Analytics on DynamoDB
Engineering groups usually must run complicated filters, aggregations and textual content searches on knowledge from DynamoDB. Nonetheless, DynamoDB is an operational database that’s optimized for transaction processing and never for real-time analytics. In consequence, many engineering groups hit limits on analytics on DynamoDB and look to different choices.
That’s as a result of operational workloads have very totally different entry patterns than complicated analytical workloads. DynamoDB solely helps a restricted set of operations, making analytics difficult and in some conditions not attainable. Even AWS, the corporate behind DynamoDB, advises firms to think about offloading analytics to different purpose-built options. One answer generally referenced is Elasticsearch which we can be diving into immediately.
DynamoDB is without doubt one of the hottest NoSQL databases and is utilized by many web-scale firms in gaming, social media, IoT and monetary companies. DynamoDB is the database of selection for its scalability and ease, enabling single-digit millisecond efficiency at scales of 20M requests per second. To be able to obtain this velocity at scale, DynamoDB is laser centered on nailing efficiency for operational workloads- excessive frequency, low latency operations on particular person information of knowledge.
Elasticsearch is an open-source distributed search engine constructed on Lucene and used for textual content search and log analytics use circumstances. Elasticsearch is a part of the bigger ELK stack which incorporates Kibana, a visualization instrument for analytical dashboards. Whereas Elasticsearch is thought for being versatile and extremely customizable, it’s a complicated distributed system that requires cluster and index operations and administration to remain performant. There are managed choices of Elasticsearch out there from Elastic and AWS, so that you don’t must run it your self on EC2 cases.
Shameless Plug: Rockset is a real-time analytics database constructed for the cloud. It has a built-in connector to DynamoDB and ingests and indexes knowledge for sub-second search, aggregations and joins. However this submit is about highlighting use circumstances for DynamoDB and Elasticsearch, in case you wish to discover that possibility.
Connecting DynamoDB to Elasticsearch Utilizing AWS Lambda
You need to use AWS Lambda to repeatedly load DynamoDB knowledge into Elasticsearch for analytics. Right here’s the way it works:
- Create a lambda operate to sync each replace from a DynamoDB stream into Elasticsearch
- Create a lambda operate to take a snapshot of the present DynamoDB desk and ship it to Elasticsearch. You need to use an EC2 script or an Amazon Kinesis stream to learn the DynamoDB desk contents.
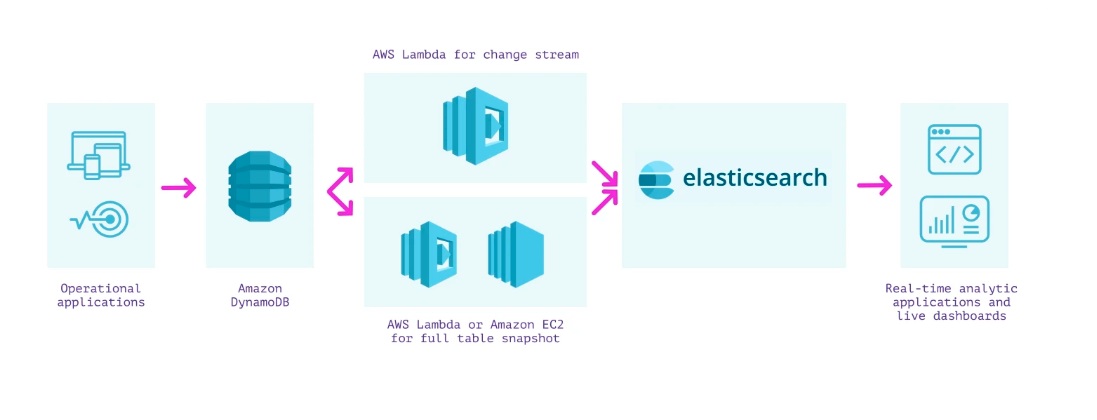
There may be an alternate strategy to syncing knowledge to Elasticsearch involving the Logstash Plugin for DynamoDB however it’s not at the moment supported and might be complicated to configure.
