Many software program firms and repair suppliers in the present day promote migration companies as a normal path towards modernization. It sounds compelling: new frameworks, quicker efficiency, and extra maintainable code.
Nonetheless, migration is sort of by no means a easy expertise substitute: it’s an costly venture that may take months and require redesigning components of the system.
Subsequently, the important thing query will not be “which tech is best,” however “will the transition yield actual enterprise advantages or will it change into a expensive initiative with out tangible outcomes?”
In follow, many migrations turn into conditions the place the prices of rewriting, testing, and stabilizing the system are monumental, whereas the enterprise receives no measurable profit: customers don’t discover the adjustments, the timelines for brand new options don’t speed up, and the dangers solely double.
What Is Software program Migration?
Typically phrases, migration is the method of transferring an current utility from one tech stack, framework, or platform to a different, and it typically kinds a central a part of legacy modernization efforts by updating outdated programs whereas preserving core performance, enterprise workflows, and integrations.
Nonetheless, migrating an utility not often entails simply “switching frameworks.” In follow, it typically requires rewriting UI parts, adjusting structure, redesigning CI/CD pipelines, offering safety compliance, and retraining groups.
Why IT Infrastructure Migration Is Usually Underestimated
In actuality, migration prices are ceaselessly underestimated as a result of many crucial dependencies are hidden.
Even when an utility appears modular, real-world enterprise programs typically include undocumented workflows, tightly coupled parts, outdated patterns, and fragile integrations that solely change into seen throughout implementation.
Think about an enterprise e-commerce platform: a seemingly remoted product catalog module may depend on customized stock companies, analytics occasions, and promotional logic scattered throughout a number of components of the codebase.
Such a state of affairs typically results in the so-called migration paradox: the best investments happen within the preliminary phases, whereas the seen advantages seem late, or generally under no circumstances.
Organizations could spend months auditing, rewriting, testing, and stabilizing a brand new system, solely to finally obtain trivial enterprise enhancements.
In different phrases, migration can flip right into a prolonged and dear modernization initiative the place the technical adjustments are actual, however the return on funding for the enterprise is minimal.
When Migration Is Justified (Excessive-ROI Situations)
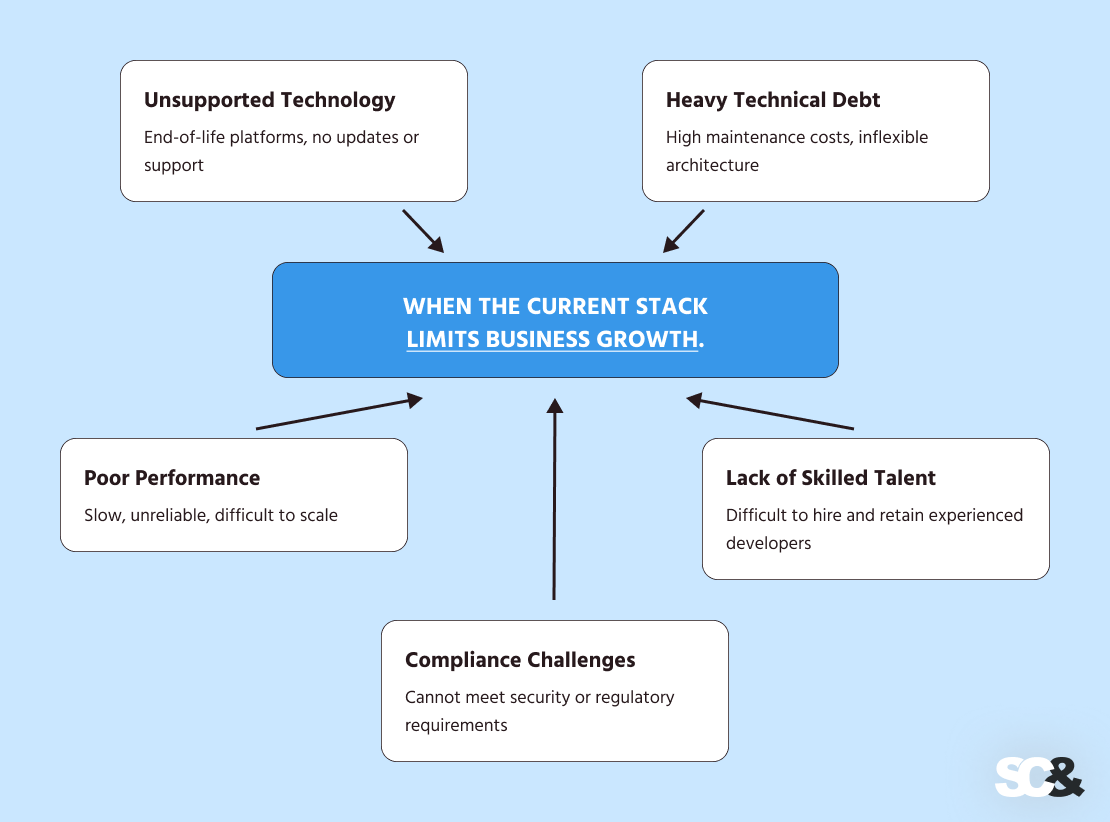
Migration turns into a strategically sound determination when the present stack begins to dam enterprise development, increase drawback areas, or restrict agility.
