Each database constructed for real-time analytics has a basic limitation. While you deconstruct the core database structure, deep within the coronary heart of it you will discover a single part that’s performing two distinct competing features: real-time knowledge ingestion and question serving. These two components operating on the identical compute unit is what makes the database real-time: queries can mirror the impact of the brand new knowledge that was simply ingested. However, these two features instantly compete for the accessible compute assets, making a basic limitation that makes it tough to construct environment friendly, dependable real-time functions at scale. When knowledge ingestion has a flash flood second, your queries will decelerate or trip making your software flaky. When you have got a sudden surprising burst of queries, your knowledge will lag making your software not so actual time anymore.
This adjustments in the present day. We unveil true compute-compute separation that eliminates this basic limitation, and makes it doable to construct environment friendly, dependable real-time functions at large scale.
Study extra in regards to the new structure and the way it delivers efficiencies within the cloud on this tech speak I hosted with principal architect Nathan Bronson Compute-Compute Separation: A New Cloud Structure for Actual-Time Analytics.
The Problem of Compute Rivalry
On the coronary heart of each real-time software you have got this sample that the info by no means stops coming in and requires steady processing, and the queries by no means cease – whether or not they come from anomaly detectors that run 24×7 or end-user-facing analytics.
Unpredictable Knowledge Streams
Anybody who has managed real-time knowledge streams at scale will let you know that knowledge flash floods are fairly widespread. Even essentially the most behaved and predictable real-time streams may have occasional bursts the place the quantity of the info goes up in a short time. If left unchecked the info ingestion will fully monopolize your complete real-time database and lead to question sluggish downs and timeouts. Think about ingesting behavioral knowledge on an e-commerce web site that simply launched a giant marketing campaign, or the load spikes a cost community will see on Cyber Monday.
Unpredictable Question Workloads
Equally, while you construct and scale functions, unpredictable bursts from the question workload are par for the course. On some events they’re predictable primarily based on time of day and seasonal upswings, however there are much more conditions when these bursts can’t be predicted precisely forward of time. When question bursts begin consuming all of the compute within the database, then they’ll take away compute accessible for the real-time knowledge ingestion, leading to knowledge lags. When knowledge lags go unchecked then the real-time software can not meet its necessities. Think about a fraud anomaly detector triggering an intensive set of investigative queries to know the incident higher and take remedial motion. If such question workloads create extra knowledge lags then it should actively trigger extra hurt by growing your blind spot on the actual mistaken time, the time when fraud is being perpetrated.
How Different Databases Deal with Compute Rivalry
Knowledge warehouses and OLTP databases have by no means been designed to deal with excessive quantity streaming knowledge ingestion whereas concurrently processing low latency, excessive concurrency queries. Cloud knowledge warehouses with compute-storage separation do provide batch knowledge masses operating concurrently with question processing, however they supply this functionality by giving up on actual time. The concurrent queries is not going to see the impact of the info masses till the info load is full, creating 10s of minutes of knowledge lags. So they aren’t appropriate for real-time analytics. OLTP databases aren’t constructed to ingest large volumes of knowledge streams and carry out stream processing on incoming datasets. Thus OLTP databases should not suited to real-time analytics both. So, knowledge warehouses and OLTP databases have not often been challenged to energy large scale real-time functions, and thus it’s no shock that they haven’t made any makes an attempt to deal with this problem.
Elasticsearch, Clickhouse, Apache Druid and Apache Pinot are the databases generally used for constructing real-time functions. And in the event you examine each certainly one of them and deconstruct how they’re constructed, you will notice all of them wrestle with this basic limitation of knowledge ingestion and question processing competing for a similar compute assets, and thereby compromise the effectivity and the reliability of your software. Elasticsearch helps particular goal ingest nodes that offload some components of the ingestion course of reminiscent of knowledge enrichment or knowledge transformations, however the compute heavy a part of knowledge indexing is completed on the identical knowledge nodes that additionally do question processing. Whether or not these are Elasticsearch’s knowledge nodes or Apache Druid’s knowledge servers or Apache Pinot’s real-time servers, the story is just about the identical. A number of the programs make knowledge immutable, as soon as ingested, to get round this problem – however actual world knowledge streams reminiscent of CDC streams have inserts, updates and deletes and never simply inserts. So not dealing with updates and deletes just isn’t actually an possibility.
Coping Methods for Compute Rivalry
In observe, methods used to handle this problem typically fall into certainly one of two classes: overprovisioning compute or making replicas of your knowledge.
Overprovisioning Compute
It is vitally widespread observe for real-time software builders to overprovision compute to deal with each peak ingest and peak question bursts concurrently. This can get value prohibitive at scale and thus just isn’t or sustainable resolution. It’s common for directors to tweak inner settings to arrange peak ingest limits or discover different methods to both compromise knowledge freshness or question efficiency when there’s a load spike, whichever path is much less damaging for the appliance.
Make Replicas of your Knowledge
The opposite strategy we’ve seen is for knowledge to be replicated throughout a number of databases or database clusters. Think about a major database doing all of the ingest and a duplicate serving all the appliance queries. When you have got 10s of TiBs of knowledge this strategy begins to grow to be fairly infeasible. Duplicating knowledge not solely will increase your storage prices, but additionally will increase your compute prices for the reason that knowledge ingestion prices are doubled too. On prime of that, knowledge lags between the first and the reproduction will introduce nasty knowledge consistency points your software has to take care of. Scaling out would require much more replicas that come at a good increased value and shortly your entire setup turns into untenable.
How We Constructed Compute-Compute Separation
Earlier than I’m going into the main points of how we solved compute rivalry and carried out compute-compute separation, let me stroll you thru a couple of essential particulars on how Rockset is architected internally, particularly round how Rockset employs RocksDB as its storage engine.