Textual content Search on DynamoDB Information Utilizing Elasticsearch
Textual content search is the looking out of textual content inside a doc to seek out probably the most related outcomes. Oftentimes, you’ll wish to seek for part of a phrase, a synonym or antonyms of phrases or a string of phrases collectively to seek out the very best consequence. Some functions will even weight search phrases otherwise based mostly on their significance.
DynamoDB can assist some restricted textual content search use circumstances simply through the use of partitioning to assist filter knowledge down. As an example, if you’re an ecommerce web site, you may partition knowledge in DynamoDB based mostly on a product class after which run the search in-memory. Apparently, that is how Amazon.com retail division handles numerous textual content search use circumstances. DynamoDB additionally helps a incorporates operate that allows you to discover a string that incorporates a selected substring of knowledge.
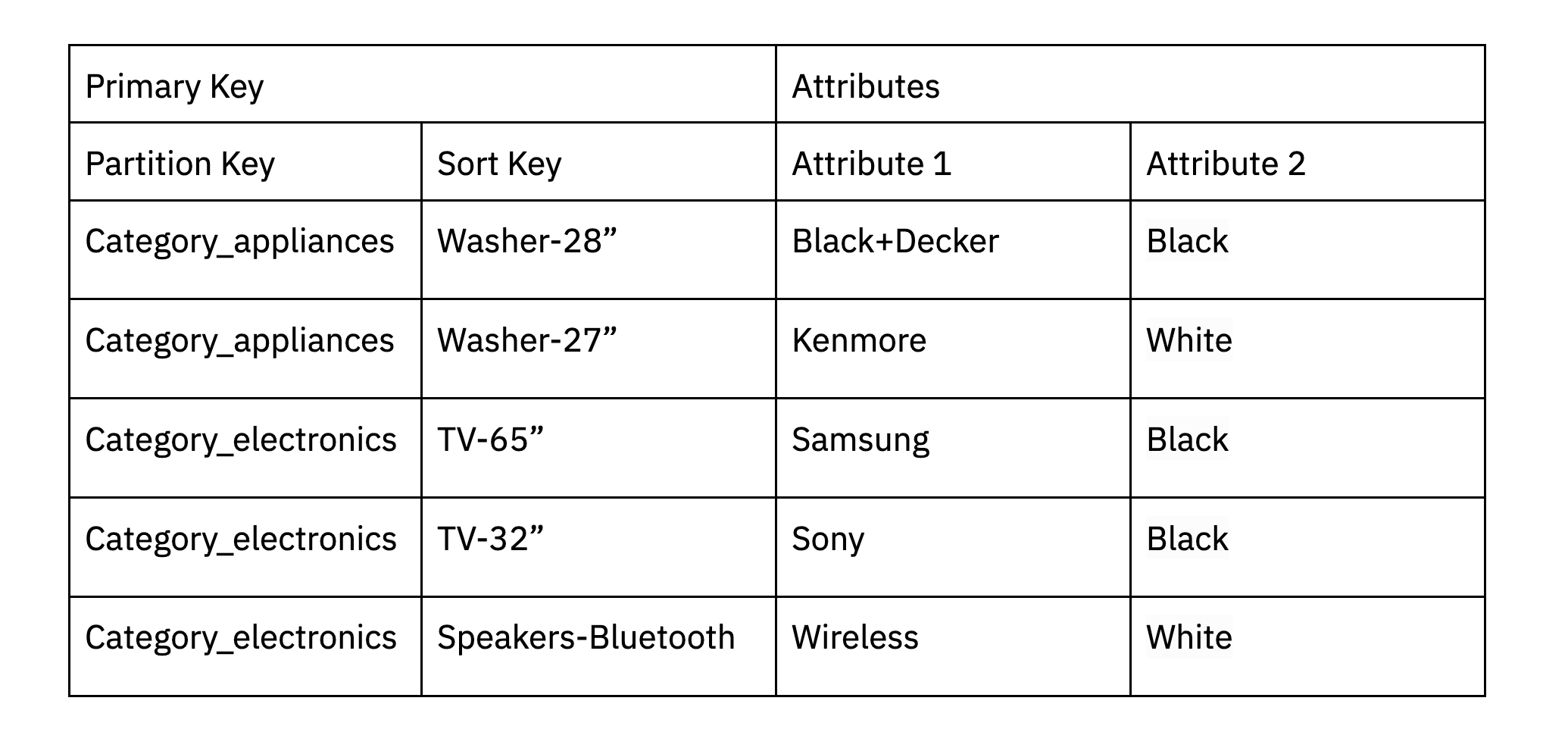
An e-commerce web site may partition knowledge based mostly on product class. Extra attributes could also be proven with the information being searched just like the model and coloration.
