scratch. A human weighs deadlines, prices, and dangers. AI, in flip, usually follows a template with out taking hidden prices into consideration.
Third, it’s architectural flexibility. An skilled programmer can really feel when a mission is beginning to “develop” pointless layers and is aware of when it’s the fitting time to cease. AI, alternatively, usually creates extreme buildings just because that’s what it has seen in its coaching examples.
Fourth comes interested by the product’s future. Scalability, maintainability, and dealing with edge circumstances are constructed right into a developer’s mindset. AI will not be but able to anticipating such nuances.
And at last, communication. A real software program engineer works with the shopper, clarifies necessities, and adjusts the strategy because the mission evolves. AI will not be able to actual dialogue or a delicate understanding of human priorities.
Subsequently, in at this time’s software program improvement panorama, synthetic intelligence remains to be a device — not a strategist. And within the foreseeable future, the human position in creating excessive‑high quality software program will stay important.
The desk beneath compares how people and AI deal with key facets of improvement, and why the human position within the course of remains to be necessary.
| Criterion | Software program Developer | Generative AI |
| Understanding enterprise context | Analyzes mission objectives, target market, and long-term aims | Sees solely the given immediate, with out understanding the larger image |
| Making architectural choices | Balances pace, price, simplicity, and maintainability | Follows a template with out contemplating hidden prices |
| Structure optimization | Avoids pointless modules and simplifies when potential | Liable to overengineering, creating additional layers |
| Working with current techniques | Considers integration with present infrastructure | Could generate incompatible options |
| Foresight | Plans for scalability, error dealing with, and edge circumstances | Typically ignores non‑normal situations |
| Collaboration | Engages with the shopper, clarifies necessities, gives options | Understands the request in a restricted approach, requires exact and detailed prompts |
| Flexibility in course of | Adapts to altering necessities on the fly | Requires code regeneration or a brand new immediate |
| Velocity of code technology | Focuses on correctness and stability over uncooked pace | Generates code immediately, however it’s not at all times helpful or appropriate |
| Closing deliverable | Prepared‑to‑use product | A set of code requiring overview and refinement |
Human Builders vs AI in Software program Improvement
The place AI Coding Instruments and Agentic AI Can Assist Software program Engineers
Regardless of its limitations, AI instruments have some strengths that make them useful assistants for software program engineers. In accordance with Statista (2024), 81% of builders worldwide reported elevated productiveness when utilizing AI, and greater than half famous improved work effectivity.
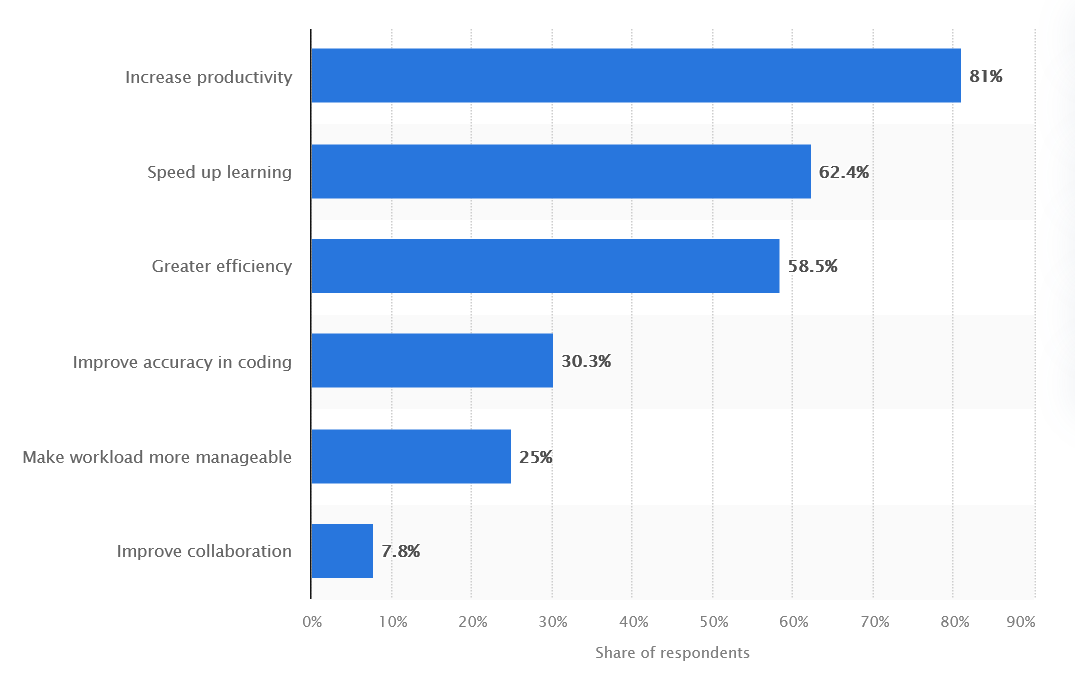
Advantages of utilizing AI within the improvement workflow, Statista
In day‑to‑day improvement, AI can considerably pace up routine duties and simplify supporting processes, reminiscent of:
- Producing boilerplate code. Generative AI can produce repetitive code buildings in seconds, saving time and permitting builders to give attention to enterprise logic.