RocksDB is among the hottest Log Structured Merge tree storage engines on the planet. Again after I used to work at fb, my workforce, led by superb builders reminiscent of Dhruba Borthakur and Igor Canadi (who additionally occur to be the co-founder and founding architect at Rockset), forked the LevelDB code base and turned it into RocksDB, an embedded database optimized for server-side storage. Some understanding of how Log Structured Merge tree (LSM) storage engines work will make this half simple to comply with and I encourage you to confer with some glorious supplies on this topic such because the RocksDB Structure Information. In order for you absolutely the newest analysis on this area, learn the 2019 survey paper by Chen Lou and Prof. Michael Carey.
In LSM Tree architectures, new writes are written to an in-memory memtable and memtables are flushed, after they replenish, into immutable sorted strings desk (SST) information. Distant compactors, just like rubbish collectors in language runtimes, run periodically, take away stale variations of the info and forestall database bloat.
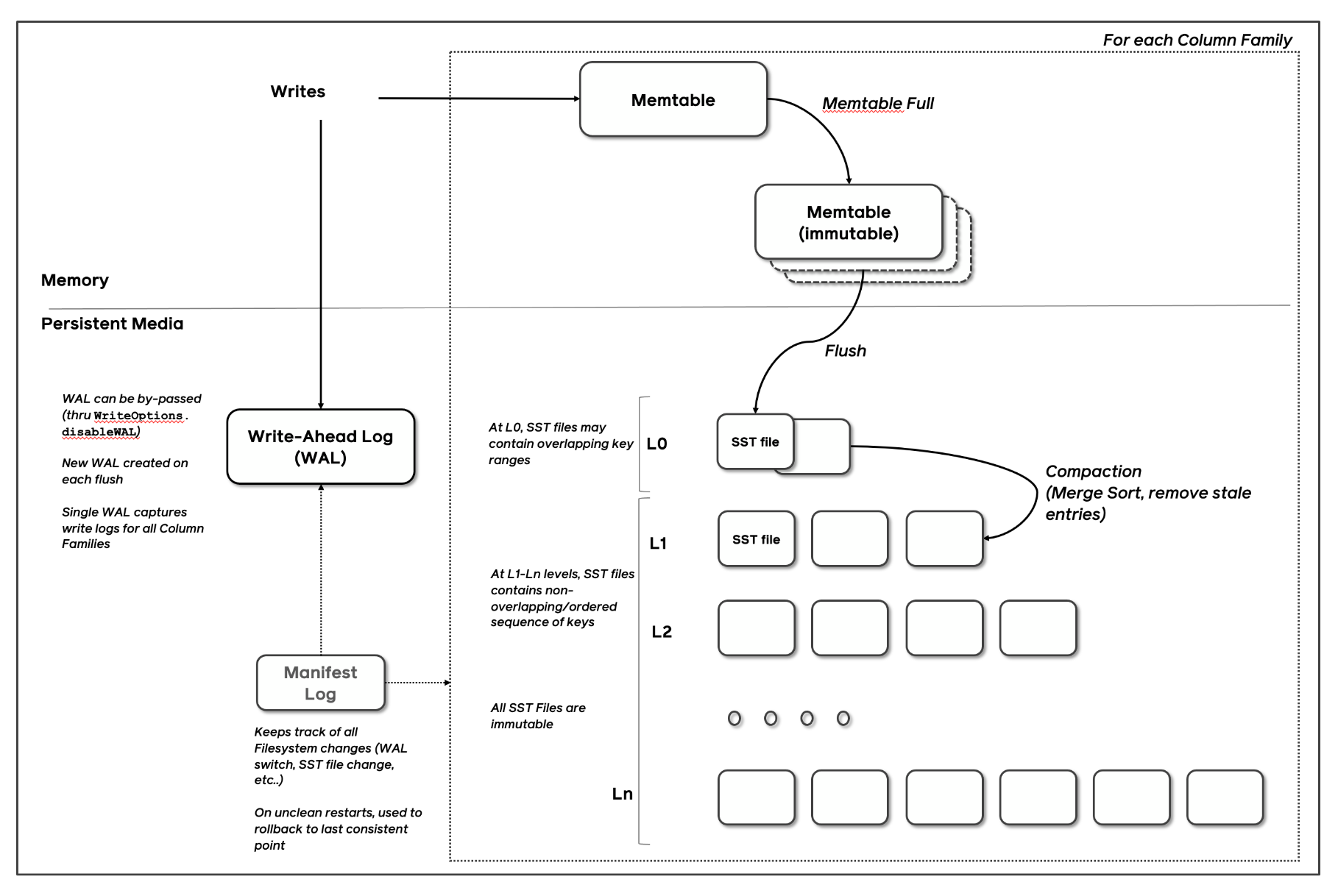
Each Rockset assortment makes use of a number of RocksDB cases to retailer the info. Knowledge ingested right into a Rockset assortment can also be written to the related RocksDB occasion. Rockset’s distributed SQL engine accesses knowledge from the related RocksDB occasion throughout question processing.
Step 1: Separate Compute and Storage
One of many methods we first prolonged RocksDB to run within the cloud was by constructing RocksDB Cloud, by which the SST information created upon a memtable flush are additionally backed into cloud storage reminiscent of Amazon S3. RocksDB Cloud allowed Rockset to fully separate the “efficiency layer” of the info administration system chargeable for quick and environment friendly knowledge processing from the “sturdiness layer” chargeable for guaranteeing knowledge isn’t misplaced.