In eventualities the place full textual content search is core to your software, you’ll wish to use a search engine like Elasticsearch with a relevancy rating. Right here’s how textual content search works at a excessive degree in Elasticsearch:
- Relevance rating: Elasticsearch has a relevance rating that it provides to the search outcomes out-of-the-box or you may customise the rating on your particular software use case. By default, Elasticsearch will create a rating rating based mostly on the time period frequency, inverse doc frequency and the field-length norm.
- Textual content evaluation: Elasticsearch breaks textual content down into tokens to index the information, known as tokenizing. Analyzers are then utilized to the normalized phrases to reinforce search outcomes. The default customary analyzer splits the textual content in line with the Unicode Consortium to offer normal, multi-language assist.
Elasticsearch additionally has ideas like fuzzy search, auto-complete search and much more superior relevancy might be configured to satisfy the specifics of your software.
Complicated Filters on DynamoDB Information Utilizing Elasticsearch
Complicated filters are used to slim down the consequence set, thereby retrieving knowledge sooner and extra effectively. In lots of search eventualities, you’ll wish to mix a number of filters or filter on a spread of knowledge, similar to over a time period.
DynamoDB partitions knowledge and selecting an excellent partition key might help make filtering knowledge extra environment friendly. DynamoDB additionally helps secondary indexes in an effort to replicate your knowledge and use a special main key to assist extra filters. Secondary indexes might be useful when there are a number of entry patterns on your knowledge.
As an example, a logistics software might be designed to filter objects based mostly on their supply standing. To mannequin this situation in DynamoDB, we’ll create a base desk for logistics with a partition key of Item_ID, a kind key of Standing and attributes purchaser, ETA and SLA.
We additionally must assist a further entry sample in DynamoDB for when supply delays exceed the SLA. Secondary indexes in DynamoDB might be leveraged to filter down for less than the deliveries that exceed the SLA.
An index can be created on the sphere ETADelayedBeyondSLA which is a reproduction of the ETA attribute already within the base desk. This knowledge is barely included in ETADelayedBeyondSLA when the ETA exceeds the SLA. The secondary index is a sparse index, lowering the quantity of knowledge that must be scanned within the question. The purchaser is the partition key and the type secret’s ETADelayedBeyondSLA.