- Creating easy parts. AI can rapidly construct buttons, kinds, tables, and different UI components that may later be tailored to the mission’s wants.
- Changing codecs. Synthetic intelligence can simply rework information and code — from JSON to YAML or from TypeScript to JavaScript, and again.
- Refactoring. AI can counsel code enhancements, simplify buildings, and take away duplicates.
- Fast prototyping. AI can construct a fundamental model of performance to check concepts or exhibit ideas to a shopper.
Nevertheless, even in these use circumstances, AI stays only a device. The ultimate model of the code ought to at all times undergo human overview and integration to make sure it meets architectural necessities, high quality requirements, and the mission’s enterprise context.
SCAND’s Strategy — AI + Human Experience within the Age of AI
At SCAND, we see synthetic intelligence not as a competitor to builders, however as a device that strengthens the group. Our initiatives are constructed on a easy precept: AI accelerates — people information.
We use Copilot, ChatGPT, Cursor, and different AI instruments the place they really add worth — for rapidly creating templates, producing easy parts, and testing concepts. This enables us to save hours and days on routine duties.
However code technology is barely the start. Each AI‑produced resolution goes by means of the fingers of our skilled builders who:
- Verify the correctness and safety of the code, together with potential license and copyright violations, since some items of the recommended code could replicate fragments from open repositories.
- Optimize the structure for the duty and mission specifics.
- Adapt technical options to the enterprise logic and mission necessities.
We additionally pay particular consideration to information safety and confidentiality:
- We don’t switch confidential information to public cloud-based AI with out safety, except the shopper particularly requests in any other case. In initiatives involving delicate or regulated data (for instance, medical or monetary information), we use native AI assistants — Ollama, LM Studio, llama.cpp, and others — deployed on the shopper’s safe servers.
- We signal clear contracts that specify: who owns the ultimate code, whether or not AI instruments are allowed, and who’s chargeable for reviewing and fixing the code if it violates licenses or accommodates errors.
- We embrace obligations for documentation (AI utilization logs indicating when precisely and which instruments have been used) to trace the supply of potential points and guarantee transparency for audits.
- We offer group coaching on AI finest practices, together with understanding the restrictions of AI-generated content material, licensing dangers, and the significance of handbook validation.
Will AI Exchange Software program Engineers? The Sensible Actuality Verify
Immediately, synthetic intelligence in software program improvement is on the identical stage that calculators have been in accounting just a few a long time in the past: a device that hastens calculations, however doesn’t perceive why and what numbers have to be calculated.
Generative AI can already do lots — from producing parts to performing automated refactoring. However constructing a software program product is not only about writing code. It’s about understanding the viewers, designing structure, assessing dangers, integrating with current techniques, and planning lengthy‑time period assist for years forward. And that is the place the human issue stays irreplaceable.
As an alternative of the “AI replaces builders” state of affairs, we’re transferring towards a combined‑group mannequin, the place AI brokers turn into a part of the workflow and builders use them as accelerators and assistants. This synergy is already reshaping the software program improvement panorama and can proceed to outline it within the coming years.
The primary takeaway: the age of AI doesn’t eradicate the career of software program engineer — it transforms it, including new instruments and shifting priorities from routine coding towards structure, integration, and strategic design.
Steadily Requested Questions (FAQs)
Can AI write a whole app?
Sure, however usually with out optimization, with over‑engineered structure, and with out contemplating lengthy‑time period maintainability.
Will AI change frontend/backend builders?
Not but, since most improvement choices require enterprise context, commerce‑offs, and expertise that AI doesn’t possess.
What’s the most important impression of AI-generated code?
An elevated danger of technical debt, maintainability points, and architectural misalignment — all of which might finally drive up the price of rework.