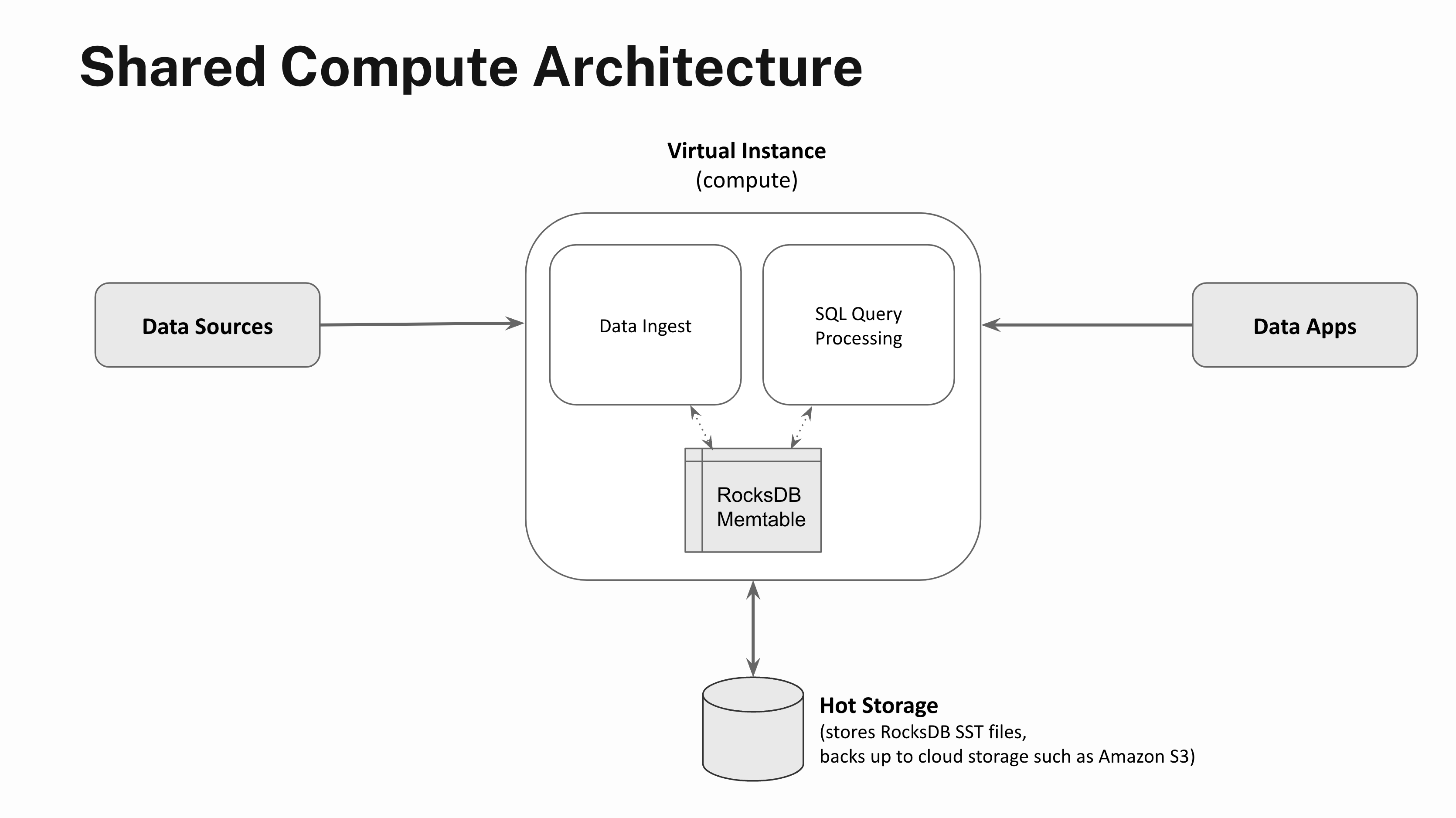
Actual-time functions demand low-latency, high-concurrency question processing. So whereas constantly backing up knowledge to Amazon S3 gives strong sturdiness ensures, knowledge entry latencies are too sluggish to energy real-time functions. So, along with backing up the SST information to cloud storage, Rockset additionally employs an autoscaling scorching storage tier backed by NVMe SSD storage that enables for full separation of compute and storage.
Compute items spun as much as carry out streaming knowledge ingest or question processing are referred to as Digital Situations in Rockset. The recent storage tier scales elastically primarily based on utilization and serves the SST information to Digital Situations that carry out knowledge ingestion, question processing or knowledge compactions. The recent storage tier is about 100-200x sooner to entry in comparison with chilly storage reminiscent of Amazon S3, which in flip permits Rockset to offer low-latency, high-throughput question processing.
Step 2: Separate Knowledge Ingestion and Question Processing Code Paths
Let’s go one stage deeper and take a look at all of the totally different components of knowledge ingestion. When knowledge will get written right into a real-time database, there are basically 4 duties that have to be carried out:
- Knowledge parsing: Downloading knowledge from the info supply or the community, paying the community RPC overheads, knowledge decompressing, parsing and unmarshalling, and so forth
- Knowledge transformation: Knowledge validation, enrichment, formatting, kind conversions and real-time aggregations within the type of rollups
- Knowledge indexing: Knowledge is encoded within the database’s core knowledge constructions used to retailer and index the info for quick retrieval. In Rockset, that is the place Converged Indexing is carried out
- Compaction (or vacuuming): LSM engine compactors run within the background to take away stale variations of the info. Be aware that this half isn’t just particular to LSM engines. Anybody who has ever run a VACUUM command in PostgreSQL will know that these operations are important for storage engines to offer good efficiency even when the underlying storage engine just isn’t log structured.
The SQL processing layer goes by way of the standard question parsing, question optimization and execution phases like every other SQL database.
