Microsoft is asserting the preview of Signing Transparency to deal with software program provide chain threats that conventional code signing alone can’t absolutely stop, constructing on the Zero Belief precept of “by no means belief, at all times confirm.” Signing Transparency makes use of an append-only log to verifiably document every signature, with keys protected in a safe confidential computing enclave.
Right now, Microsoft is asserting the preview of Signing Transparency to deal with software program provide chain threats that conventional code signing alone can’t absolutely stop, constructing on the Zero Belief precept of “by no means belief, at all times confirm.” Signing Transparency makes use of an append-only log to verifiably document every signature, with keys protected in a safe confidential computing enclave. This enables organizations and auditors to independently confirm cryptographic proof of service releases, enhancing safety and accountability. Enhanced transparency ensures direct visibility into enforced safety insurance policies for each launch, growing belief and tamper-evidence throughout enterprise deployments.
Want for transparency within the software program provide chain
Trendy software program provide chain safety faces subtle threats. Attackers have repeatedly exploited the belief in signed software program–from compromised construct techniques to stolen code-signing certificates–to distribute malicious updates. In actual fact, what is required is a mechanism to make code signing verifiable and accountable at scale, in order that any sudden modifications turn into evident.
On the subject of software program, Signing Transparency means each signed artifact signature is recorded in a tamper-evident, open supply, publicly accessible ledger. This manner, anybody can later question and audit the ledger to verify when and what was signed, and by whom, together with the ledger itself, making it a lot more durable for attackers to cover malicious signatures.
Transparency logs assist lengthen belief in instances the place code signing can’t, particularly when paired with Trusted Execution Environments (TEE). For instance, if an adversary manages to steal or misuse a trusted signing key, they might signal malware with a superbly legitimate signature. A transparency service forces an adversary to cover from the log (elevating purple flags) or make their assault indelibly seen. In different phrases, even when attackers compromise signing keys, they can’t cowl their tracks–any tampering or sudden signing might be detected, by any social gathering, by way of the transparency log. This considerably boosts confidence within the software program provide chain’s integrity.
What’s Microsoft’s Signing Transparency?
Microsoft’s Signing Transparency is a cloud-managed service designed to reinforce belief and safety in software program provide chains. At its core, it acts as an neutral notary for software program signatures, making a everlasting, auditable document of who signed what and when. By doing so, it supplies impartial verification {that a} given software program launch has not been secretly changed or modified and that each one signing occasions comply with anticipated patterns.
Particularly, it maintains a public, append-only ledger of software program signing occasions, leveraging robust cryptography and confidential {hardware} to make sure the ledger’s integrity for exterior customers. Each time software program is signed (for instance, an utility binary, a container picture, a firmware replace, and so on.), the signature is submitted to the Signing Transparency service. The service makes use of insurance policies to confirm and document a reference signature in an immutable log (captured as a Merkle tree) and indicators them with a key that’s created in and may by no means go away a safe confidential computing enclave, issuing a universally verifiable, tamper-proof receipt as proof of the occasion.
This service makes use of COSE (CBOR Object Signing and Encryption) envelopes that are compliant with the Draft IETF commonplace for Provide Chain Integrity, Transparency, and Belief (SCITT), underlining Microsoft’s dedication to open requirements in provide chain safety.
| Countersigning COSE envelopes | Immutable Merkle tree ledger | Receipts for auditing and compliance |
| Signing Transparency can add a receipt for digital signatures packaged as COSE envelopes (an IETF commonplace format. By including its personal signature to signed artifacts envelope, it creates a second layer of attestation. Any modification to the artifact or its authentic signature would break this countersignature, making tampering instantly detectable. This ensures the integrity of the signed object is independently verifiable. | All counter signed information are saved in an append-only ledger applied as a Merkle tree. Every new signing even turns into a leaf within the tree, and the tree’s root hash is cryptographically up to date. The Merkle construction supplies a compact, verifiable proof of inclusion for every entry. Additional, no entry might be altered or eliminated with out breaking the cryptographic hyperlinks, giving robust ensures of immutability and transparency. | For each submitted signature, the service points a clear assertion receipt (i.e. cryptographic receipt). This receipt comprises proof that the signature was logged (together with the Merkle tree root and inclusion proof) and is signed by the transparency service. Organizations can retailer these receipts as proof for compliance audits, and anybody can later use them to independently confirm that an artifact’s signature was certainly recorded within the ledge at a selected time. |
How does it work in observe?
When a developer or automated construct system indicators a chunk of code, the signing service generates a COSE_Sign1 signature envelope, a compact binary signing format and RFC 9052 trade commonplace, containing signature, metadata, and the payload. That signed object (the COSE envelope) is then despatched to the Signing Transparency service. The service verifies the signature and the signer’s id towards its belief coverage, then appends a countersignature to the COSE envelope. This countersignature doesn’t exchange the unique—it augments it with Microsoft’s attestation and a pointer to the immutable ledger and the cryptographic inclusion proof.
