The Problem of Manufacturing Knowledge Purposes
Constructing production-ready information functions is complicated. You typically want separate instruments to host the app, handle the database, and transfer information between techniques. Every layer provides setup, upkeep, and deployment overhead.
Databricks simplifies this by consolidating all the pieces on a single platform – the Databricks Knowledge Intelligence Platform. Databricks Apps runs your internet functions on serverless compute. Lakebase gives a managed Postgres database that syncs with Unity Catalog, giving your app quick entry to ruled information. And with Databricks Asset Bundles (DABs), you may package deal code, infrastructure, and information pipelines collectively and deploy them with a single command.
This weblog exhibits how these three items work collectively to construct and deploy an actual information utility from syncing Unity Catalog information to Lakebase, to working an internet app on Databricks and automating deployment with Asset Bundles.
Structure and The way it Works
We’ll stroll by a taxi journey utility that demonstrates all the sample: a React and FastAPI utility that reads from Lakebase synced tables, with computerized information updates from Unity Catalog Delta tables taking place inside seconds.
The next diagram gives a simplified view of the answer structure:
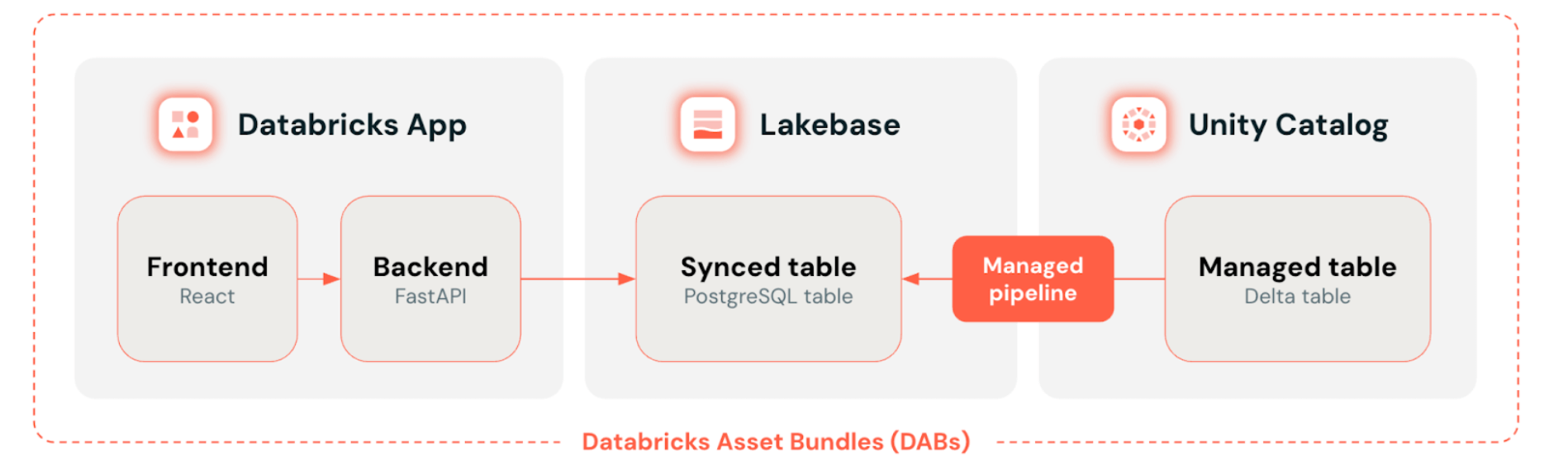
At a excessive degree, Databricks Apps serves because the entrance finish the place customers discover and visualize information. Lakebase gives the Postgres database that the app queries, preserving it near dwell information from Unity Catalog with synced tables. Databricks Asset Bundles tie all the pieces collectively by defining and deploying all sources—app, database, and information synchronization—as one version-controlled unit.
Principal answer elements:
The instance app shows current taxi journeys in each desk and chart format and mechanically polls for brand spanking new journeys. It reads information from a Lakebase synced desk, which mirrors a Delta desk in Unity Catalog.