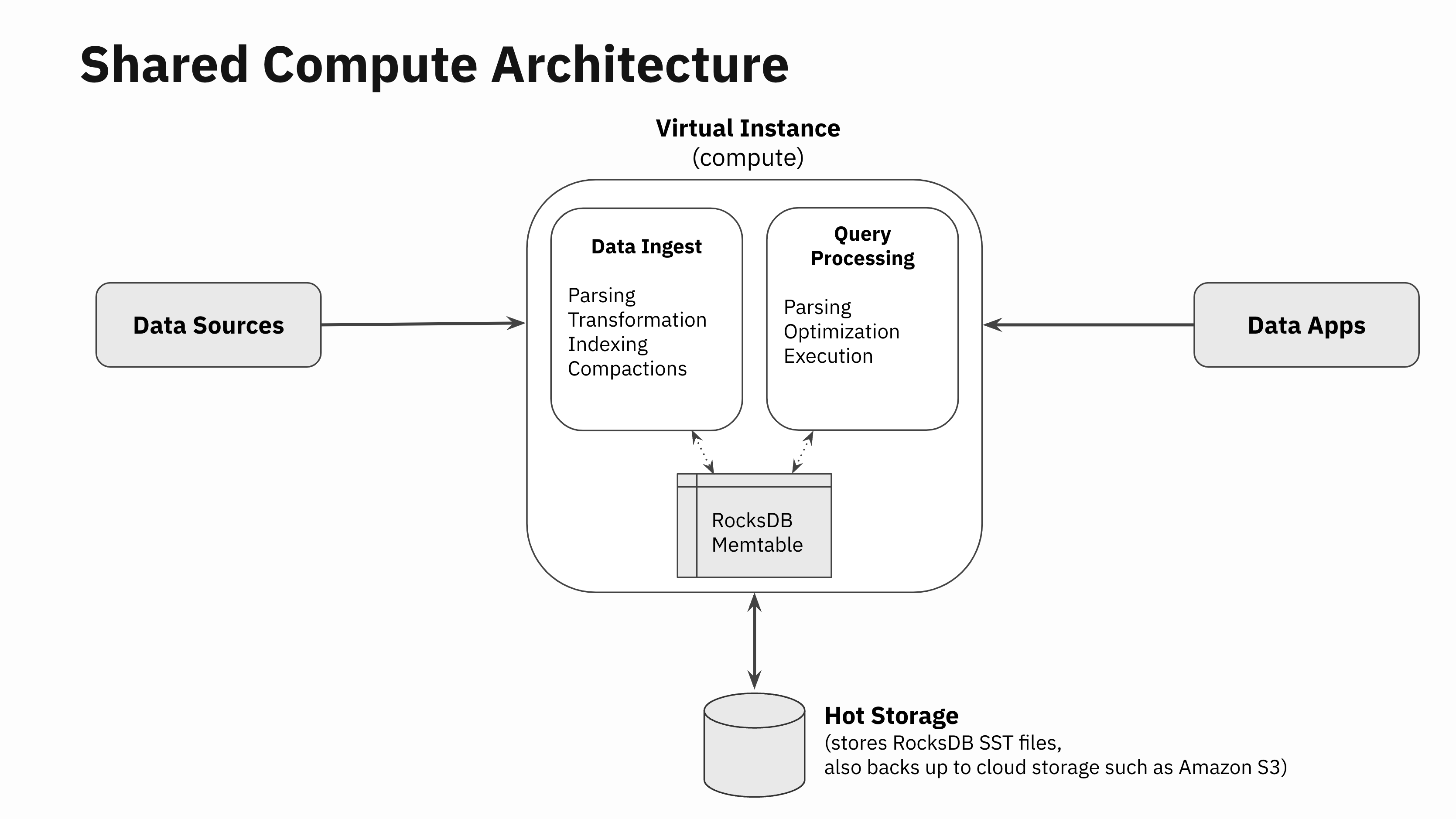
Constructing compute-compute separation has been a long run objective for us for the reason that very starting. So, we designed Rockset’s SQL engine to be fully separated from all of the modules that do knowledge ingestion. There are not any software program artifacts reminiscent of locks, latches, or pinned buffer blocks which are shared between the modules that do knowledge ingestion and those that do SQL processing exterior of RocksDB. The information ingestion, transformation and indexing code paths work fully independently from the question parsing, optimization and execution.
RocksDB helps multi-version concurrency management, snapshots, and has an enormous physique of labor to make varied subcomponents multi-threaded, remove locks altogether and cut back lock rivalry. Given the character of RocksDB, sharing state in SST information between readers, writers and compactors could be achieved with little to no coordination. All these properties enable our implementation to decouple the info ingestion from question processing code paths.
So, the one motive SQL question processing is scheduled on the Digital Occasion doing knowledge ingestion is to entry the in-memory state in RocksDB memtables that maintain essentially the most just lately ingested knowledge. For question outcomes to mirror essentially the most just lately ingested knowledge, entry to the in-memory state in RocksDB memtables is important.
Step 3: Replicate In-Reminiscence State
Somebody within the Seventies at Xerox took a photocopier, cut up it right into a scanner and a printer, related these two components over a phone line and thereby invented the world’s first phone fax machine which fully revolutionized telecommunications.
Related in spirit to the Xerox hack, in one of many Rockset hackathons a couple of 12 months in the past, two of our engineers, Nathan Bronson and Igor Canadi, took RocksDB, cut up the half that writes to RocksDB memtables from the half that reads from the RocksDB memtable, constructed a RocksDB memtable replicator, and related it over the community. With this functionality, now you can write to a RocksDB occasion in a single Digital Occasion, and inside milliseconds replicate that to a number of distant Digital Situations effectively.
Not one of the SST information should be replicated since these information are already separated from compute and are saved and served from the autoscaling scorching storage tier. So, this replicator solely focuses on replicating the in-memory state in RocksDB memtables. The replicator additionally coordinates flush actions in order that when the memtable is flushed on the Digital Occasion ingesting the info, the distant Digital Situations know to go fetch the brand new SST information from the shared scorching storage tier.