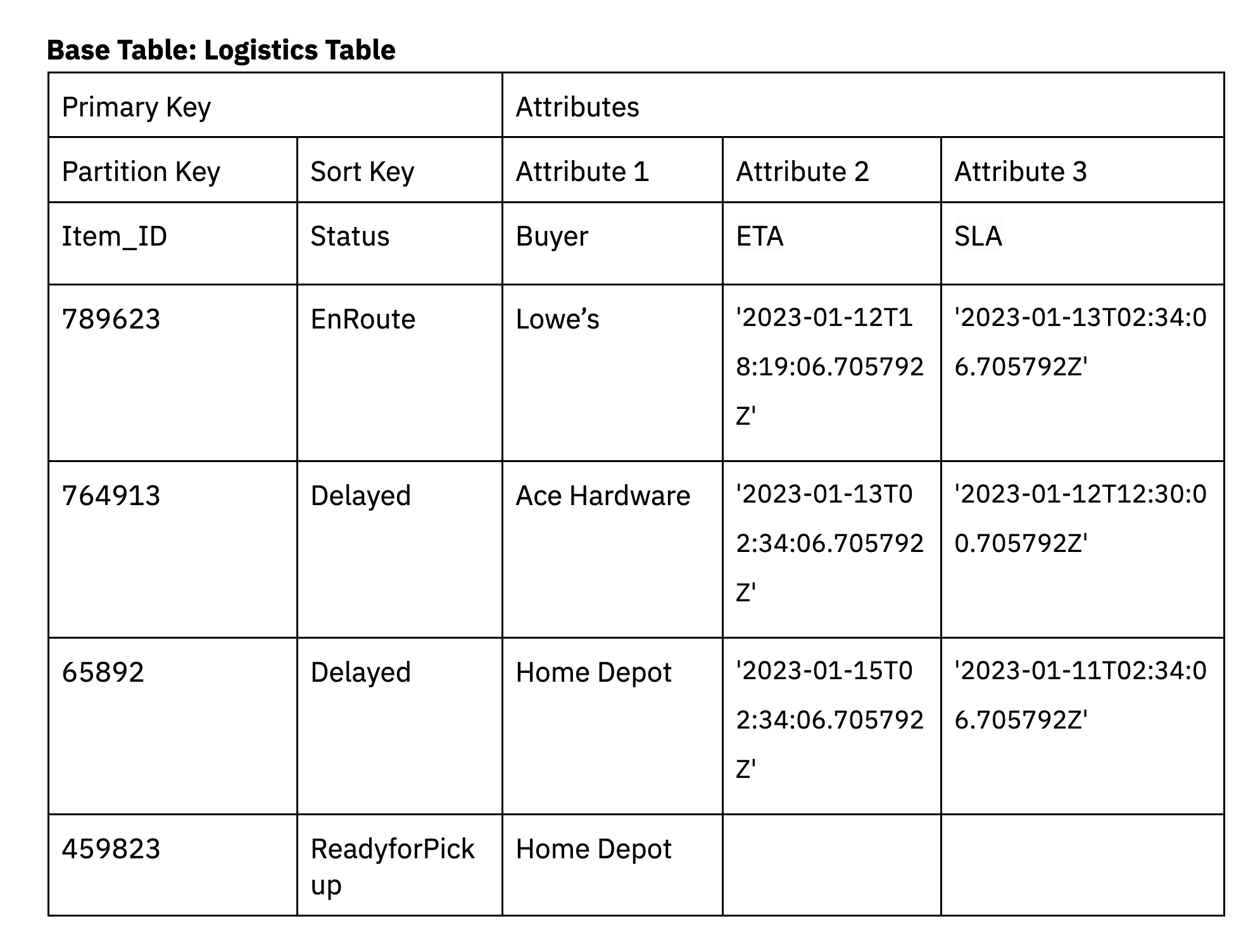
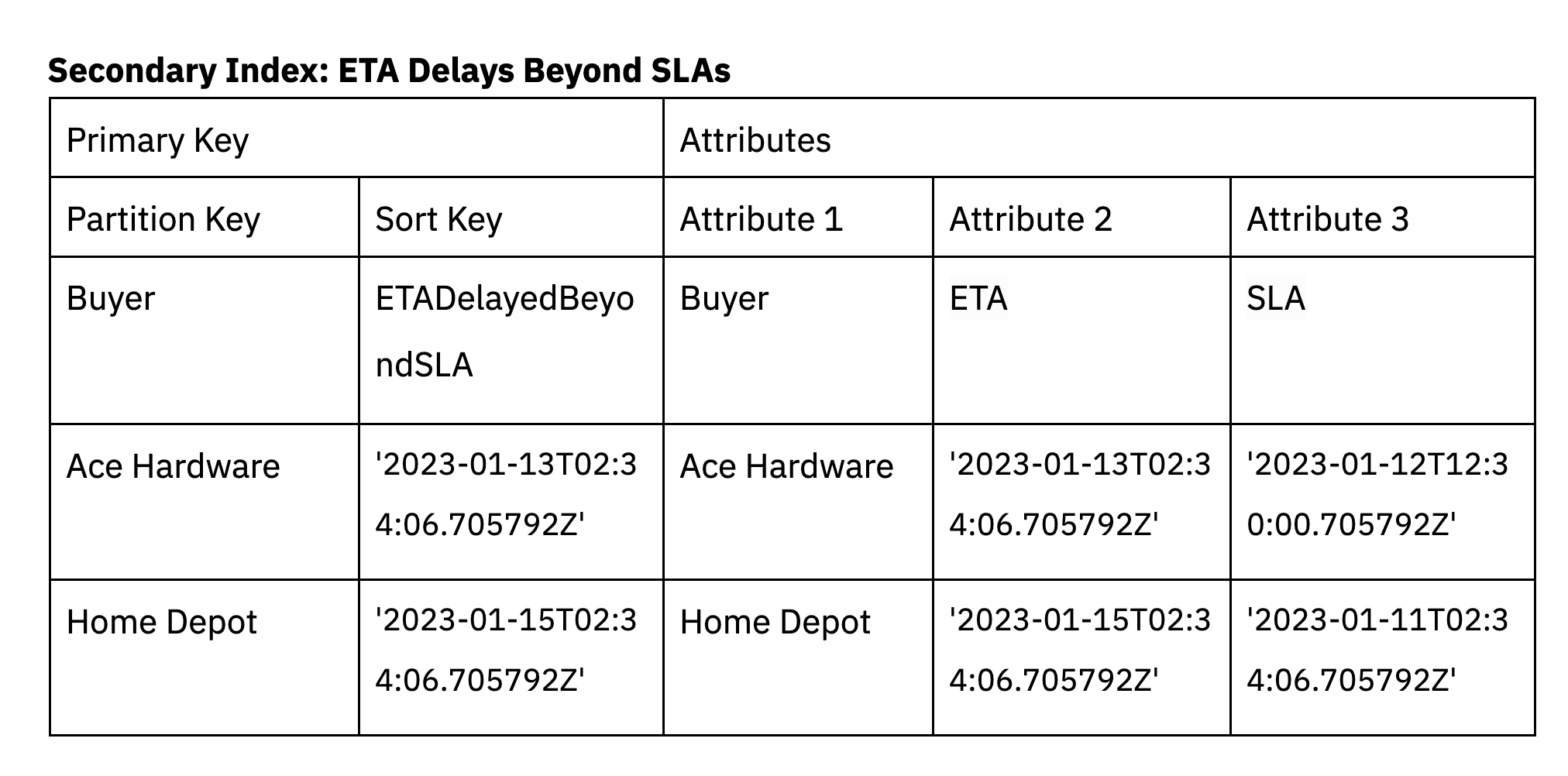
Secondary indexes can be utilized to assist a number of entry patterns within the software, together with entry patterns involving complicated filters.
DynamoDB does have a filterexpression operation in its Question and Scan API to filter outcomes that don’t match an expression. The filterexpression is utilized solely after a question or scan desk operation so you’re nonetheless sure to the 1MB of knowledge restrict for a question. That mentioned, the filterexpression is useful at simplifying the appliance logic, lowering the response payload measurement and validating time-to-live expiry. In abstract, you’ll nonetheless must partition your knowledge in line with the entry patterns of your software or use secondary indexes to filter knowledge in DynamoDB.
DynamoDB organizes knowledge in keys and values for quick knowledge retrieval and isn’t preferrred for complicated filtering. If you require complicated filters you might wish to transfer to a search engine like Elasticsearch as these techniques are perfect for needle within the haystack queries.
In Elasticsearch, knowledge is saved in a search index that means the listing of paperwork for which column-value is saved as a posting listing. Any question that has a predicate (ie: WHERE consumer=A) can rapidly fetch the listing of paperwork satisfying the predicate. Because the posting lists are sorted, they are often merged rapidly at question time so that every one filtering standards is met. Elasticsearch additionally makes use of easy caching to hurry up the retrieval means of steadily accessed complicated filter queries.
Filter queries, generally known as non-scoring queries in Elasticsearch, can retrieve knowledge sooner and extra effectively than textual content search queries. That’s as a result of relevance just isn’t wanted for these queries. Moreover, Elasticsearch additionally helps vary queries making it attainable to retrieve knowledge rapidly between an higher and decrease boundary (ie: age between 0-5).
