When constructing a software-intensive system, a key half in making a safe and sturdy answer is to develop a cyber risk mannequin. It is a mannequin that expresses who is perhaps thinking about attacking your system, what results they may wish to obtain, when and the place assaults might manifest, and the way attackers would possibly go about accessing the system. Menace fashions are vital as a result of they information necessities, system design, and operational selections. Results can embody, for instance, compromise of confidential data, modification of knowledge contained within the system, and disruption of operations. There are various functions for reaching these sorts of results, starting from espionage to ransomware.
This weblog submit focuses on a technique risk modelers can use to make credible claims about assaults the system might face and to floor these claims in observations of adversary ways, methods, and procedures (TTPs).
Brainstorming, subject material experience, and operational expertise can go a great distance in growing a listing of related risk eventualities. Throughout preliminary risk situation era for a hypothetical software program system, it will be doable to think about, What if attackers steal account credentials and masks their motion by placing false or unhealthy knowledge into the person monitoring system? The tougher process—the place the angle of risk modelers is crucial—substantiates that situation with recognized patterns of assaults and even particular TTPs. These may very well be knowledgeable by potential risk intentions based mostly on the operational function of the system.
Creating sensible and related mitigation methods for the recognized TTPs is a crucial contributor to system necessities formulation, which is likely one of the targets of risk modeling.
This SEI weblog submit outlines a technique for substantiating risk eventualities and mitigations by linking to industry-recognized assault patterns powered by model-based programs engineering (MBSE).
In his memo Directing Fashionable Software program Acquisition to Maximize Lethality, Secretary of Protection Pete Hegseth wrote, “Software program is on the core of each weapon and supporting system we area to stay the strongest, most deadly combating pressure on this planet.” Whereas understanding cyber threats to those advanced software program intensive programs is vital, figuring out threats and mitigations to them early within the design of a system helps scale back the fee to repair them. In response to Govt Order (EO) 14028, Enhancing the Nation’s Cybersecurity, the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST) advisable 11 practices for software program verification. Menace modeling is on the prime of the checklist.
Menace Modeling Objectives: 4 Key Questions
Menace modeling guides the necessities specification and early design selections to make a system sturdy towards assaults and weaknesses. Menace modeling may also help software program builders and cybersecurity professionals know what sorts of defenses, mitigation methods, and controls to place in place.
Menace modelers can body the method of risk modeling round solutions to 4 key questions (tailored from Adam Shostack):
- What are we constructing?
- What can go flawed?
- What ought to we do about these wrongs?
- Was the evaluation ample?
What Are We Constructing?
The muse of risk modeling is the mannequin of the system targeted on its potential interactions with threats. A mannequin is a graphical, mathematical, logical, or bodily illustration that abstracts actuality to handle a selected set of issues whereas omitting particulars not related to the issues of the mannequin builder. There are various methodologies that present steering on how one can assemble risk fashions for various kinds of programs and use circumstances. For already constructed programs the place the design and implementation are recognized and the place the principal issues relate to faults and errors (relatively than acts by intentioned adversaries), methods resembling fault tree evaluation could also be extra acceptable. These methods usually assume that desired and undesired states are recognized and will be characterised. Equally, kill chain evaluation will be useful to grasp the complete end-to-end execution of a cyber assault.
Nevertheless, present high-level programs engineering fashions is probably not acceptable to establish particular vulnerabilities used to conduct an assault. These programs engineering fashions can create helpful context, however extra modeling is important to handle threats.
On this submit I exploit the Unified Structure Framework (UAF) to information our modeling of the system. For bigger programs using MBSE, the risk mannequin can construct on DoDAF, UAF, or different architectural framework fashions. The widespread thread with all of those fashions is that risk modeling is enabled by fashions of knowledge interactions and flows amongst elements. A typical mannequin additionally offers advantages in coordination throughout massive groups. When a number of teams are engaged on and deriving worth from a unified mannequin, the up-front prices will be extra manageable.