When Migration Is Justified (Excessive-ROI Situations)
Expertise Is No Longer Supported
Migration turns into vital when the present platform or framework reaches end-of-life. Unsupported instruments introduce safety vulnerabilities, stop entry to updates, and complicate upkeep.
Examples embrace AngularJS, which formally reached end-of-life in December 2021, or older variations of the .NET Framework not supported by Microsoft. Legacy JavaScript libraries like jQuery 1.x or outdated cellular frameworks corresponding to PhoneGap/Cordova additionally fall into this class.
In such circumstances, migrating to a contemporary framework like React, Angular, or .NET Core supplies help and stability, in addition to reduces problematic areas.
Technical Debt Blocks the Roadmap
When each new function requires advanced workarounds or prolonged growth time, technical debt slows down additional development.
Legacy code can embrace tightly coupled UI parts, outdated state administration patterns, or hard-coded enterprise guidelines which are troublesome to refactor.
For instance:
- A legacy CRM system constructed on an previous model of Spine.js could require a number of interdependent adjustments simply so as to add a brand new reporting module.
- An e-commerce platform utilizing jQuery 1.x for interactive parts may want intensive rewrites to implement fashionable cost workflow sequences.
- A monetary dashboard counting on outdated server-rendered templates might decelerate the rollout of latest analytics widgets, growing time-to-market.
Migrating to a contemporary stack permits groups to scale back technical debt, simplify upkeep, and develop and deploy new options means quicker.
Expertise Shortages Have an effect on Supply
Difficulties in hiring builders proficient in outdated frameworks can restrict venture growth.
Switching to extensively used applied sciences supplies entry to a broader pool of specialists, simplifying workforce scaling and accelerating the event course of. This method is commonly utilized by firms that have to rapidly develop their engineering groups to fulfill enterprise wants.
Efficiency Impacts Income
Functions with gradual consumer interfaces, excessive infrastructure prices, or restricted scalability can straight have an effect on income. For instance, a legacy journey reserving portal constructed on server-rendered templates may expertise lengthy load occasions throughout peak site visitors.
Rebuilding its frontend with a contemporary, component-based structure can drastically scale back web page load occasions, enhance responsiveness, and improve reserving conversion charges (although the complete efficiency features typically additionally rely on backend optimizations).
Compliance Necessities Can not Be Met
Industries corresponding to fintech, healthcare, and insurance coverage typically require frameworks that help fashionable safety, audit, and compliance requirements.
Older programs could lack the pliability to combine the required measures, making migration the one approach to successfully meet regulatory necessities.
Structure Can not Scale
Monolithic or tightly coupled programs can hinder modular growth, the implementation of microfrontends, or distributed deployment. Migration (partial or full) permits groups to implement scalable, simply maintainable architectures that present long-term development and practical resilience.
When Migration Is NOT Justified (Most Frequent Low-ROI Circumstances)
Although software program builders typically promise long-term features with migrations, not each initiative is definitely definitely worth the funding. Understanding the frequent low-ROI circumstances helps keep away from expensive initiatives that devour assets in useless.
Recognition Alone Is Not a Motive
Adopting a expertise just because it’s at the moment “fashionable” not often results in significant enterprise advantages.