Aggregations on DynamoDB Information Utilizing Elasticsearch
Aggregations are when knowledge is gathered and expressed in a abstract kind for enterprise intelligence or pattern evaluation. For instance, you might wish to present utilization metrics on your software in real-time.
DynamoDB doesn’t assist combination capabilities. The workaround advisable by AWS is to make use of DynamoDB and Lambda to take care of an aggregated view of knowledge in a DynamoDB desk.
Let’s use aggregating likes on a social media web site like Twitter for instance. We’ll make the tweet_ID the first key after which the type key the time window by which we’re aggregating likes. On this case, we’ll allow DynamoDB streams and connect a Lambda operate in order that as tweets are appreciated (or disliked) they’re tabulated in like_count with a timestamp (ie: last_ up to date).
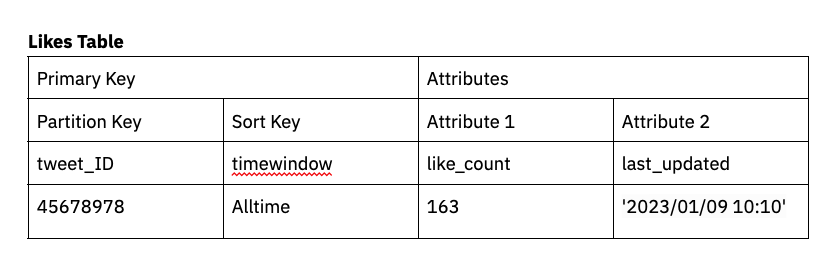
On this situation, DynamoDB streams and Lambda capabilities are used to tabulate a like_count as an attribute on the desk.
Another choice is to dump aggregations to a different database, like Elasticsearch. Elasticsearch is a search index at its core and has added extensions to assist aggregation capabilities. A kind of extensions is doc values, a construction constructed at index time to retailer doc values in a column-oriented manner. The construction is utilized by default to fields that assist doc values and there may be some storage bloat that comes with doc values. For those who solely require assist for aggregations on DynamoDB knowledge, it might be more cost effective to make use of an information warehouse that may compress knowledge effectively for analytical queries over extensive datasets.
- Right here’s a high-level overview of Elasticsearch’s aggregation framework:
- Bucket aggregations: You’ll be able to consider bucketing as akin to
GROUP BYon the planet of SQL databases. You’ll be able to group paperwork based mostly on discipline values or ranges. Elasticsearch bucket aggregations additionally embody the nested aggregation and parent-child aggregation which can be widespread workarounds to the shortage of be a part of assist. - Metric aggregations: Metrics will let you carry out calculations like
SUM,COUNT,AVG,MIN,MAX, and many others. on a set of paperwork. Metrics may also be used to calculate values for a bucket aggregation. - Pipeline aggregations: The inputs on pipeline aggregations are different aggregations reasonably than paperwork. Frequent makes use of embody averages and sorting based mostly on a metric.
There might be efficiency implications when utilizing aggregations, particularly as you scale Elasticsearch.
Different to Elasticsearch for Search, Aggregations and Joins on DynamoDB
Whereas Elasticsearch is one answer for doing complicated search and aggregations on knowledge from DynamoDB, many serverless proponents have echoed issues with this selection. Engineering groups select DynamoDB as a result of it’s severless and can be utilized at scale with little or no operational overhead. We’ve evaluated a couple of different choices for analytics on DynamoDB, together with Athena, Spark and Rockset on ease of setup, upkeep, question functionality and latency in one other weblog.
Rockset is an alternative choice to Elasticsearch and Alex DeBrie has walked by filtering and aggregating queries utilizing SQL on Rockset. Rockset is a cloud-native database with a built-in connector to DynamoDB, making it simple to get began and scale analytical use circumstances, together with use circumstances involving complicated joins. You’ll be able to discover Rockset as an alternative choice to Elasticsearch in our free trial with $300 in credit.

