Companies usually have to mixture subjects as a result of it’s important for organizing, simplifying, and optimizing the processing of streaming information. It permits environment friendly evaluation, facilitates modular improvement, and enhances the general effectiveness of streaming purposes. For instance, if there are separate clusters, and there are subjects with the identical objective within the completely different clusters, then it’s helpful to mixture the content material into one subject.
This weblog put up walks you thru how you should use prefixless replication with Streams Replication Supervisor (SRM) to mixture Kafka subjects from a number of sources. To be particular, we might be diving deep right into a prefixless replication state of affairs that includes the aggregation of two subjects from two separate Kafka clusters into a 3rd cluster.
This tutorial demonstrates how one can arrange the SRM service for prefixless replication, how one can create and replicate subjects with Kafka and SRM command line (CLI) instruments, and how one can confirm your setup utilizing Streams Messaging Manger (SMM). Safety setup and different superior configurations will not be mentioned.
Earlier than you start
The next tutorial assumes that you’re aware of SRM ideas like replications and replication flows, replication insurance policies, the fundamental service structure of SRM, in addition to prefixless replication. If not, you may try this associated weblog put up. Alternatively, you may examine these ideas in our SRM Overview.
Situation overview
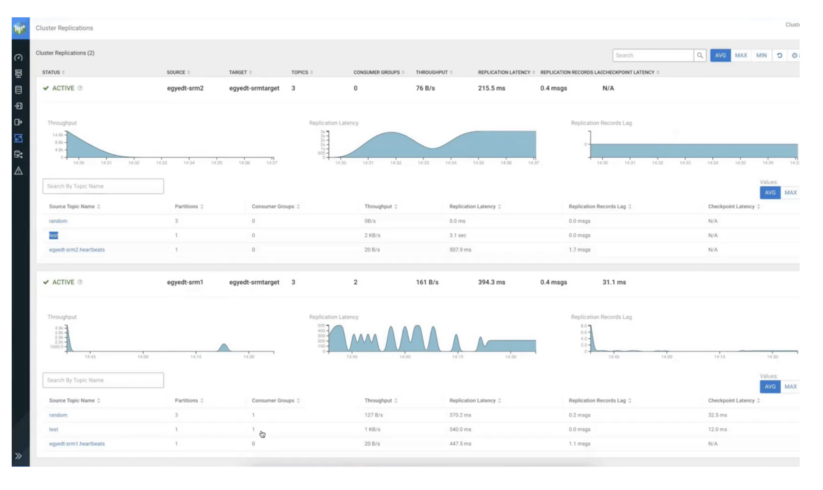
On this state of affairs you may have three clusters. All clusters comprise Kafka. Moreover, the goal cluster (srm-target) has SRM and SMM deployed on it.
The SRM service on srm-target is used to drag Kafka information from the opposite two clusters. That’s, this replication setup might be working in pull mode, which is the Cloudera-recommended structure for SRM deployments.
In pull mode, the SRM service (particularly the SRM driver function situations) replicates information by pulling from their sources. So quite than having SRM on supply clusters pushing the information to focus on clusters, you employ SRM situated on the goal cluster to drag the information into its co-located Kafka cluster.Pull mode is really helpful as it’s the deployment kind that was discovered to supply the best quantity of resilience towards numerous timeout and community instability points. You’ll find a extra in-depth rationalization of pull mode in the official docs.
The information from each supply subjects might be aggregated right into a single subject on the goal cluster. All of the whereas, it is possible for you to to make use of SMM’s highly effective UI options to observe and confirm what’s occurring.