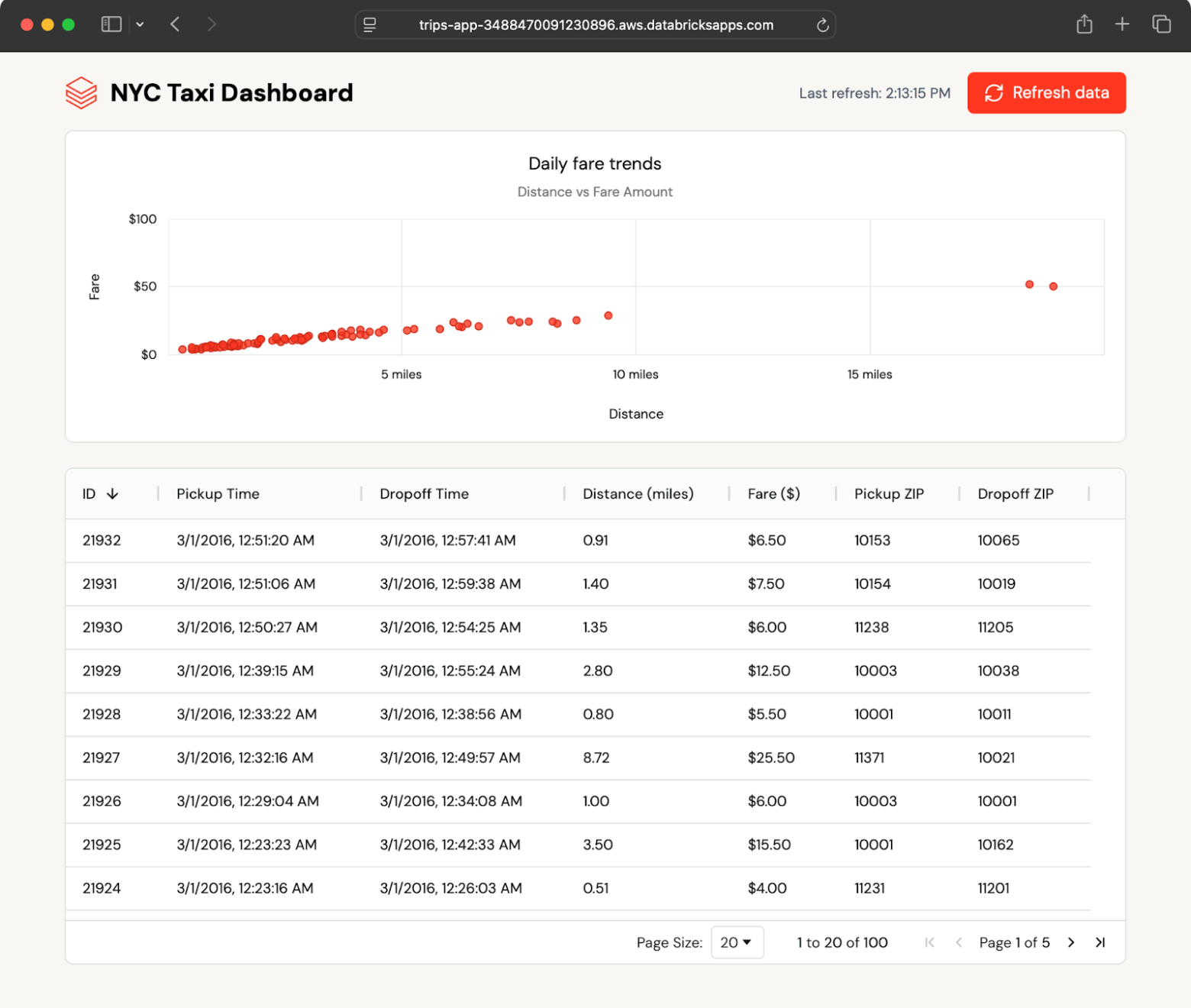
As a result of the synced desk updates mechanically, any change within the Unity Catalog desk seems within the app inside seconds—no customized ETL wanted.
You possibly can check this by inserting new information into the supply Delta desk after which refreshing the synced desk:
Then set off a refresh of the synced trips_synced desk.