Rewriting a secure product simply to make use of a extra well-liked framework typically consumes important time and funds with out bettering efficiency, maintainability, or consumer expertise.
For example, a well-functioning logistics administration system constructed on a reasonably older however secure platform could run as meant for years. Switching applied sciences solely for hype might stall function supply and influence day-to-day operations.
The Present System Fulfills Enterprise Wants
If current applied sciences successfully help the product growth plan and each day operations, migration could show to be an pointless expense. Firms typically underestimate the effectiveness of mature programs.
For instance, an stock monitoring platform that reliably directs 1000’s of transactions per day could not considerably profit from migration. It might be higher to give attention to refining current work cycles or enhancing particular person modules.
Cleanup Objectives Are Higher Served by Refactoring
Not all technical issues require a whole system overhaul. Refactoring problematic parts or upgrading particular person modules can remove bottlenecks quicker and at a a lot decrease price than a whole transition.
Let’s say, updating cost processing logic or report era modules in a legacy system can scale back errors and enhance maintainability with out the necessity to substitute your entire utility.
Speedy Pace Features Are Unrealistic
Migration initiatives inevitably decelerate the implementation of latest options for a number of months, as groups be taught new approaches, rewrite modules, and conduct intensive testing.
Sustaining two programs in parallel throughout a phased migration additional complicates the method and reduces general productiveness.
For example, a buyer help portal might even see delayed rollout of latest ticketing options if the shift is tried mid-year, doubtlessly affecting service KPIs.
Lack of Clear Possession or Success Metrics
With out clearly specified objectives, KPIs, or possession, a transition initiative turns into open-ended and costly. Groups could spend months rewriting modules or reconfiguring structure with out seen outcomes.
For example, a advertising and marketing automation platform might bear a full tech migration, but nonetheless fail to enhance marketing campaign launch pace if success metrics are usually not established upfront.
The Angular → React Instance: Why Migration Produces Weak ROI
Utility re-platforming can generally really feel just like the pure step ahead, particularly when a expertise appears “outdated” or when the market promoting suggests a swap.
Nonetheless, in lots of circumstances, migration will not be the wisest selection. A transparent instance comes from frontend growth, significantly when an organization decides to maneuver from Angular to React.
Transferring an current Angular utility to React is commonly assumed to modernize the frontend and scale back upkeep prices, however this assumption will be deceptive.
First, it’s necessary to notice that older Angular functions are usually not routinely “legacy.” Usually, it may be a lot less complicated and extra affordable to improve an current Angular app to the newest model fairly than rewriting it from scratch.
Upgrading retains the present codebase and avoids the huge upfront bills related to a whole rewrite. Rewriting a whole frontend in a brand new framework is at all times dearer, and enterprise stakeholders are not often keen to incur pointless losses.
In line with tough estimates, 90% of firms would favor to take care of a legacy Angular utility and pay for continued help fairly than make investments a big sum in a full transition which will bear new bugs.
After all, there are conditions the place migration might make sense. For example, if the present Angular model is simply too previous to improve feasibly, or if the present structure prevents implementing fashionable options, a swap to a different framework may be justified.
However even in such circumstances, it’s essential to conduct a radical evaluation and examine the bills of making and sustaining the present Angular-based system with the potential prices of a brand new expertise.
Developer availability, wage variations, and familiarity with associated applied sciences (e.g., builders skilled in Nest.js typically already know TypeScript and Angular ideas) could make transitioning to a brand new framework simpler than it appears.
This manner, the efficiency advantages of switching to React seldom justify the price and time wanted for a full migration. A React-based model of the identical utility is unlikely to have efficiency features massive sufficient to offset the time of re-development work.
Typically, retraining current builders or progressively modernizing the present Angular utility proves way more sensible and financially acceptable.
Learn how to Consider Migration ROI Earlier than Approving It
Earlier than committing to re-platforming, it’s necessary to grasp if the trouble and value will really carry worth. Here’s a structured plan that will help you consider the return on funding.
- Assess Firm Objectives: Step one is to acknowledge the principle causes for re-platforming. Is it to enhance efficiency, scale back bills, entry a bigger expertise pool, or scale a system? If the present expertise already helps these objectives, migration will not be justified.