Arrange SRM
First, you could arrange the SRM service situated on the goal cluster.
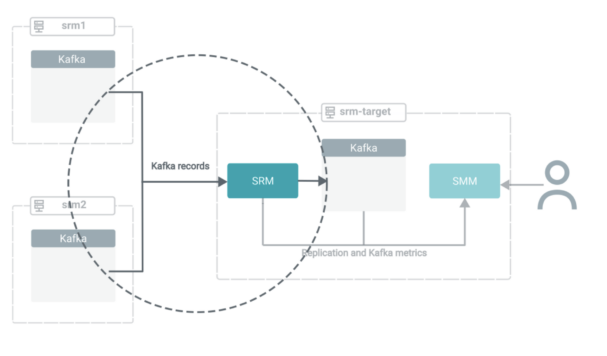
SRM must know which Kafka clusters (or Kafka companies) are targets and which of them are sources, the place they’re situated, the way it can join and talk with them, and the way it ought to replicate the information. That is configured in Cloudera Supervisor and is a two-part course of. First, you outline Kafka credentials, you then configure the SRM service.
Outline Kafka credentials
You outline your supply (exterior) clusters utilizing Kafka Credentials. A Kafka Credential is an merchandise that accommodates the properties required by SRM to ascertain a reference to a cluster. You possibly can consider a Kafka credential because the definition of a single cluster. It accommodates the title (alias), handle (bootstrap servers), and credentials that SRM can use to entry a selected cluster.
- In Cloudera supervisor, go to the Administration > Exterior Accounts > Kafka Credentials web page.
- Click on “Add Kafka Credentials.”
- Configure the credential.
The setup on this tutorial is minimal and unsecure, so that you solely have to configure Identify, Bootstrap Servers, and Safety Protocol traces. The safety protocol on this case is PLAINTEXT.
4. Click on “Add” when you’re executed, and repeat the earlier step for the opposite cluster (srm2).
Configure the SRM service
After the credentials are arrange, you’ll have to configure numerous SRM service properties. These properties specify the goal (co-located) cluster, inform SRM what replications must be enabled, and that replication ought to occur in prefixless mode. All of that is executed on the configuration web page of the SRM service.
1. From the Cloudera Supervisor dwelling web page, choose the “Streams Replication Supervisor” service.
2. Go to “Configuration.”
3. Specify the co-located cluster alias with “Streams Replication Supervisor Co-located Kafka Cluster Alias.”
The co-located cluster alias is the alias (quick title) of the Kafka cluster that SRM is deployed along with. All clusters in an SRM deployment have aliases. You employ the aliases to confer with clusters when configuring properties and when working the srm-control instrument. Set this to:
Discover that you just solely have to specify the alias of the co-located Kafka cluster, coming into connection info such as you did for the exterior clusters is just not ended. It’s because Cloudera Supervisor passes this info mechanically to SRM.
4. Specify Exterior Kafka Accounts.
This property should comprise the names of the Kafka credentials that you just created in a earlier step. This tells SRM which Kafka credentials it ought to import to its configuration. Set this to:

5. Specify all cluster aliases with “Streams Replication Supervisor Cluster” alias.
The property accommodates a comma-delimited record of all cluster aliases. That’s, all aliases you beforehand added to the Streams Replication Supervisor Co-located Kafka Cluster Alias and Exterior Kafka Accounts properties. Set this to:

6. Specify the motive force function goal with Streams Replication Supervisor Driver Goal Cluster.
The property accommodates a comma-delimited record of all cluster aliases. That’s, all aliases you beforehand added to the Streams Replication Supervisor Co-located Kafka Cluster Alias and Exterior Kafka Accounts properties. Set this to:

7. Specify service function targets with Streams Replication Supervisor Service Goal Cluster.
This property specifies the cluster that the SRM service function will collect replication metrics from (i.e. monitor). In pull mode, the service roles should at all times goal their co-located cluster. Set this to:

8. Specify replications with Streams Replication Supervisor’s Replication Configs.
This property is a jack-of-all-trades and is used to set many SRM properties that aren’t instantly obtainable in Cloudera Supervisor. However most significantly, it’s used to specify your replications. Take away the default worth and add the next:

9. Choose “Allow Prefixless Replication”
This property permits prefixless replication and tells SRM to make use of the IdentityReplicationPolicy, which is the ReplicationPolicy that replicates with out prefixes.
10. Evaluation your configuration, it ought to seem like this:
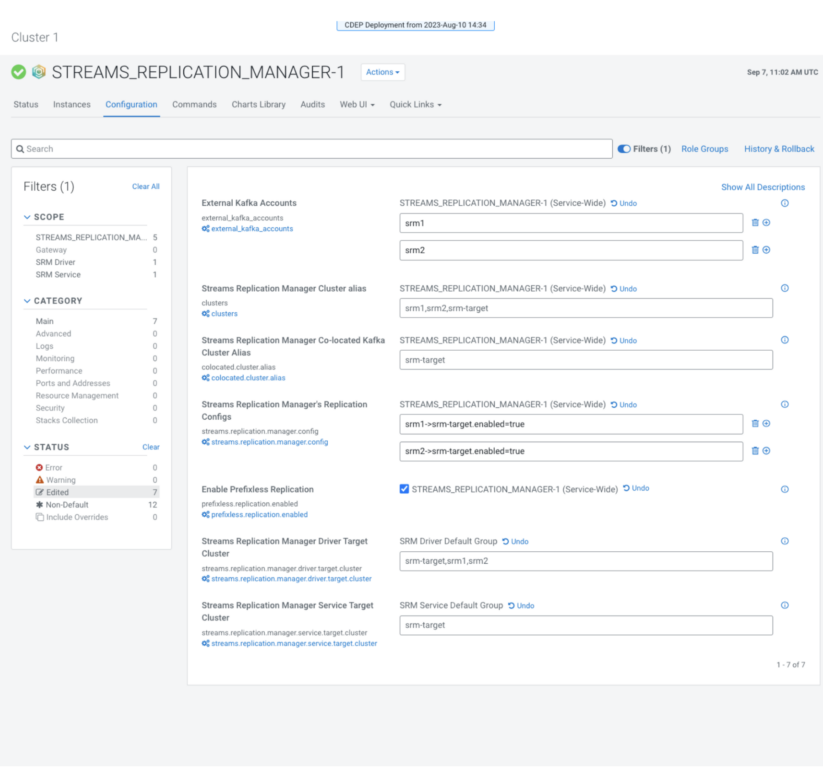
13. Click on “Save Adjustments” and restart SRM.
Create a subject, produce some information
Now that SRM setup is full, you could create one in all your supply subjects and produce some information. This may be executed utilizing the kafka-producer-perf-test CLI instrument.
This instrument creates the subject and produces the information in a single go. The instrument is on the market by default on all CDP clusters, and could be referred to as instantly by typing its title. No have to specify full paths.
- Utilizing SSH, log in to one in all your supply cluster hosts.
- Create a subject and produce some information.
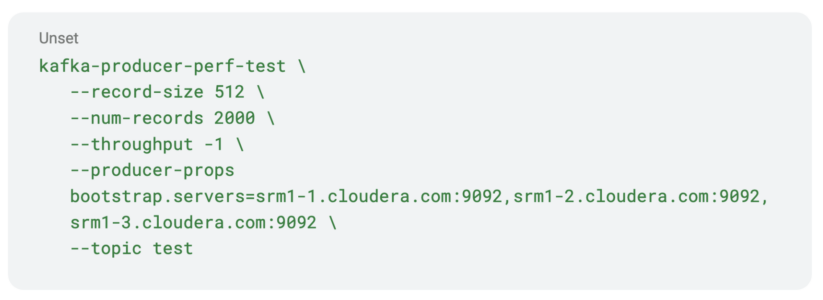
Discover that the instrument will produce 2000 information. This might be essential in a while after we confirm replication on the SMM UI.
Replicate the subject
So, you may have SRM arrange, and your subject is prepared. Let’s replicate.
Though your replications are arrange, SRM and the supply clusters are related, information is just not flowing, the replication is inactive. To activate replication, you could use the srm-control CLI instrument to specify what subjects must be replicated.
Utilizing the instrument you may manipulate the replication to permit and deny lists (or subject filters), which management what subjects are replicated. By default, no subject is replicated, however you may change this with a couple of easy instructions.
- Utilizing SSH, log in to the goal cluster (srm-target).
- Run the next instructions to start out replication.