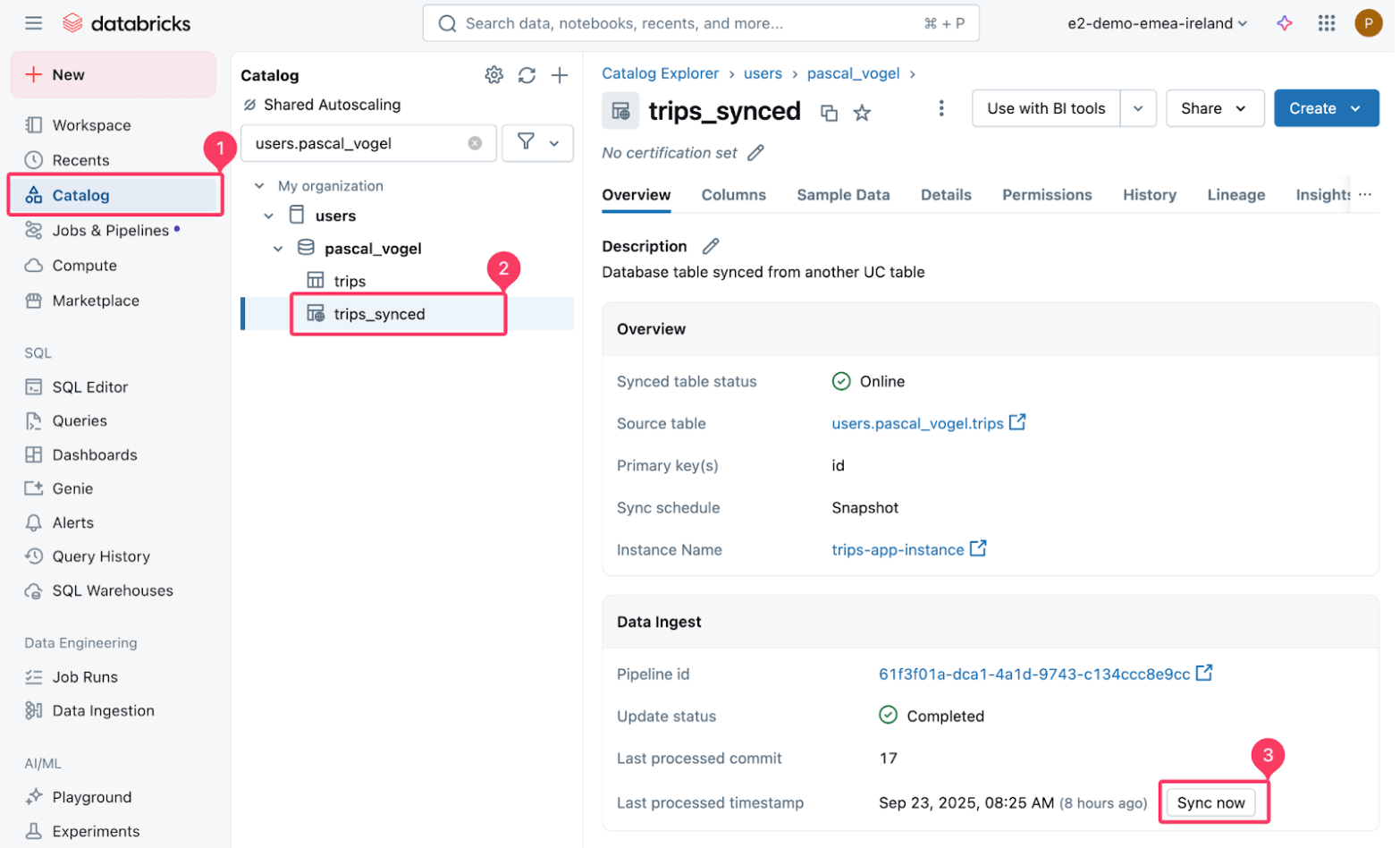
The managed pipeline that powers the sync performs a snapshot copy of the supply Delta desk to the goal Postgres desk.
Inside a couple of seconds, the brand new data seem within the dashboard. The app polls for updates and lets customers refresh on demand, exhibiting how Lakebase retains operational information present with out additional engineering.