There are various notations for modeling knowledge flows or interactions. We discover on this weblog using an MBSE software paired with a normal architectural framework to create fashions with advantages past easier diagramming software or drawings. For present programs with no mannequin, it’s nonetheless doable to make use of MBSE. This may be finished incrementally. For example, if new options are being added to an present system, it could be essential to mannequin simply sufficient of the system interacting with the brand new data flows or knowledge shops and create risk fashions for this subset of recent components.
What Can Go Incorrect?
Menace modeling is much like programs modeling in that there are lots of frameworks, instruments, and methodologies to assist information growth of the mannequin and establish potential drawback areas. STRIDE is risk identification taxonomy that may be a helpful a part of fashionable risk modeling strategies, having initially been developed at Microsoft in 1999. Earlier work by the SEI has been carried out to increase UAF with a profile that enables us to mannequin the outcomes of the risk identification step that makes use of STRIDE. We proceed that method on this weblog submit.
STRIDE itself is an acronym standing for spoofing, tampering, repudiation, data disclosure, denial of service, and elevation of privilege. This mnemonic helps modelers to categorize the impacts of threats on totally different knowledge shops and knowledge flows. Earlier work by Scandariato et al., of their paper A descriptive examine of Microsoft’s risk modeling method has additionally proven that STRIDE is adaptable to a number of ranges of abstraction. This paper exhibits that a number of groups modeling the identical system did so with various dimension and composition of the information stream diagrams used. When engaged on new programs or a high-level structure, a risk modeler could not have all the main points wanted to make the most of some extra in-depth risk modeling approaches. It is a good thing about the STRIDE method.
Along with the taxonomic structuring supplied by STRIDE, having a normal format for capturing the risk eventualities allows simpler evaluation. This format brings collectively the weather from the programs mannequin, the place now we have recognized belongings and knowledge flows, the STRIDE technique for figuring out risk sorts, and the identification of potential classes of risk actors who may need intent and means to create conequences. Menace actors can vary from insider threats to nation-state actors and superior persistent threats. The next template exhibits every of those components on this customary format and accommodates the entire important particulars of a risk situation.
An [ACTOR] performs an [ACTION] to [ATTACK] an [ASSET] to realize an [EFFECT] and/or [OBJECTIVE].
ACTOR | The individual or group that’s behind the risk situation
ACTION | A possible incidence of an occasion which may harm an asset or objective of a strategic imaginative and prescient
ATTACK | An motion taken that makes use of a number of vulnerabilities to appreciate a risk to compromise or harm an asset or circumvent a strategic objective
ASSET | A useful resource, individual, or course of that has worth
EFFECT | The specified or undesired consequence
OBJECTIVE | The risk actor’s motivation or goal for conducting the assault
With formatted risk eventualities in hand, we are able to begin to combine the weather of the eventualities into our system mannequin. On this mannequin, the risk actor components describe the actors concerned in a risk situation, and the risk component describes the risk situation, goal, and impact. From these two components, we are able to, inside the mannequin, create relations to the precise components affected or in any other case associated to the risk situation. Determine 1 exhibits how the totally different risk modeling items work together with parts of the UAF framework.

Determine 1: Menace Modeling Profile
For the diagram components highlighted in pink, our crew has prolonged the usual UAF with new components (<<Assault>>, <<Menace>>, <<Menace Actor>> and <<Safety Requirement>> blocks) in addition to new relationships between them (<<Causes>>, <<Realizes Assault>> and <<Compromises>>). These additions seize the consequences of a risk situation in our mannequin. Capturing these eventualities helps reply the query, What can go flawed?
Right here I present an instance of how one can apply this profile. First, we have to outline a part of a system we wish to construct and a number of the elements and their interactions. If we’re constructing a software program system that requires a monitoring and logging functionality, there may very well be a risk of disruption of that monitoring and logging service. An instance risk situation written within the model of our template can be, A risk actor spoofs a respectable account (person or service) and injects falsified knowledge into the monitoring system to disrupt operations, create a diversion, or masks the assault. It is a good begin. Subsequent, we are able to incorporate the weather from this situation into the mannequin. Represented in a safety taxonomy diagram, this risk situation would resemble Determine 2 under.
