Overview
This weblog publish describes help for materialized views for the Iceberg desk format in Cloudera Knowledge Warehouse.
Apache Iceberg is a high-performance open desk format for petabyte-scale analytic datasets. It has been designed and developed as an open group normal to make sure compatibility throughout languages and implementations. It brings the reliability and ease of SQL tables to massive information whereas enabling engines like Hive, Impala, Spark, Trino, Flink, and Presto to work with the identical tables on the similar time. Apache Iceberg kinds the core basis for Cloudera’s Open Knowledge Lakehouse with the Cloudera Knowledge Platform (CDP).
Materialized views are worthwhile for accelerating widespread courses of enterprise intelligence (BI) queries that include joins, group-bys and mixture features. Cloudera Knowledge Warehouse (CDW) working Hive has beforehand supported creating materialized views towards Hive ACID supply tables. Ranging from the CDW Public Cloud DWX-1.6.1 launch and the matching CDW Personal Cloud Knowledge Companies launch, Hive additionally helps creating, utilizing, and rebuilding materialized views for Iceberg desk format.
The important thing traits of this performance are:
- Supply tables of the materialized view are Iceberg tables (the underlying file format may very well be Parquet, ORC).
- The materialized view itself is an Iceberg desk.
- Materialized views may be partitioned on a number of columns.
- Queries containing joins, filters, projections, group-by, or aggregations with out group-by may be transparently rewritten by the Hive optimizer to make use of a number of eligible materialized views. This may probably result in orders of magnitude enchancment in efficiency.
- Each full and incremental rebuild of the materialized view are supported. Incremental rebuild may be executed beneath qualifying circumstances.
Create Iceberg materialized view
For the examples on this weblog, we’ll use three tables from the TPC-DS dataset as our base tables: store_sales, buyer and date_dim.
These tables are created as Iceberg tables. As an example:
create desk store_sales ( `ss_sold_time_sk` int, … … `ss_net_profit` decimal(7,2)) PARTITIONED BY ( `ss_sold_date_sk` int) saved by iceberg saved as orc ;
It’s the similar for the opposite two tables. We populated the tables utilizing INSERT-SELECT statements by studying from textual content format supply tables however they are often populated by any ETL course of.
Let’s create a materialized view that joins the three tables, has filter circumstances, and does grouped aggregation. Such a question sample is kind of widespread in BI queries. Notice that the materialized view definition incorporates the ‘saved by iceberg’ clause. Moreover, it’s partitioned on the d_year column.
drop materialized view year_total_mv1; create materialized view year_total_mv1 PARTITIONED ON (dyear) saved by iceberg saved as orc tblproperties ('format-version'='2') AS choose c_birth_country customer_birth_country ,d_year dyear ,sum(ss_ext_sales_price) year_total_sales ,depend(ss_ext_sales_price) total_count from buyer ,store_sales ,date_dim the place c_customer_sk = ss_customer_sk and ss_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk and d_year between 1999 and 2023 group by c_birth_country ,d_year ;
Present materialized view metadata
Much like an everyday desk, you may describe the materialized view to indicate metadata.
DESCRIBE FORMATTED year_total_mv1;Just a few key traits are listed beneath (extracted from the DESCRIBE output):

As proven above, this materialized view is enabled for rewrites and isn’t outdated. The snapshotId of the supply tables concerned within the materialized view are additionally maintained within the metadata. Subsequently, these snapshot IDs are used to find out the delta modifications that needs to be utilized to the materialized view rows.
SHOW MATERIALIZED VIEWS;

The final column signifies that the materialized view may be incrementally maintained within the presence of insert operations solely. If the bottom desk information is modified by an UPDATE/DELETE/MERGE operation, then the materialized view should undergo a full rebuild. In a future model, we intend to help incremental rebuild for such instances.
A materialized view will also be explicitly disabled for rewrites. That is just like disabling indexes in databases for sure causes.