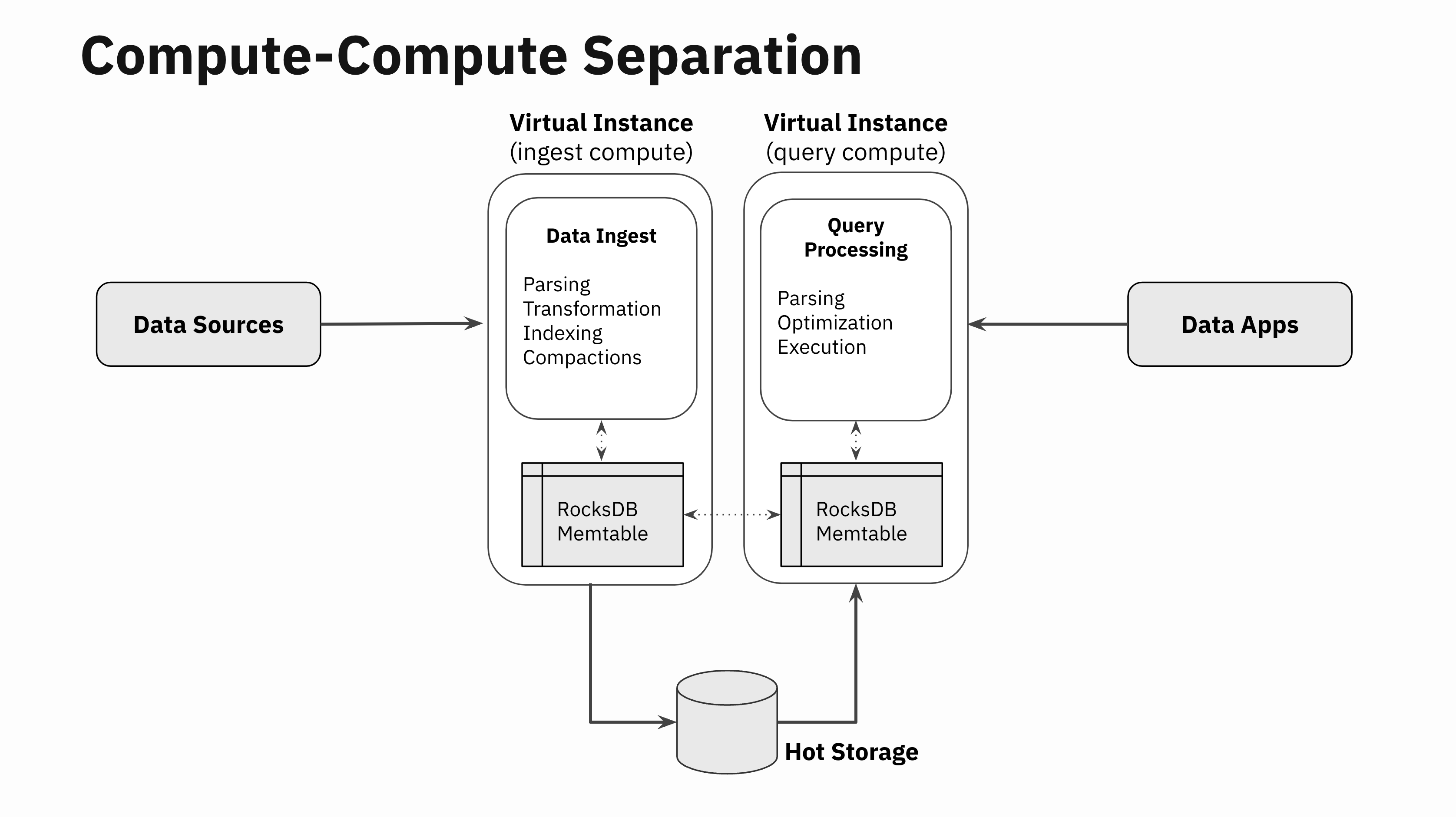
This straightforward hack of replicating RocksDB memtables is an enormous unlock. The in-memory state of RocksDB memtables could be accessed effectively in distant Digital Situations that aren’t doing the info ingestion, thereby essentially separating the compute wants of knowledge ingestion and question processing.
This explicit methodology of implementation has few important properties:
- Low knowledge latency: The extra knowledge latency from when the RocksDB memtables are up to date within the ingest Digital Situations to when the identical adjustments are replicated to distant Digital Situations could be stored to single digit milliseconds. There are not any large costly IO prices, storage prices or compute prices concerned, and Rockset employs nicely understood knowledge streaming protocols to maintain knowledge latencies low.
- Strong replication mechanism: RocksDB is a dependable, constant storage engine and might emit a “memtable replication stream” that ensures correctness even when the streams are disconnected or interrupted for no matter motive. So, the integrity of the replication stream could be assured whereas concurrently retaining the info latency low. Additionally it is actually essential that the replication is going on on the RocksDB key-value stage in any case the key compute heavy ingestion work has already occurred, which brings me to my subsequent level.
- Low redundant compute expense: Little or no extra compute is required to duplicate the in-memory state in comparison with the overall quantity of compute required for the unique knowledge ingestion. The way in which the info ingestion path is structured, the RocksDB memtable replication occurs after all of the compute intensive components of the info ingestion are full together with knowledge parsing, knowledge transformation and knowledge indexing. Knowledge compactions are solely carried out as soon as within the Digital Occasion that’s ingesting the info, and all of the distant Digital Situations will merely decide the brand new compacted SST information instantly from the recent storage tier.
It must be famous that there are different naive methods to separate ingestion and queries. A technique could be by replicating the incoming logical knowledge stream to 2 compute nodes, inflicting redundant computations and doubling the compute wanted for streaming knowledge ingestion, transformations and indexing. There are a lot of databases that declare related compute-compute separation capabilities by doing “logical CDC-like replication” at a excessive stage. Try to be doubtful of databases that make such claims. Whereas duplicating logical streams could appear “adequate” in trivial circumstances, it comes at a prohibitively costly compute value for large-scale use circumstances.
Leveraging Compute-Compute Separation
There are quite a few real-world conditions the place compute-compute separation could be leveraged to construct scalable, environment friendly and strong real-time functions: ingest and question compute isolation, a number of functions on shared real-time knowledge, limitless concurrency scaling and dev/check environments.