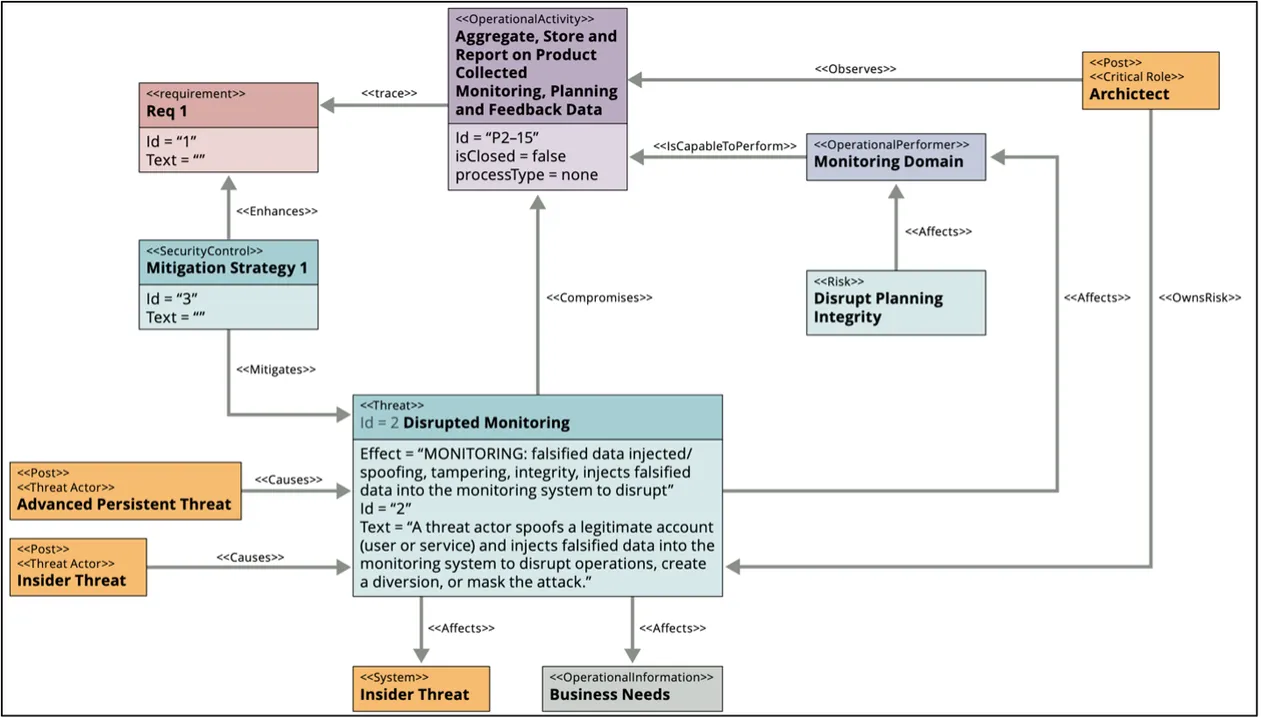
Determine 2: Disrupted Monitoring Menace Situation
What’s vital to notice right here is that the risk situation a risk modeler creates drives mitigation methods that place necessities on the system to implement these mitigations. That is, once more, the objective of risk modeling. Nevertheless, these mitigation methods and necessities in the end constrain the system design and will impose extra prices. A major profit to figuring out threats early in system growth is a discount in value; nonetheless, the true value of mitigating a risk situation won’t ever be zero. There may be at all times some trade-off. Given this value of mitigating threats, it’s vitally vital that risk eventualities be grounded in fact. Ideally, noticed TTPs ought to drive the risk eventualities and mitigation methods.
Introduction to CAPEC
MITRE’s Frequent Assault Sample Enumerations and Classifications (CAPEC) challenge goals to create simply such a listing of assault patterns. These assault patterns at various ranges of abstraction enable a straightforward mapping from risk eventualities for a selected system to recognized assault patterns that exploit recognized weaknesses. For every of the entries within the CAPEC checklist, we are able to create <<Assault>> components from the prolonged UAF viewpoint proven in Determine 1. This offers many advantages that embody refining the eventualities initially generated, serving to decompose high-level eventualities, and, most crucially, creating the tie to recognized assaults.
