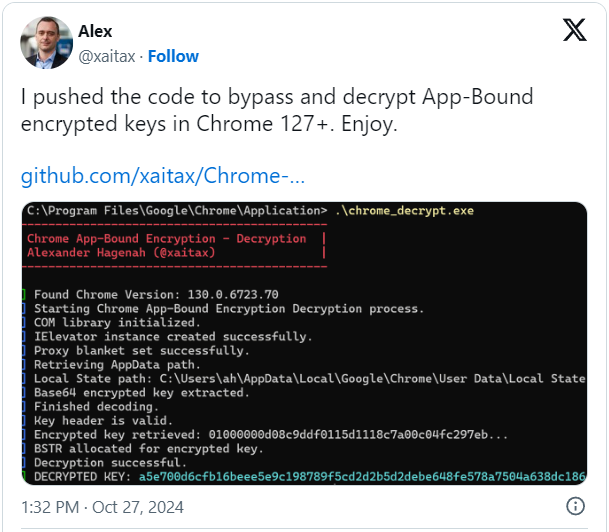
A researcher has launched a instrument to bypass Google’s new App-Certain encryption cookie-theft defenses and extract saved credentials from the Chrome net browser.
The instrument, named ‘Chrome-App-Certain-Encryption-Decryption,’ was launched by cybersecurity researcher Alexander Hagenah after he seen that others have been already determining related bypasses.
Though the instrument achieves what a number of infostealer operations have already added to their malware, its public availability raises the chance for Chrome customers who proceed to retailer delicate knowledge of their browsers.
Google’s app-bound encryption issues
Google launched Software-Certain (App-Certain) encryption in July (Chrome 127) as a brand new safety mechanism that encrypts cookies utilizing a Home windows service that runs with SYSTEM privileges.
The purpose was to guard delicate info from infostealer malware, which runs with the permissions of the logged consumer, making it unattainable for it to decrypt stolen cookies with out first gaining SYSTEM privileges and doubtlessly elevating alarms in safety software program.
“As a result of the App-Certain service is working with system privileges, attackers have to do extra than simply coax a consumer into working a malicious app,” defined Google in July.
“Now, the malware has to achieve system privileges, or inject code into Chrome, one thing that authentic software program should not be doing.”
Nevertheless, by September, a number of info stealers had discovered methods to bypass the brand new safety function and supply their cybercriminal clients the power to as soon as once more steal and decrypt delicate info from Google Chrome.
Google advised BleepingComputer then that the “cat and mouse” recreation between info-stealer builders and its engineers was at all times anticipated and that they by no means assumed that their protection mechanisms could be bulletproof.
As a substitute, with the introduction of App-Certain encryption, they hoped they might lastly lay the bottom for step by step constructing a extra sound system. Under is Google’s response from the time:
“We’re conscious of the disruption that this new protection has precipitated to the infostealer panorama and, as we acknowledged within the weblog, we count on this safety to trigger a shift in attacker habits to extra observable strategies comparable to injection or reminiscence scraping. This matches the brand new habits now we have seen.
We proceed to work with OS and AV distributors to attempt to extra reliably detect these new varieties of assaults, in addition to persevering with to iterate on hardening defenses to enhance safety towards infostealers for our customers.” – A Google spokesperson
Bypass now publicly accessible
Yesterday, Hagenah made his App-Certain encryption bypass instrument accessible on GitHub, sharing supply code that permits anybody to be taught from and compile the instrument.
“This instrument decrypts App-Certain encrypted keys saved in Chrome’s Native State file, utilizing Chrome’s inside COM-based IElevator service,” reads the undertaking description.
“The instrument supplies a strategy to retrieve and decrypt these keys, which Chrome protects by way of App-Certain Encryption (ABE) to forestall unauthorized entry to safe knowledge like cookies (and doubtlessly passwords and fee info sooner or later).”
To make use of the instrument, customers should copy the executable into the Google Chrome listing often situated at C:Program FilesGoogleChromeApplication. This folder is protected, so customers should first acquire administrator privileges to repeat the executable to that folder.
Nevertheless, that is generally simple to realize as many Home windows customers, particularly shoppers, use accounts which have administrative privileges.
By way of its precise impression on Chrome safety, researcher g0njxa advised BleepingComputer that Hagenah’s instrument demonstrates a fundamental technique that almost all infostealers have now surpassed to steal cookies from all variations of Google Chrome.
Toyota malware analyst Russian Panda additionally confirmed to BleepingComputer that Hagenah’s technique appears to be like much like the early bypassing approaches infostealers took when Google first applied App-Certain encryption in Chrome.
“Lumma used this technique – instantiating the Chrome IElevator interface by means of COM to entry Chrome’s Elevation Service to decrypt the cookies, however this may be fairly noisy and straightforward to detect,” Russian Panda advised BleepingComputer.
“Now, they’re utilizing oblique decryption with out straight interacting with Chrome’s Elevation Service”.
Nevertheless, g0njxa commented that Google has nonetheless not caught up, so consumer secrets and techniques saved in Chrome might be simply stolen utilizing the brand new instrument.
In response to the discharge of this instrument, Google shared the next assertion with BleepingComputer:
“This code [xaitax’s] requires admin privileges, which reveals that we have efficiently elevated the quantity of entry required to efficiently pull off any such assault,” Google advised BleepingComputer.
Whereas it’s true admin privileges are required, it doesn’t appear to have impacted information-stealing malware operations, which have solely elevated over the previous six months, focusing on customers by means of zero-day vulnerabilities, pretend fixes to GitHub points, and even solutions on StackOverflow.