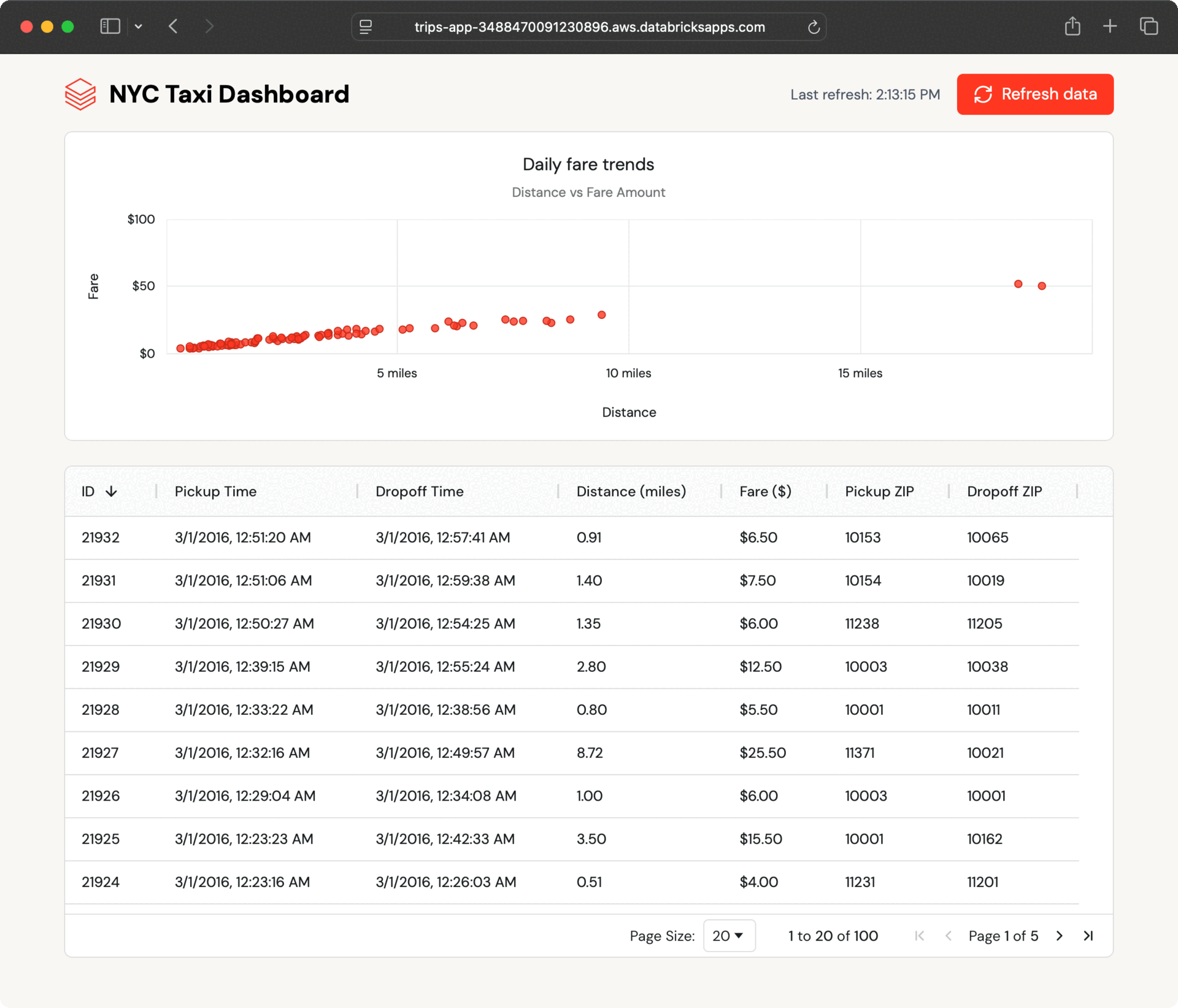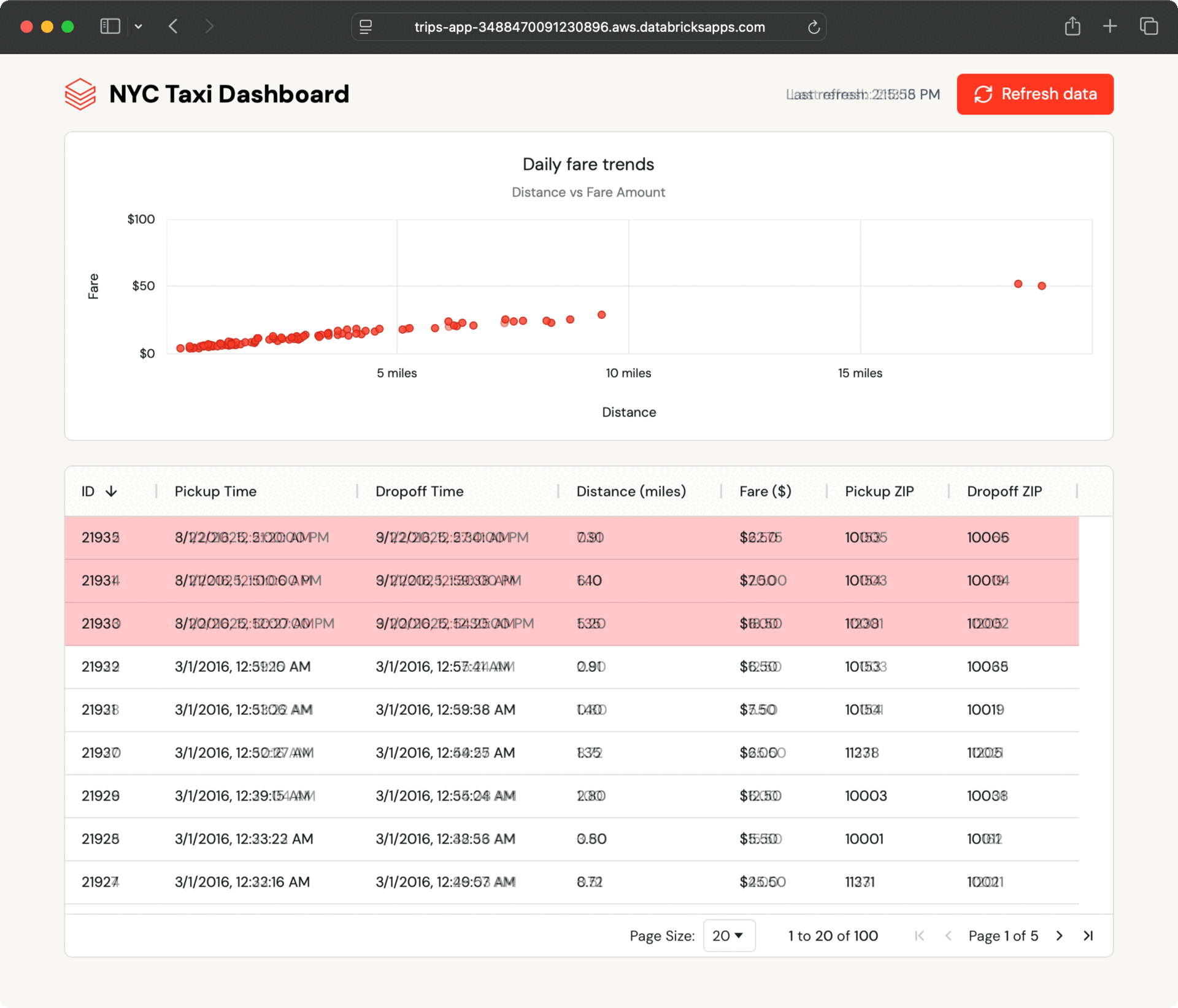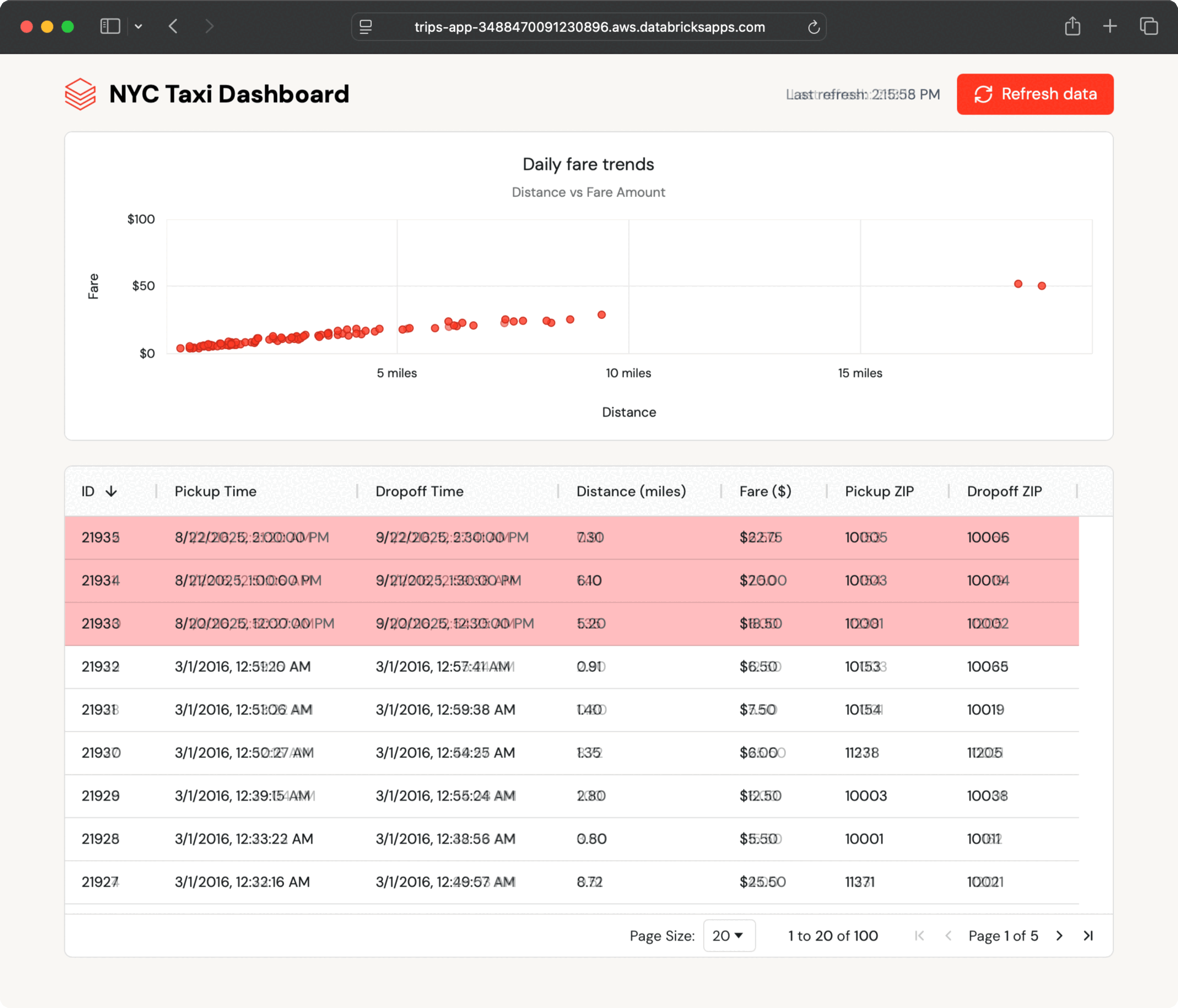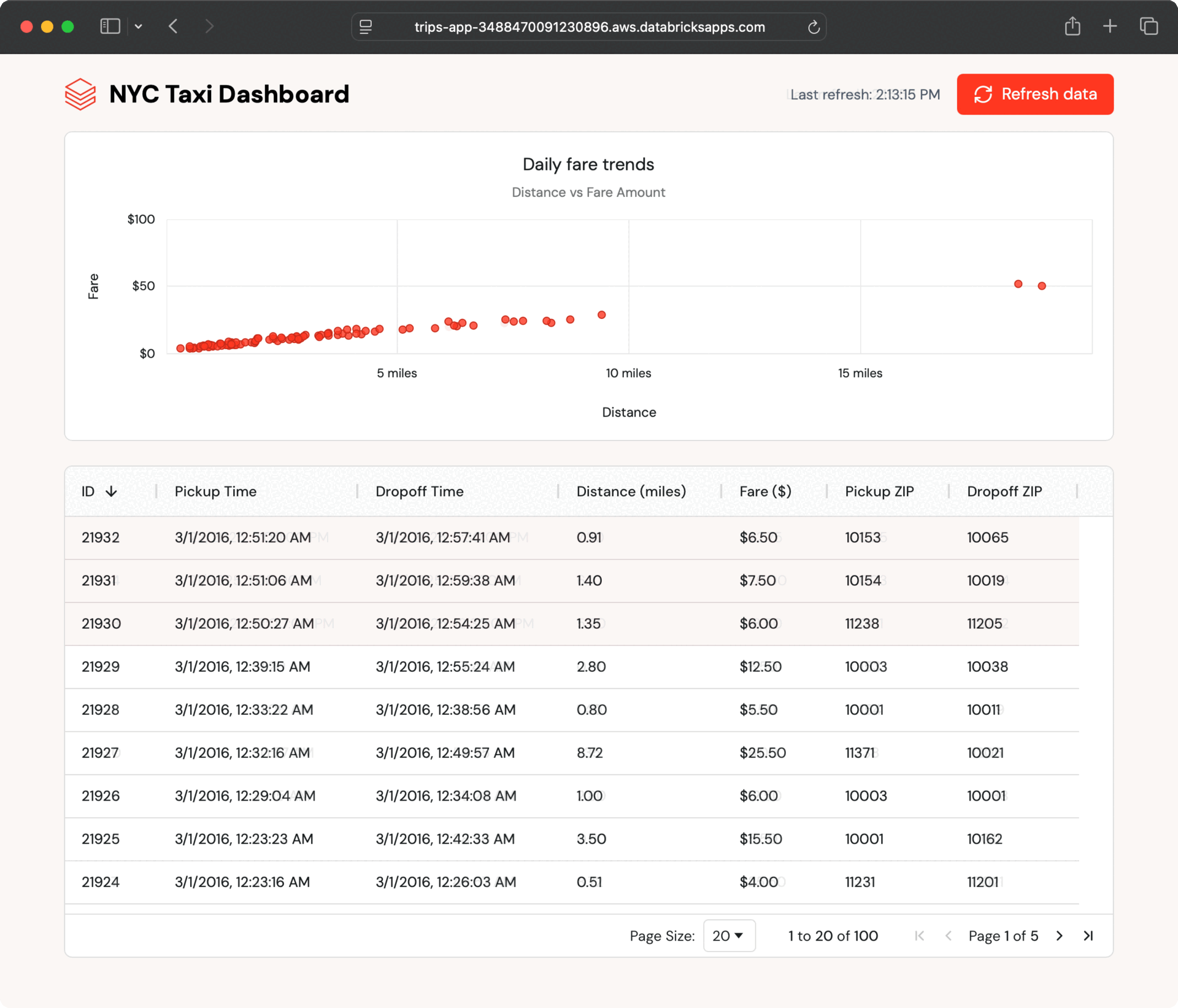
This seamless information movement occurs as a result of Lakebase synced tables deal with all of the synchronization mechanically, with out the necessity for customized ETL code or coordination between groups.
Anatomy of the Databricks App
Let’s check out how the completely different parts of the answer come collectively within the Databricks App.
Authentication and database connection
Every Databricks App has a singular service principal id assigned on creation that the app makes use of to work together with different Databricks sources, together with Lakebase.
Lakebase helps OAuth machine-to-machine (M2M) authentication. An app can receive a legitimate token utilizing the Databricks SDK for Python’s WorkspaceClient and its service principal credentials. The WorkspaceClient takes care of refreshing the short-lived (one hour) OAuth token.
The app then makes use of this token when establishing a connection to Lakebase utilizing the Psycopg Python Postgres adapter:
The Postgres host and database title are mechanically set as setting variables for the Databricks App when utilizing the Lakebase useful resource for apps.
The Postgres person is both the app service principal (when deployed to Databricks Apps) or the Databricks person title of the person working the app regionally.
RESTful FastAPI backend
The app’s FastAPI backend makes use of this connection to question Lakebase and fetch the most recent journeys information from the synced desk:
Along with serving API endpoints, FastAPI also can serve static information utilizing the StaticFiles class. By bundling our React frontend (app/frontend) utilizing Vite’s construct course of, we will generate a set of static information that we will serve utilizing FastAPI.
React frontend
The React frontend calls the FastAPI endpoint to show the information:
The instance utility makes use of ag-grid and ag-charts for visualization and mechanically checks for brand spanking new information each few seconds:
Defining Databricks Asset Bundles (DABs) Assets
All of the Databricks sources and utility code proven above may be maintained as a DABs bundle in a single supply code repository. This additionally implies that all sources may be deployed to a Databricks workspace with a single command. See the GitHub repository for detailed deployment directions.
This simplifies the software program growth lifecycle and allows deployments by way of CI/CD greatest practices throughout growth, staging, and manufacturing environments.
The next sections clarify the bundle information in additional element.
Bundle configuration
The databricks.yml incorporates the DABs bundle configuration within the type of bundle settings and included sources:
In our instance, we solely outline a growth and a staging setting. For a manufacturing use case, think about including further environments. See the databricks-dab-examples repository and the DABs documentation for extra superior configuration examples.
Lakebase setup and sync with Unity Catalog
To outline a Lakebase occasion in DABs, use the database_instances useful resource. At a minimal, we have to outline the capability subject of the occasion.
As well as, we outline a synced_database_tables useful resource, which units up a managed synchronization pipeline between a Unity Catalog desk and a Postgres desk.
For this, outline a supply desk by way of source_table_full_name. The supply desk in Unity Catalog wants a singular (composite) major key to have the ability to course of updates outlined within the primary_key_columns subject.
The placement of the goal desk in Lakebase is set by the goal database object specified as logical_database_name and the desk title outlined as title.
A synced desk can also be a Unity Catalog object. On this useful resource definition, we place the synced desk in the identical catalog and schema because the supply desk utilizing DABs variables outlined in databricks.yml. You possibly can override these defaults by setting completely different variable values.
For our use case, we use the SNAPSHOP sync mode. See the concerns and greatest practices sections for a dialogue of the obtainable choices.