- Estimate Prices: Calculate the whole effort required, together with rewriting code, redesigning structure, retraining builders, testing, and briefly working parallel programs. Don’t neglect the prices for sustaining the brand new system in the course of the transition.
- Evaluate Advantages vs. Dangers: Think about each tangible and intangible advantages, corresponding to quicker growth, higher UI efficiency, or decreased technical debt. Stability these towards delayed function supply, potential bugs, and enterprise disruption.
- Think about Expertise and Useful resource Availability: Consider in case your workforce has the required abilities for the brand new expertise. Hiring builders for a brand new framework or retraining current ones provides time and value.
- Use Metrics and Benchmarks: At any time when attainable, quantify anticipated features. For instance, estimate enhancements in load occasions, function supply pace, or upkeep. Evaluate these figures towards migration prices to see if the venture is more likely to repay.
| Issue | What to Verify | If Danger Is Excessive… | Greatest Motion |
| Agility vs. Stability | Can the software program adapt rapidly to vary? | Structure is simply too inflexible | Think about transition |
| Hiring Danger | Is it laborious/costly to rent for the present stack? | Expertise pool is shrinking | Migration could repay |
| Roadmap Strain | Does tech gradual function supply? | Options take too lengthy | Swap or modernize |
| Compliance & Safety | Can the answer meet laws and audits? | Gaps can’t be mounted simply | Migration justified |
| Structure Limits | Can it scale and evolve? | Monolith blocks development | Transition or modularization |
| Consumer Efficiency Affect | Does UI pace have an effect on retention/income? | Customers really feel the lag | Optimize or migrate |
A Sensible Determination Framework
Migration Technique Choices and Commerce-Offs
Upgrading an utility can observe totally different paths, and it’s necessary to differentiate which approaches actually represent a re-platforming versus less complicated modernization actions.
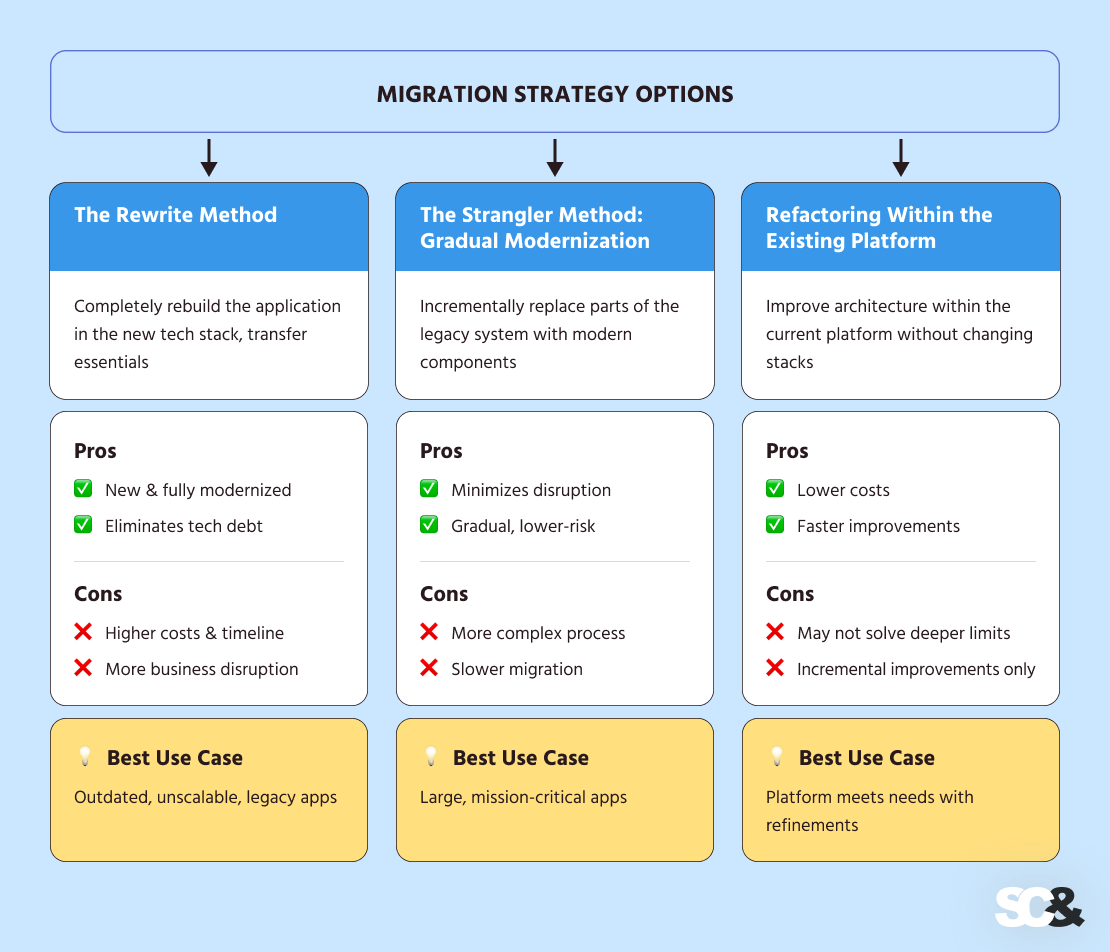
The Rewrite Technique
This technique entails creating a very new utility, transferring solely essentially the most important enterprise logic from the previous system.
