This submit examines issues that come up from a shared DevSecOps platform. As a result of a DevSecOps platform and gear pipeline is simply too complicated and costly to create and handle individually for every program, the platform usually must be a shared functionality. This case creates dependencies and cooperation points.
These issues are examples of an acquisition archetype, which is how we check with a sample of organizational system behaviors which have been seen throughout the SEI’s experiences in conducting invited unbiased technical assessments (ITAs) on technical and programmatic facets of the DoD acquisition packages. In these ITAs, program administration workplace (PMO) employees, contractor employees, customers, and different exterior stakeholder organizations present open and candid responses below the situation of anonymity that present the SEI group perception into what is actually taking place in a program. These insights counsel that comparable, recurring issues in software program acquisition and growth—archetypes—come up throughout separate and seemingly dissimilar packages.
A earlier SEI Weblog submit examined an archetype of clinging to the previous methods. On this submit, I talk about the recurring downside of cross-program dependencies. I describe the habits within the context of a real-world state of affairs and supply suggestions on recovering from and stopping future occurrences of this downside.
About Acquisition Archetypes
Our use of the phrase, “acquisition archetypes” relies on the extra normal notion of system archetypes and is supposed to explain recurring patterns of failure noticed in acquisition packages to boost consciousness, together with offering approaches to mitigate or keep away from these antagonistic patterns. The incentives that drive these patterns are comparable throughout packages and have a tendency to drive comparable behaviors.
Cross-Program Dependencies
Generally a corporation could must construct a brand new widespread infrastructure functionality. As an example, a corporation would possibly deploy a DevSecOps platform and gear pipeline (e.g., compilers, code scanners, containers, and orchestration) that’s too complicated and costly to create and handle individually for every program or undertaking. These packages or initiatives is likely to be reluctant to just accept an exterior dependency on the infrastructure program providing a typical infrastructure functionality, resulting in inside stress. If the widespread infrastructure has points similar to poor efficiency, problem of integration, incapacity to completely carry out its operate, or unavailability throughout the required timeframe, the initiatives offering and supporting that functionality are prone to develop into disenchanted or reluctant to proceed to assist the infrastructure, and should criticize and even undermine it. For instance, present packages migrating to make use of the infrastructure is likely to be conversant in utilizing a selected model-based programs engineering (MBSE) software or a code scanner that implements a selected set of scanning guidelines. Making the change from utilizing the software they’re conversant in to utilizing a wholly completely different software could have each up-front prices when it comes to modifications to the instruments and the system, and longer-term prices as customers should study new methods to perform the identical impact.
Initiatives utilizing DevSecOps infrastructure will usually must make important modifications to their parts of the potential to accommodate the brand new infrastructure (e.g., modified interfaces, extra performance, or architectural variations). Supporting the brand new infrastructure will make their very own work tougher, require extra effort and sources, adversely have an effect on their present programs, and require rework of facets of these programs. Consequently, these initiatives have little incentive to completely assist the brand new system. Fairly than being a win-win throughout the group, the widespread DevSecOps infrastructure could develop into primarily a win for headquarters on the expense of the opposite initiatives.
Report from the Area
The way in which a program is established impacts the flexibility of a number of, semi-independent organizations to cooperate to attain a typical purpose (Determine 1). In the middle of supporting acquisition packages, the SEI usually encounters and should assist tackle some of these organizational points. In a single such dialog a program chief mentioned, “Some packages get involved after they have dependencies on different packages. It’s an issue when completely different teams management completely different providers, and also you don’t have all of it below your management…. The infrastructure program asks us for stuff, and typically there’s funding, and typically there isn’t.” One other chief acknowledged that, in delivering capabilities, “Totally different organizations are in cost, funded individually, with completely different budgets, and they also’re required to ship towards necessities that don’t keep in mind issues they could need.”
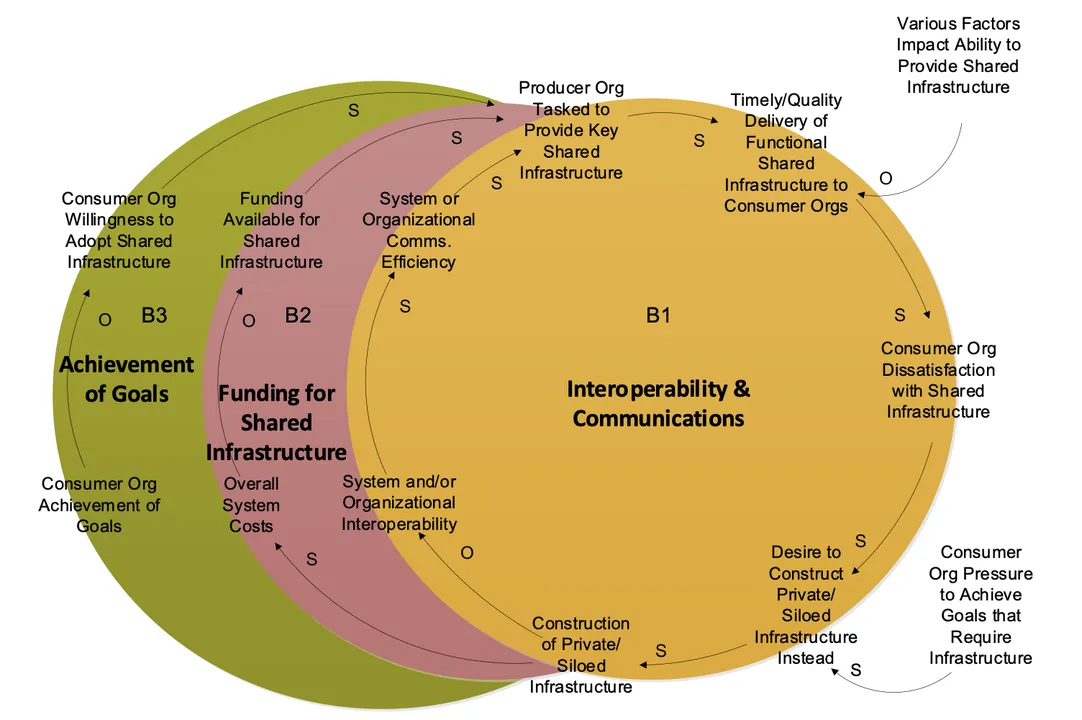
Determine 1: The way in which a program is established impacts cooperation towards a typical purpose.