Ingest and Question Compute Isolation
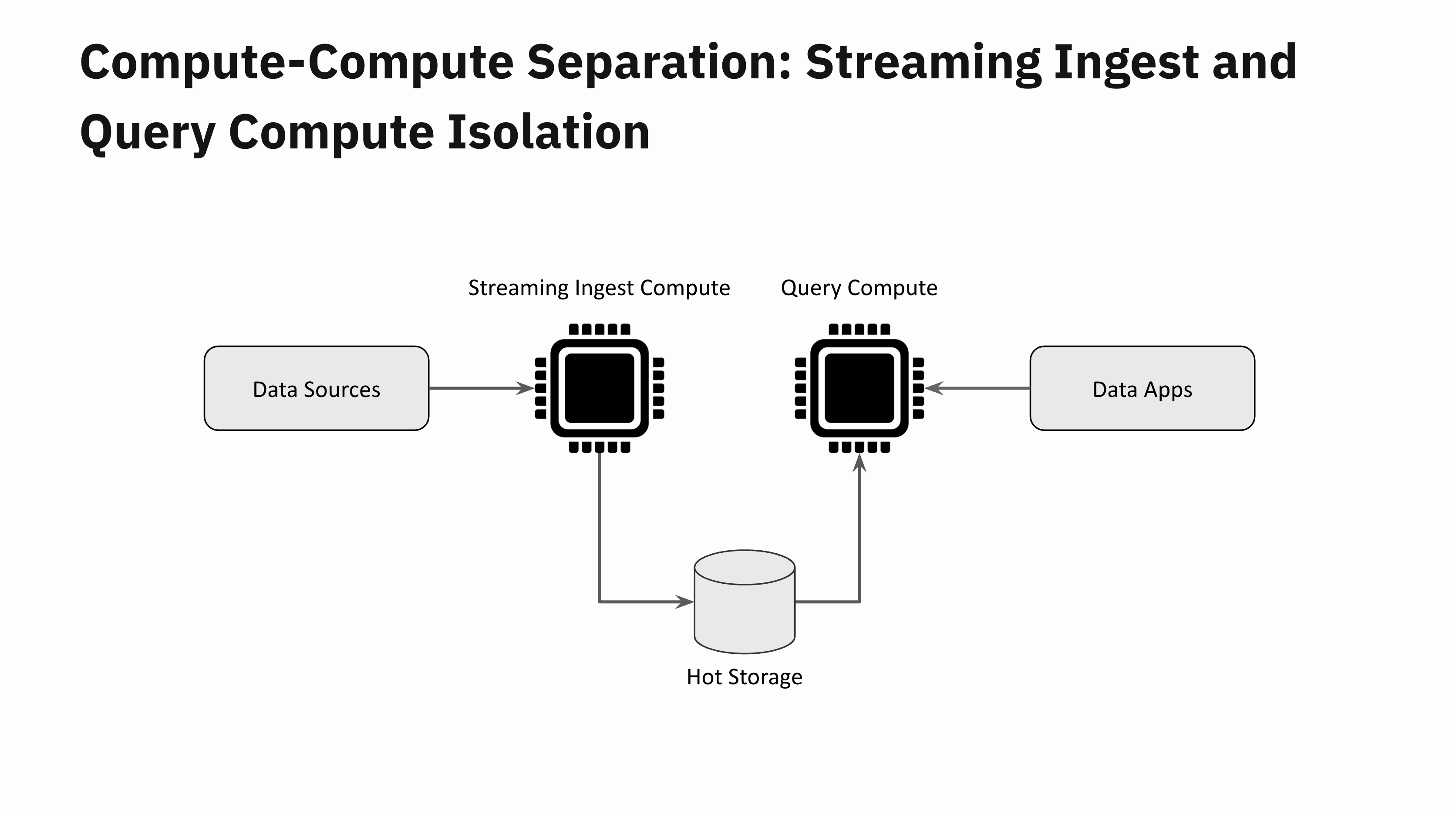
Think about a real-time software that receives a sudden flash flood of latest knowledge. This must be fairly easy to deal with with compute-compute separation. One Digital Occasion is devoted to knowledge ingestion and a distant Digital Occasion one for question processing. These two Digital Situations are absolutely remoted from one another. You may scale up the Digital Occasion devoted to ingestion if you wish to preserve the info latencies low, however regardless of your knowledge latencies, your software queries will stay unaffected by the info flash flood.
A number of Functions on Shared Actual-Time Knowledge
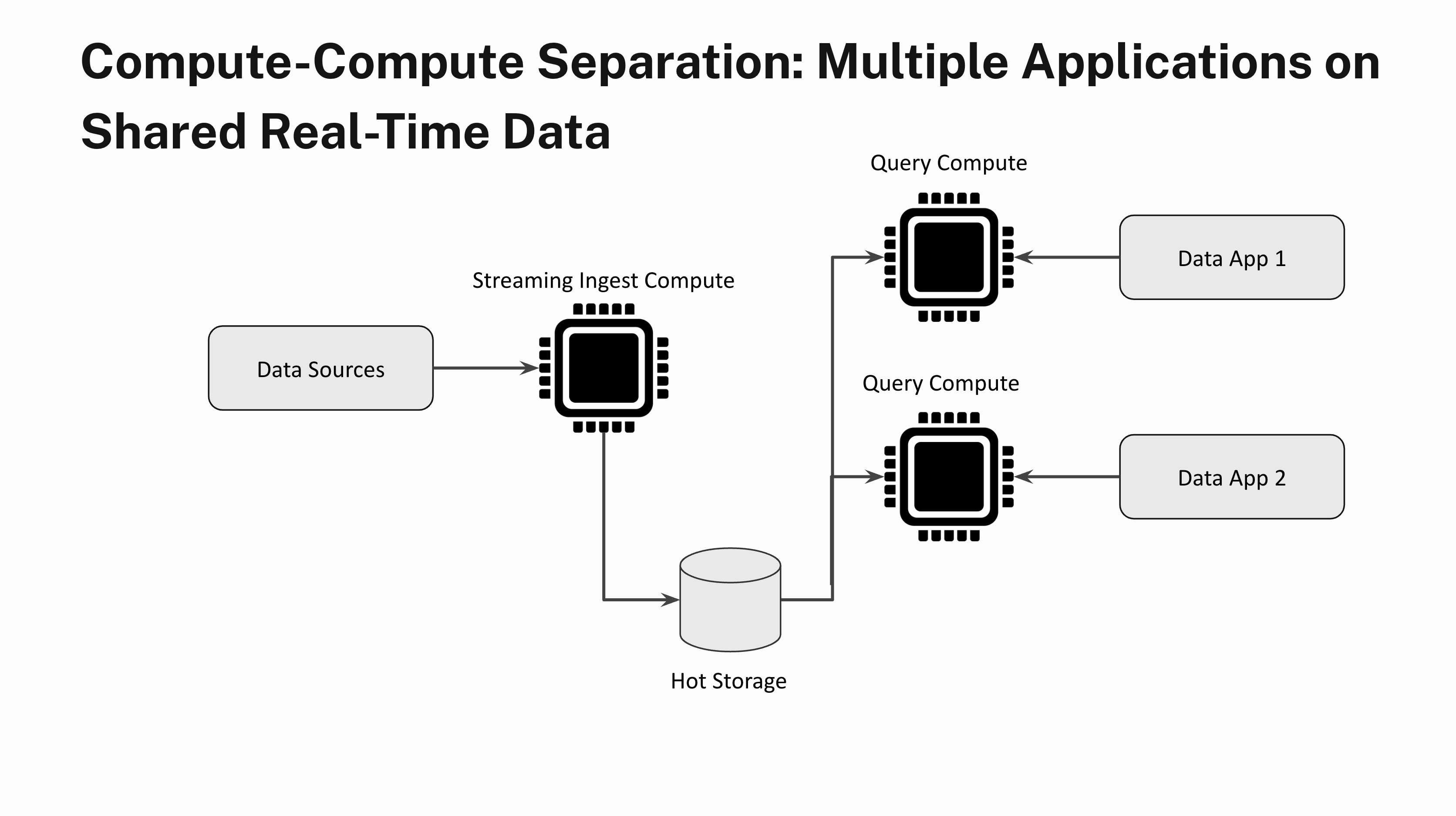
Think about constructing two totally different functions with very totally different question load traits on the identical real-time knowledge. One software sends a small variety of heavy analytical queries that aren’t time delicate and the opposite software is