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW year_total_mv1 DISABLE REWRITE;
Conversely, it may be enabled as follows:
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW year_total_mv1 ENABLE REWRITE;
Question planning utilizing materialized view
Let’s first contemplate a easy case the place the grouping columns and mixture expression precisely match one of many materialized views.
clarify cbo choose c_birth_country customer_birth_country ,d_year dyear ,sum(ss_ext_sales_price) year_total_sales from buyer ,store_sales ,date_dim the place c_customer_sk = ss_customer_sk and ss_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk and d_year between 2000 and 2003 group by c_birth_country ,d_year ;
CBO PLAN:
HiveProject(customer_birth_country=[$0], dyear=[$3], year_total_sales=[$1]) HiveFilter(situation=[BETWEEN(false, $3, 2000, 2003)]) HiveTableScan(desk=[[tpcds_iceberg, year_total_mv1]], desk:alias=[tpcds_iceberg.year_total_mv1])
The above CBO (value based mostly optimizer) plan reveals that solely the year_total_mv1 materialized view is scanned and a filter situation utilized for the reason that vary filter within the question is a subset of the vary within the materialized view. Thus, the scans and joins of the three tables within the unique question usually are not wanted and this will enhance efficiency considerably as a consequence of each I/O value saving and the CPU value saving of computing the joins and aggregations.
Now contemplate a extra superior utilization the place the group-by and mixture expressions within the question don’t precisely match the materialized view however can probably be derived.
clarify cbo choose c_birth_country customer_birth_country ,avg(ss_ext_sales_price) year_average_sales from buyer ,store_sales ,date_dim the place c_customer_sk = ss_customer_sk and ss_sold_date_sk = d_date_sk and d_year between 2000 and 2003 group by c_birth_country ;
CBO PLAN:
HiveProject(customer_birth_country=[$0], year_average_sales=[CAST(/($1, COALESCE($2, 0:BIGINT))):DECIMAL(11, 6)]) HiveAggregate(group=[{0}], agg#0=[sum($1)], agg#1=[sum($2)]) HiveFilter(situation=[BETWEEN(false, $3, 2000, 2003)]) HiveTableScan(desk=[[tpcds_iceberg, year_total_mv1]], desk:alias=[tpcds_iceberg.year_total_mv1])
Right here, the materialized view year_total_mv1 incorporates the SUM and COUNT mixture expressions that are used to derive the AVG(ss_ext_sales_price) expression for the question. Additional, for the reason that question incorporates GROUP BY c_birth_country solely, a second-level grouping is finished on c_birth_country to provide the ultimate output.
Incremental and full rebuild of materialized view
We’ll insert rows into the bottom desk and study how the materialized view may be up to date to replicate the brand new information.

Because of the desk modification, Iceberg creates new snapshots and the metadata desk “snapshots” may be examined to view the brand new snapshot model:
SELECT * FROM tpcds_iceberg.store_sales.snapshots;Notice that the materialized view is now marked outdated for rewriting as a result of their contents at the moment are stale:
DESCRIBE FORMATTED year_total_mv1;Outdated for Rewriting: Sure
Operating the unique question now is not going to leverage the materialized view and as an alternative do the complete scan of the supply tables adopted by the joins and group-by.
Allow us to now rebuild the materialized view:
ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW year_total_mv1 REBUILD;This does an incremental rebuild of the materialized view by studying solely the delta modifications from the store_sales desk. Hive does this by asking the Iceberg library to return solely the rows inserted since that desk’s final snapshot when the materialized view was final rebuilt/created. It then computes the combination values for these delta rows after becoming a member of them with the opposite tables. Lastly, this set of rows is outer joined with the materialized view utilizing the grouping columns because the be part of key and the suitable mixture values are consolidated—for instance, the outdated sum and the brand new sum are added collectively and the outdated min/max mixture values could also be changed with the brand new one relying on whether or not the brand new worth is decrease/increased than the outdated one.
The rebuild of the materialized view is triggered manually right here nevertheless it will also be executed on a periodic interval utilizing the scheduled question strategy.
At this level, the materialized view needs to be out there for question rewrites:
DESCRIBE FORMATTED year_total_mv1; Outdated for Rewriting: No
Re-running the unique question will once more use the materialized view.