Within the Determine 2 instance situation, a minimum of three totally different entries might apply to the situation as written. CAPEC-6: Argument Injection, CAPEC-594: Site visitors Injection, and CAPEC-194: Pretend the Supply of Information. This relationship is proven in Determine 3.

Determine 3: Menace Situation to Assault Mapping
<<Assault>> blocks present how a situation will be realized. By tracing the <<Menace>> block to <<Assault>> blocks, a risk modeler can present some stage of assurance that there are actual patterns of assault that may very well be used to realize the target or impact specified by the situation. Utilizing STRIDE as a foundation for forming the risk eventualities helps to map to those CAPEC entries in following means. CAPEC will be organized by mechanisms of assault (resembling “Interact in misleading interactions”) or by Domains of assault (resembling “{hardware}” or “provide chain”). The previous technique of group aids the risk modeler within the preliminary seek for discovering the proper entries to map the threats to, based mostly on the STRIDE categorization. This isn’t a one-to-one mapping as there are semantic variations; nonetheless, basically the next desk exhibits the STRIDE risk sort and the mechanism of assault that’s more likely to correspond.
STRIDE risk sort | CAPEC Mechanism of Assault | |
Spoofing | Interact in Misleading Interactions | |
Tampering | Manipulate Information Constructions, Manipulate System Assets | |
Repudiation | Inject Sudden Objects | |
Info Disclosure | Gather and Analyze Info | |
Denial of Service | Abuse Current Performance | |
Elevation of Privilege | Subvert Entry Management |
As beforehand famous, this isn’t a one-to-one mapping. For example, the “Make use of probabilistic methods” and “Manipulate timing and state” mechanisms of assault are usually not represented right here. Moreover, there are STRIDE assault sorts that span a number of mechanisms of assault. This isn’t stunning provided that CAPEC is just not oriented round STRIDE.
Figuring out Menace Modeling Mitigation Methods and the Significance of Abstraction Ranges
As proven in Determine 2, having recognized the affected belongings, data flows, processes and assaults, the subsequent step in risk modeling is to establish mitigation methods. We additionally present how the unique risk situation was in a position to be mapped to totally different assaults at totally different ranges of abstraction and why standardizing on a single abstraction stage offers advantages.
When coping with particular points, it’s simple to be particular in making use of mitigations. One other instance is a laptop computer operating macOS 15. The Apple macOS 15 STIG Guide states that, “The macOS system should restrict SSHD to FIPS-compliant connections.” Moreover, the handbook says, “Working programs utilizing encryption should use FIPS-validated mechanisms for authenticating to cryptographic modules.” The handbook then particulars check procedures to confirm this for a system and what precise instructions to run to repair the problem if it’s not true. It is a very particular instance of a system that’s already constructed and deployed. The extent of abstraction may be very low, and all knowledge flows and knowledge shops all the way down to the bit stage are outlined for SSHD on macOS 15. Menace modelers should not have that stage of element at early phases of the system growth lifecycle.
Particular points additionally are usually not at all times recognized even with an in depth design. Some software program programs are small and simply replaceable or upgradable. In different contexts, resembling in main protection programs or satellite tv for pc programs, the flexibility to replace, improve, or change the implementation is restricted or tough. That is the place engaged on a better abstraction stage and specializing in design components and knowledge flows can remove broader courses of threats than will be eradicated by working with extra detailed patches or configurations.
To return to the instance proven in Determine 2, on the present stage of system definition it’s recognized that there shall be a monitoring answer to mixture, retailer, and report on collected monitoring and suggestions data. Nevertheless, will this answer be a industrial providing, a home-grown answer, or a mixture? What particular applied sciences shall be used? At this level within the system design, these particulars are usually not recognized. Nevertheless, that doesn’t imply that the risk can’t be modeled at a excessive stage of abstraction to assist inform necessities for the eventual monitoring answer.
CAPEC consists of three totally different ranges of abstraction concerning assault patterns: Meta, Commonplace, and Detailed. Meta assault patterns are excessive stage and don’t embody particular expertise. This stage is an effective match for our instance. Commonplace assault patterns do name out some particular applied sciences and methods. Detailed assault patterns give the complete view of how a selected expertise is attacked with a selected method. This stage of assault sample can be extra widespread in a answer structure.