latency delicate and has very excessive QPS. With compute-compute separation you may absolutely isolate a number of software workloads by spinning up one Digital Occasion for the primary software and a separate Digital Occasion for the second software.
Limitless Concurrency Scaling
Limitless Concurrency Scaling
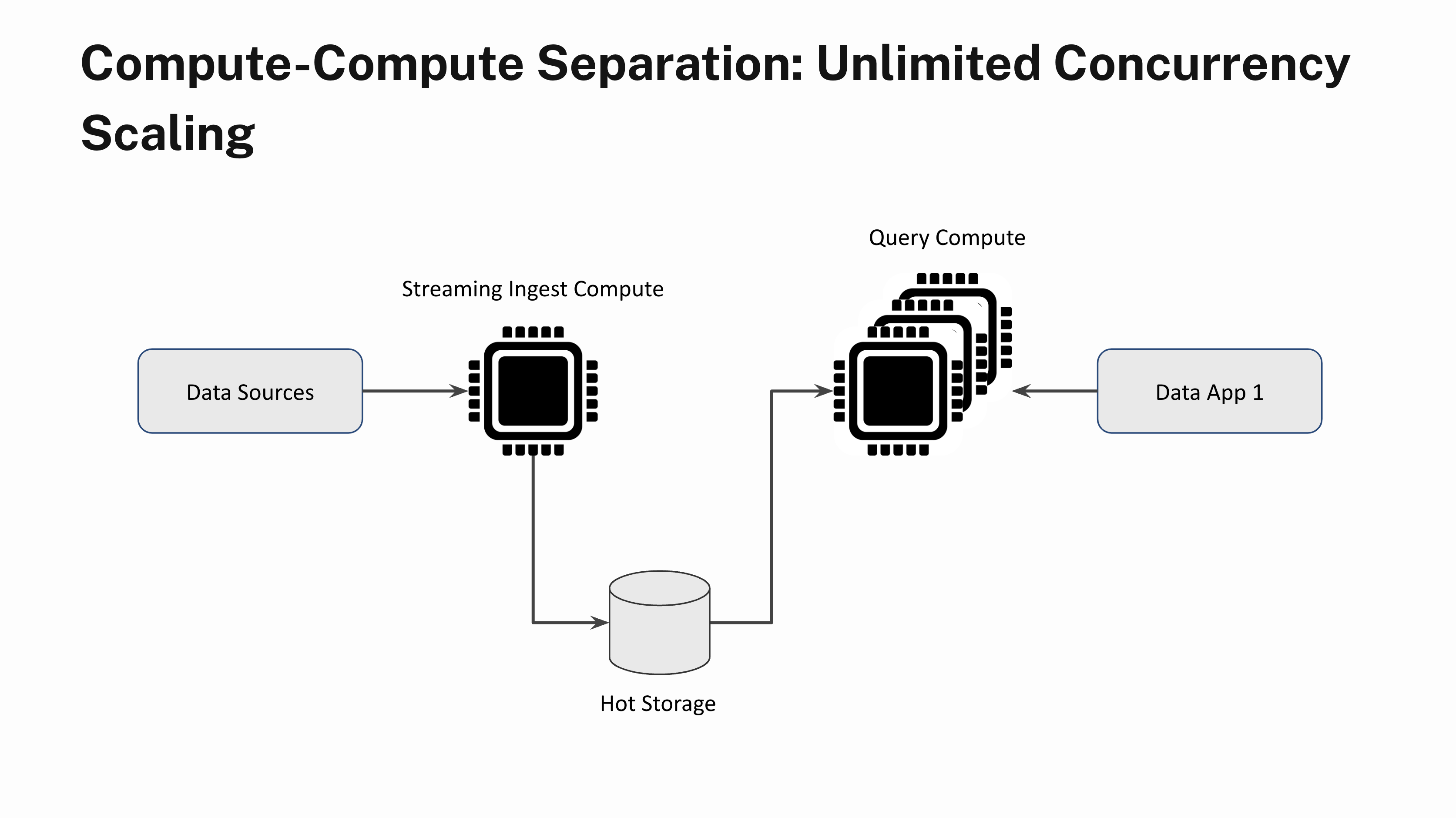
Say you have got a real-time software that sustains a gentle state of 100 queries per second. Often, when a whole lot of customers login to the app on the similar time, you see question bursts. With out compute-compute separation, question bursts will lead to a poor software efficiency for all customers during times of excessive demand. With compute-compute separation, you may immediately add extra Digital Situations and scale out linearly to deal with the elevated demand. You can too scale the Digital Situations down when the question load subsides. And sure, you may scale out with out having to fret about knowledge lags or stale question outcomes.