- Execs: Gives a completely modernized system, reduces collected technical debt.
- Cons: Excessive preliminary prices, longer implementation occasions, and potential disruptions to enterprise operations in the course of the transition interval.
- Greatest Use Case: Appropriate when the present utility is outdated, closely coupled, or can not scale to fulfill future necessities.
The Strangler Technique: Gradual Modernization
As a substitute of rewriting the whole lot without delay, this method replaces components of the legacy software program progressively. New modules are constructed within the goal expertise and built-in alongside the previous software program till the legacy system is absolutely retired.
- Execs: Minimizes disruptions to enterprise operations, permits for the distribution of prices over time, and permits testing and verification of parts earlier than full substitute.
- Cons: Extra advanced to handle a number of programs, doubtlessly slower general migration, requires cautious integration planning.
- Greatest Use Case: Preferrred when the applying is massive, mission-critical, or can’t be shut down for an entire overhaul.
Refactoring Inside the Current Platform
Generally, modernization doesn’t require switching applied sciences in any respect. Refactoring or bettering structure throughout the present platform can resolve technical debt, enhance efficiency, and help new options with no full migration.
- Execs: Decrease prices in comparison with a full swap, quicker implementation, and preservation of current investments within the present platform.
- Cons: Could not clear up deeper architectural limitations, incremental enhancements could ultimately attain a ceiling.
- Greatest Use Case: When the platform remains to be supported, and present expertise fulfills the corporate’s wants with minor enhancements.
Conclusion
Expertise migration generally is a nice transfer, however solely when it solves an actual drawback, not when it follows market hype.
Typically, the very best worth comes from treating migration as a strategic modernization initiative: lowering technical debt, bettering supply pace, and enabling future scalability.
Earlier than approving a transition, decision-makers ought to consider whether or not the present answer will be upgraded, refactored, or partially modernized at a decrease price. If a full transition remains to be justified, the venture should be pushed by clear enterprise objectives, real looking ROI expectations, and a structured roadmap targeted on stability and continuity.
Steadily Requested Questions (FAQs)
Are you able to outline a migration transition?
A migration transition is the method of transferring an current utility, system, or platform from one expertise, framework, or atmosphere to a different whereas preserving its core performance, workflows, and integrations.
When does software program migration make enterprise sense?
Migration is a bonus when the present tech blocks development, will increase operational prices, creates safety or compliance dangers, or prevents the product roadmap from transferring ahead at an inexpensive pace.
How have you learnt if migration will ship ROI?
A swap has robust ROI when it solves a measurable enterprise drawback, corresponding to lowering upkeep prices, bettering scalability, or accelerating releases, brought on by unsupported platforms.
How a lot does a typical migration price?
Re-platforming price (together with cloud migration) will depend on utility measurement, architectural complexity, information dependencies, and the way a lot of the system should be rebuilt versus reused. Correct estimates normally require an audit.
Will software program transition disrupt current customers?
It may well, however disruption is avoidable. A phased method (incremental substitute) helps maintain the system working whereas new modules are launched progressively.
What’s the distinction between migration, modernization, and refactoring?
Migration adjustments the platform or tech stack. Modernization improves structure, deployment, or scalability with out essentially altering the stack. Refactoring restructures code internally whereas holding the identical performance.