Discover that though the subject on srm2 doesn’t exist but, we added the subject to the replication enable record as effectively. The subject might be created later. On this case, we’re activating its replication forward of time.
Insights with SMM
Now that replication is activated, the deployment is within the following state:
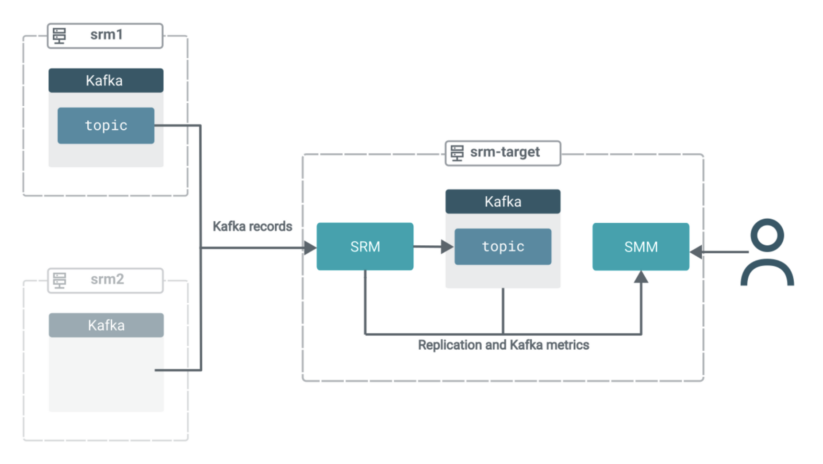
Within the subsequent few steps, we’ll shift the main target to SMM to exhibit how one can leverage its UI to achieve insights into what is definitely happening in your goal cluster.

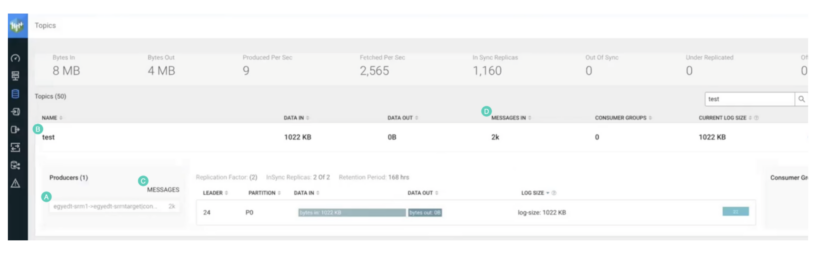
Discover the next:
- The title of the replication is included within the title of the producer that created the subject. The -> notation means replication. Subsequently, the subject was created with replication.
- The subject title is similar as on the supply cluster. Subsequently, it was replicated with prefixless replication. It doesn’t have the supply cluster alias as a prefix.
- The producer wrote 2,000 information. This is similar quantity of information that you just produced within the supply subject with kafka-producer-perf-test.
- “MESSAGES IN” exhibits 2,000 information. Once more, the identical quantity that was initially produced.
On to aggregation
After efficiently replicating information in a prefixless trend, its time transfer ahead and mixture the information from the opposite supply cluster. First you’ll have to arrange the take a look at subject within the second supply cluster (srm2), because it doesn’t exist but. This subject will need to have the very same title and configurations because the one on the primary supply cluster (srm1).
To do that, you could run kafka-producer-perf-test once more, however this time on a bunch of the srm2 cluster. Moreover, for bootstrap you’ll have to specify srm2 hosts.