Advert-hoc Analytics and Dev/Check/Prod Separation
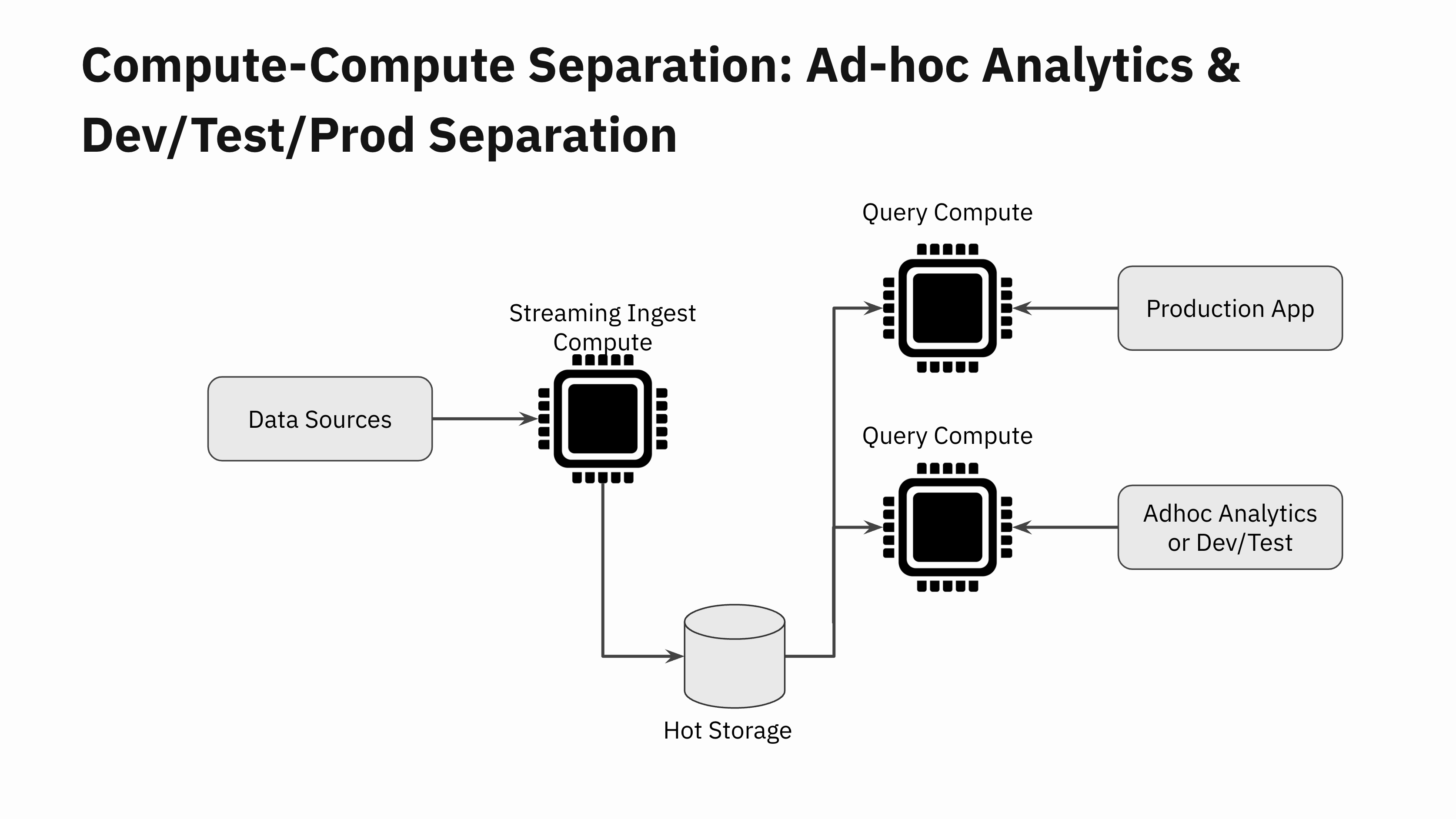
The subsequent time you carry out ad-hoc analytics for reporting or troubleshooting functions in your manufacturing knowledge, you are able to do so with out worrying in regards to the adverse impression of the queries in your manufacturing software.
Many dev/staging environments can not afford to make a full copy of the manufacturing datasets. So that they find yourself doing testing on a smaller portion of their manufacturing knowledge. This may trigger surprising efficiency regressions when new software variations are deployed to manufacturing. With compute-compute separation, now you can spin up a brand new Digital Occasion and do a fast efficiency check of the brand new software model earlier than rolling it out to manufacturing.
The chances are countless for compute-compute separation within the cloud.
Future Implications for Actual-Time Analytics
Ranging from the hackathon undertaking a 12 months in the past, it took an excellent workforce of engineers led by Tudor Bosman, Igor Canadi, Karen Li and Wei Li to show the hackathon undertaking right into a manufacturing grade system. I’m extraordinarily proud to unveil the aptitude of compute-compute separation in the present day to everybody.
That is an absolute sport changer. The implications for the way forward for real-time analytics are large. Anybody can now construct real-time functions and leverage the cloud to get large effectivity and reliability wins. Constructing large scale real-time functions don’t must incur exorbitant infrastructure prices as a consequence of useful resource overprovisioning. Functions can dynamically and shortly adapt to altering workloads within the cloud, with the underlying database being operationally trivial to handle.
On this launch weblog, I’ve simply scratched the floor on the brand new cloud structure for compute-compute separation. I’m excited to delve additional into the technical particulars in a speak with Nathan Bronson, one of many brains behind the memtable replication hack and core contributor to Tao and F14 at Meta. Come be part of us for the tech speak and look beneath the hood of the brand new structure and get your questions answered!