Databricks Apps useful resource
DABs permits us to outline each the Databricks Apps compute useful resource as an apps useful resource in addition to the applying supply code in a single bundle. This permits us to maintain each Databricks useful resource definition and supply code in a single repository. In our case, the app supply code primarily based on FastAPI and Vite is saved within the top-level app listing of the venture.
The configuration dynamically references the database_name and instance_name outlined within the database.yml useful resource definition.
database is a supported app useful resource that may be outlined in DABs. By defining the database as an app useful resource, we mechanically create a Postgres function for use by the app service principal when interacting with the Lakebase occasion.
Concerns and Finest Practices
Create modular and reusable bundles
Whereas this instance deploys to growth and staging environments, DABs makes it simple to outline a number of environments to suit your growth lifecycle. Automate deployment throughout these environments by organising CI/CD pipelines with Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, or different DevOps platforms.
Use DABs substitutions and variables to outline environment-specific configurations. As an illustration, you may outline completely different Lakebase occasion capability configurations for growth and manufacturing to scale back price. Equally, you may outline completely different Lakebase sync modes on your synced tables to satisfy environment-specific information latency necessities.
Select Lakebase sync modes and optimize efficiency
Choosing the proper Lakebase sync mode is essential to steadiness price and information freshness.
Snapshot | Triggered | Steady | |
Replace technique | Full desk substitute on every run | Preliminary full copy + incremental modifications | Preliminary load + real-time streaming updates |
Efficiency | 10x extra environment friendly than different modes | Balanced price and efficiency | Greater price (constantly working) |
Latency | Excessive latency (scheduled/guide) | Medium latency (on-demand) | Lowest latency (real-time, ~15 sec) |
Finest for |
|
|
|
Limitations |
|
|
|
Arrange notifications on your managed sync pipeline to be alerted in case of failures.
To enhance question efficiency, right-size your Lakebase database occasion by selecting an acceptable occasion capability. Take into account creating indexes on the synced desk in Postgres that match your question patterns. Use the pre-installed pg_stat_statements extension to research question efficiency.
Put together your app for manufacturing
The instance utility implements a polling-based method to get the most recent information from Lakebase. Relying in your necessities, you can even implement a push-based method primarily based on WebSockets or Server-Despatched-Occasions to make use of server sources extra effectively and improve the timeliness of knowledge updates.
To scale to a bigger variety of app customers by decreasing the necessity for the FastAPI backend to set off database operations, think about implementing caching, for instance, utilizing fastapi-cache for caching question outcomes in-memory.
Authentication and authorization
Use OAuth 2.0 for authorization and authentication–don’t depend on legacy private entry tokens (PATs). Throughout growth in your native machine, use the Databricks CLI to arrange OAuth U2M authentication to seamlessly work together with dwell Databricks sources reminiscent of Lakebase.
Equally, your deployed app makes use of its related service principal for OAuth M2M authentication and authorization with different Databricks companies. Alternatively, arrange person authorization on your app to carry out actions on Databricks sources on behalf of your app customers.
See additionally Finest practices for apps within the Databricks Apps documentation for added common and safety greatest practices.
Conclusion
Constructing manufacturing information functions should not imply juggling separate instruments for deployment, information synchronization, and infrastructure administration. Databricks Apps provides you serverless compute to run your Python and Node.js functions with out managing infrastructure. Lakebase synced tables mechanically ship low-latency information from Unity Catalog Delta tables to Postgres, eliminating customized ETL pipelines. Databricks Asset Bundles tie all of it collectively by permitting you to package deal your utility code, infrastructure definitions, and information sync configurations right into a single, version-controlled bundle that deploys persistently throughout environments.
Deployment complexity kills momentum. When you may’t ship modifications shortly and confidently, you decelerate iteration, introduce setting drift, and waste time coordinating between groups. By treating your complete utility stack as code with DABs, you allow CI/CD automation, guarantee constant deployments throughout dev, staging, and manufacturing, and allow you to and your crew give attention to constructing options as an alternative of preventing deployment pipelines. That is how you progress from prototype to manufacturing with out the standard deployment complications.
The whole instance is out there within the GitHub repository with step-by-step deployment directions.
Get Began
Study extra about Lakebase, Databricks Apps, and Databricks Asset Bundles by visiting the Databricks documentation. For extra developer sources on Databricks Apps, check out the Databricks Apps Cookbook and Cookbook Useful resource Assortment.