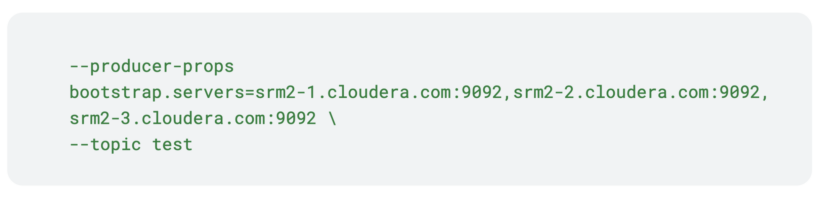
Discover how solely the bootstraps are completely different from the primary command. That is essential, the subjects on the 2 clusters have to be equivalent in title and configuration. In any other case, the subject on the goal cluster will continuously swap between two configuration states. Moreover, if the names don’t match, aggregation is not going to occur.
After the producer is completed with creating the subject and producing the 2000 information, the subject is instantly replicated. It’s because we preactivated replication of the take a look at subject in a earlier step. Moreover, the subject information are mechanically aggregated into the take a look at subject on srm-target.
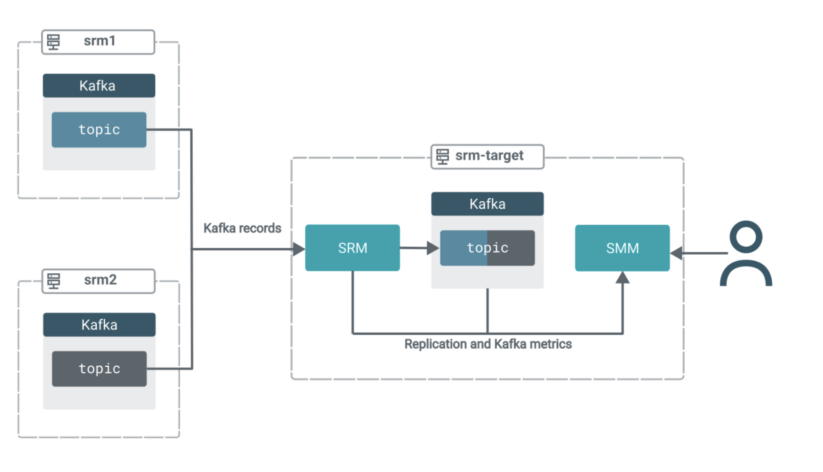
You possibly can confirm that aggregation has occurred by taking a look on the subject within the SMM UI.
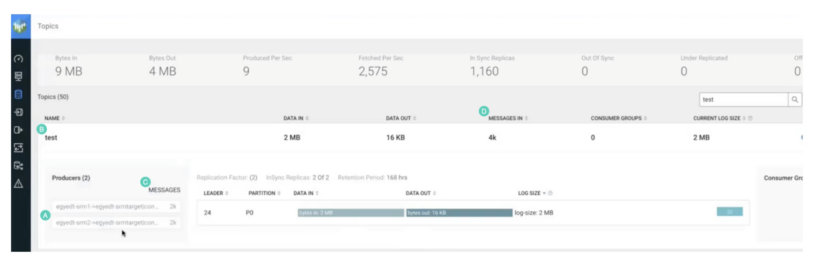
The next signifies that aggregation has occurred:
- There are actually two producers as a substitute of 1. Each comprise the title of the replication. Subsequently, the subject is getting information from two replication sources.
- The subject title continues to be the identical. Subsequently, perfixless replication continues to be working.
- Each producers wrote 2,000 information every.
- “MESSAGES IN” exhibits 4,000 information.

 Abstract
Abstract
On this weblog put up we checked out how you should use SRM’s prefixless replication function to mixture Kafka subjects from a number of clusters right into a single goal cluster.
Though aggregation was in focus, word that prefixless replication can be utilized for non-aggregation kind replication eventualities as effectively. For instance, it’s the good instrument emigrate that outdated Kafka deployment working on CDH, HDP, or HDF to CDP.
If you wish to study extra about SRM and Kafka in CDP Personal Cloud Base, jump over to Cloudera’s doc portal and see Streams Messaging Ideas, Streams Messaging How Tos, and/or the Streams Messaging Migration Information.
To get fingers on with SRM, obtain Cloudera Stream Processing Neighborhood version right here.
Occupied with becoming a member of Cloudera?
At Cloudera, we’re engaged on fine-tuning massive information associated software program bundles (primarily based on Apache open-source initiatives) to supply our clients a seamless expertise whereas they’re working their analytics or machine studying initiatives on petabyte-scale datasets. Verify our web site for a take a look at drive!
In case you are excited about massive information, wish to know extra about Cloudera, or are simply open to a dialogue with techies, go to our fancy Budapest workplace at our upcoming meetups.
Or, simply go to our careers web page, and grow to be a Clouderan!