Qualifying circumstances for incremental rebuild
An incremental rebuild is just not doable beneath the next conditions:
- If the bottom desk was modified by a DELETE/MERGE/UPDATE operation.
- If the combination operate is something aside from SUM, MIN, MAX, COUNT, AVG. Different aggregates similar to STDDEV, VARIANCE, and comparable require a full scan of the bottom information.
- If any of the supply tables had been compacted for the reason that final rebuild. Compaction creates a brand new snapshot consisting of merged information and it isn’t doable to find out the delta modifications for the reason that final rebuild operation.
In such conditions, Hive falls again to the complete rebuild. This fall-back is finished transparently as a part of the identical REBUILD command.
A Notice on Iceberg materialized view specification
At the moment, the metadata wanted for materialized views is maintained in Hive Metastore and it builds upon the materialized views metadata beforehand supported for Hive ACID tables. Over the previous yr, the Iceberg group has proposed a materialized view specification. We intend to undertake this specification sooner or later for Hive Iceberg materialized view help.
Efficiency with materialized views
With the intention to consider the efficiency of queries within the presence of materialized views in Iceberg desk format, we used a TPC-DS information set at 1 TB scale issue. The desk format was Iceberg and the underlying file format was ORC (comparable checks may be carried out with Parquet however we selected ORC as most Hive clients use ORC). We ran the ANALYZE command to assemble each desk and column statistics on all the bottom tables.
We began with twenty three TPC-DS queries and created variants of them such that we had a complete of fifty queries within the workload. Every question had between one to 3 variants. A variant was created by one of many following modifications: (a) including further columns within the GROUP-BY clause (b) including further aggregation operate within the SELECT checklist, and (c) including or modifying single desk WHERE predicates. We obtained the EXPLAIN CBO (value based mostly optimization) plan in JSON format for all of the fifty queries and provided the plans to a materialized view recommender that’s supported by Cloudera Knowledge Warehouse. Primarily based on the ranked suggestions, we picked the highest seven materialized views and created them within the Iceberg desk format. We ran the fifty question workload on a CDW Hive digital warehouse on AWS utilizing a big t-shirt measurement (see Digital Warehouse sizes) . Every question was run thrice and the minimal whole execution time was captured. The question efficiency outcomes are proven beneath with and with out the materialized view rewrite enabled. The next configuration possibility is toggled for this:
SET hive.materializedview.rewriting = false;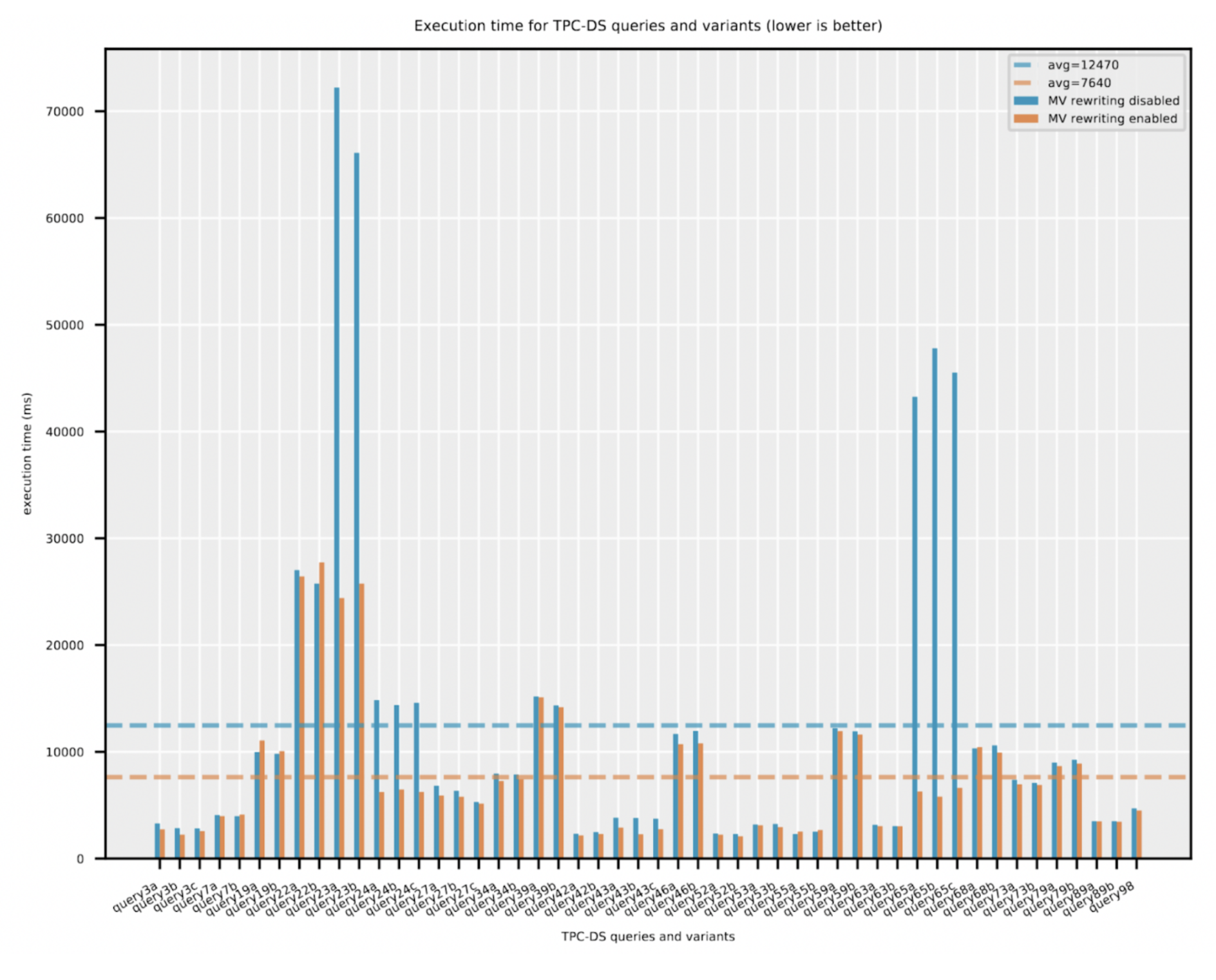
Out of the fifty queries, there are sixteen queries which the optimizer deliberate utilizing materialized views. Just a few of the longer working queries benefited essentially the most by the materialized views – for instance the query65 a, b, c variants confirmed a discount of almost 85% within the elapsed time. Total, throughout all queries, the typical discount in whole elapsed time was 40%. We additionally checked out solely the question compilation time overhead for queries that didn’t hit the materialized views. A slight enhance of 4% within the common question compilation time, roughly 60 milliseconds, was noticed because of the optimizer making an attempt to judge the feasibility of utilizing materialized views.
This efficiency analysis targeted on the question rewrite efficiency utilizing materialized views. In a future weblog, we’ll consider the incremental versus full rebuild efficiency.
Conclusion
This weblog publish describes the materialized view help in Hive for the Iceberg desk format. This performance is obtainable in Cloudera Knowledge Warehouse (CDW) Public Cloud deployments on AWS and Azure in addition to in CDW Personal Cloud Knowledge Companies deployments. Customers can create materialized views on Iceberg supply tables, and Hive will leverage these to speed up question efficiency. When the supply desk information is modified, incremental rebuild of the materialized view is supported beneath qualifying circumstances (said above); in any other case, a full rebuild is finished.
The help for Apache Iceberg because the desk format in Cloudera Knowledge Platform and the flexibility to create and use materialized views on high of such tables gives a strong mixture to construct quick analytic functions on open information lake architectures. Join considered one of our subsequent hands-on labs to strive Apache Iceberg on Cloudera’s lakehouse and see the advantages and ease of utilizing materialized views. You can too join the webinar to be taught extra about the advantages of Apache Iceberg and watch the demo to see the most recent capabilities.
Acknowledgement
The authors want to acknowledge the help of Soumyakanti Das in gathering the efficiency outcomes.