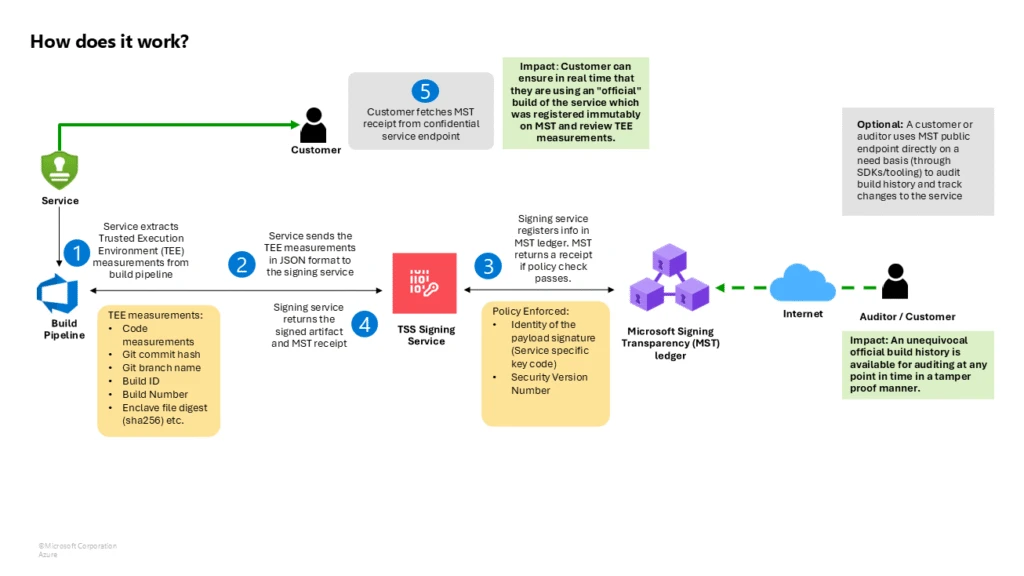
When the service commits an entry to its ledger, below the hood, this ledger is backed by Microsoft’s Confidential Ledger and Confidential Consortium Framework (CCF) operating in a TEE. Every entry sometimes consists of metadata corresponding to a hash of the signed artifact, the unique signature, the signer’s id, and the countersignature. The ledger makes use of a Merkle tree knowledge construction, so when the brand new entry is added, a brand new Merkle root is computed. The service cryptographically indicators this root and packages it (together with the trail of hashes proving the entry’s inclusion) into the receipt returned to the person. The receipt basically says, “We, the transparency service, have recorded your artifact’s signature at place X in our log (with root hash Y). Right here is the proof and our signature to vouch for it.”
As a result of the receipt is a signed proof of inclusion, and the ledger is backed by confidential computing, verification proves the thing handed the log’s belief coverage, and the signing occasion was logged for each participant—be it an automatic deployment system, an auditor, or an end-user—to see and independently confirm.
How Signing Transparency enhances safety and belief
Implementing Signing Transparency presents enterprises substantial safety by:
- Tamper-evident releases: All software program builds and updates have to be logged, making any unauthorized or modified launch instantly detectable. The immutable logs guarantee artifacts haven’t been secretly altered.
- Impartial verification: Clients and companions can confirm software program authenticity regionally utilizing transparency receipts, eliminating sole reliance on distributors or distribution channels.
- Audit path and compliance: Each software program element is linked to a signed receipt, offering clear proof for compliance audits and incident investigations. Logs might be monitored for anomalies.
- Coverage enforcement and accountability: Transparency companies implement logging insurance policies and retain information of signing actions, deterring insider threats, and guaranteeing accountability for coverage violations.
- Safety towards key compromise and replay: Any use of a compromised signing secret is seen within the log, and freshness proofs stop rollback assaults by verifying the newest variations.
- Prolonged to firmware and {hardware}: The identical rules apply to firmware and {hardware}, supporting provide chain integrity throughout all know-how layers, from servers to IoT gadgets, with initiatives like OCP-SAFE and Caliptra enabling verification.
Why verifiable code integrity and transparency are important for software program provide chain safety
With software program provide chain assaults on the rise, organizations want proof of integrity and quick detection strategies. Microsoft’s Signing Transparency service advances this by attaching a verifiable document to every signed artifact, selling belief by transparency. For enterprises, adopting this know-how allows direct verification of code, reduces danger, builds buyer confidence, and deters tampering by conserving malicious actions on document.
I’m ! How can I be taught extra?
Be a part of the preview group for a digital chat by expressing curiosity right here.