To establish mitigation methods, we should first guarantee our eventualities are normalized to some stage of abstraction. The instance situation from above has points on this regard. First the situation is compound in that the risk actor has three totally different goals (i.e., disrupt operations, create a diversion, and masks the assault). When trying to hint mitigation methods or necessities to this situation, it could be tough to see the clear linkage. The kind of account can also influence the mitigations. It could be a requirement that a normal person account not be capable of entry log knowledge whereas a service account could also be permitted to have such entry to do upkeep duties. These complexities attributable to the compound situation are additionally illustrated by the tracing of the situation to a number of CAPEC entries. These assaults signify distinctive units of weaknesses, and all require totally different mitigation methods.
To decompose the situation, we are able to first break up out the various kinds of accounts after which break up on the totally different goals. A full decomposition of those elements is proven in Determine 4.

Determine 4: Menace Situation Decomposition
This decomposition considers that totally different goals usually are achieved via totally different means. If a risk actor merely desires to create a diversion, the weak spot will be loud and ideally set off alarms or points that the system’s operators should take care of. If as an alternative the target is to masks an assault, then the attacker could should deploy quieter ways when injecting knowledge.
Determine 4 is just not the one approach to decompose the eventualities. The unique situation could also be break up into two based mostly on the spoofing assault and the information injection assault (the latter falling into the tampering class beneath STRIDE). Within the first situation, a risk actor spoofs a respectable account (CAPEC-194: Pretend the Supply of Information) to maneuver laterally via the community. Within the second situation, a risk actor performs an argument injection (CAPEC-6: Argument Injection) into the monitoring system to disrupt operations.
Given the breakdown of our authentic situation into the rather more scope-limited sub-scenarios, we are able to now simplify the mapping by mapping these to a minimum of one standard-level assault sample that offers extra element to engineers to engineer in mitigations for the threats.
Now that now we have the risk situation damaged down into extra particular eventualities with a single goal, we will be extra particular with our mapping of assaults to risk eventualities and mitigation methods.
As famous beforehand, mitigation methods, at a minimal, constrain design and, in most circumstances, can drive prices. Consequently, mitigations needs to be focused to the precise elements that can face a given risk. That is why decomposing risk eventualities is vital. With a precise mapping between risk eventualities and confirmed assault patterns, one can both extract mitigation methods straight from the assault sample entries or give attention to producing one’s personal mitigation methods for a minimally full set of patterns.
Argument injection is a superb instance of an assault sample in CAPEC that features potential mitigations. This assault sample contains two design mitigations and one implementation-specific mitigation. When risk modeling on a excessive stage of abstraction, the design-focused mitigations will usually be extra related to designers and designers.

Determine 5: Mitigations Mapped to a Menace.
Determine 5 exhibits how the 2 design mitigations hint to the risk that’s realized by an assault. On this case the assault sample we’re mapping to had mitigations linked and laid out plainly. Nevertheless, this doesn’t imply mitigation methods are restricted to what’s within the database. A great system engineer will tailor the utilized mitigations for a selected system, setting, and risk actors. It needs to be famous in the identical vein that assault components needn’t come from CAPEC. We use CAPEC as a result of it’s a customary; nonetheless, if there’s an assault not captured or not captured on the proper stage of element, one can create one’s personal assault components within the mannequin.
Bringing Credibility to Menace Modeling
The overarching objective of risk modeling is to assist defend a system from assault. To that finish, the actual product {that a} risk mannequin ought to produce is mitigation methods for threats to the system components, actions, and knowledge flows. Leveraging a combination of MBSE, UAF, the STRIDE methodology, and CAPEC can accomplish this objective. Whether or not working on a high-level summary structure or with a extra detailed system design, this technique is versatile to accommodate the quantity of knowledge available and to permit risk modeling and mitigation to happen as early within the system design lifecycle as doable. Moreover, by counting on an industry-standard set of assault patterns, this technique brings credibility to the risk modeling course of. That is completed via the traceability from an asset to the risk situation and the real-world noticed patterns utilized by adversaries to hold out the assault.