In a single case, “[a] PMO wasn’t ready for the inevitable bow wave of recent work that was coming their manner. They didn’t like being informed what to do [by a higher authority akin to a program executive office or PEO]. That created some competition.” This case typically devolved into finger pointing, fairly than producing outcomes: “The completely different organizations concerned all should work collectively to share necessities and make selections—however nobody owns it, so that they blame one another.” If the directing authority had been in a position to provide schedule aid and/or funding for the extra work, it won’t have been considered by the PMO as primarily an “unfunded mandate.”
On this case there was a misalignment of targets that every completely different group was making an attempt to attain. One official noticed, “The motivation at our program workplace is to satisfy value and schedule efficiency, whereas the infrastructure program is about functionality supply and high quality. Subsequently, the connection mismatch distracts from effectivity.”
Evaluation
Organizational tensions can happen because of the reluctance of packages to just accept an exterior dependency on one other program that will assist to supply a typical infrastructure functionality. The causal loop diagram (CLD) in Determine 1 represents a number of interacting packages and reveals that the way in which one program is established can have an effect on its skill to cooperate with different packages as all of them attain towards a typical purpose. The leftmost loop (in inexperienced) reveals that the much less in a position the “consuming” program is to attain their targets by themselves, the extra they want the shared infrastructure. The rightmost loop (in gold) reveals that when a “producer” group is tasked to supply shared infrastructure for a number of packages however is unable to satisfy all the “shopper” organizations’ expectations, the customers could develop into dissatisfied and resolve to assemble their very own personal or customized variations of the infrastructure as a substitute. Nevertheless, the center loop (in crimson) reveals how doing so typically undermines the specified diploma of interoperability the shared infrastructure was meant to allow. Developing a number of, less-interoperable, personal variations of the infrastructure prices considerably greater than a single shared model, utilizing up funding that might have been spent to construct the shared infrastructure. These personal variations are the results of wanting an instantaneous profit (eradicating the dependency) that may value everybody else—but when everybody does the identical factor, everybody finally ends up worse off because of the extra growth prices, non-standard programs, and schedule spent in growth and rework of the outcomes. It is a balancing loop, which oscillates round an equilibrium worth as assist for the infrastructure grows after which wanes. Be aware that the static mannequin described by this CLD doesn’t predict how this dynamic will play out in all circumstances however does describe the way it usually ends with shopper packages opting out of the shared infrastructure association if they’ll.
Options and Mitigations
A public good is an economics time period for a service that’s made obtainable to all members of a neighborhood the place use by one member doesn’t preclude its use by others. For instance, our nationwide protection itself is a public good for all residents. The dynamic of manufacturing a public good in human organizations has been researched extensively and has a big set of ordinary options. The event and provision of widespread infrastructure, similar to a DevSecOps platform, is a sort of public good that’s topic to cooperation issues from cross-program dependencies.
In coping with cooperation issues, there are three courses of options: motivational, strategic, and structural. These are broadly characterised as follows:
- Structural: Reframe the issue and guidelines so that folks should behave extra cooperatively as a result of there’s formal authority behind, and enforcement of, the foundations (e.g., penalties, legal guidelines).
- Strategic: Give individuals a rational and self-interested cause (i.e., incentive) to behave extra cooperatively.
- Motivational: Make individuals really feel in a different way in order that they need to behave extra cooperatively.
The cross-program dependencies dynamic could be managed by management that may acknowledge these dependencies as they come up and take steps to mitigate them. Nevertheless, on this state of affairs the management would have to be at or above the PEO stage, and the anticipated antagonistic ramifications of the problem would have to be raised to their consideration by a number of of the packages concerned. Hierarchical, authority-based organizations such because the army take this strategy, though normally after dialogue with the affected events. It’s a structural resolution, also known as “regulation by an authority,” nevertheless it requires having an authority to impose the foundations, may have enforcement of compliance, and should encourage resistance from these it’s imposed upon.
If a typical infrastructure program has overarching authority over the initiatives offering supporting capabilities, it may possibly tackle lots of the points famous above. Nevertheless, the way in which such authority may very well be granted would range considerably all through the DoD, and in some circumstances could not all the time be doable. When it is doable, it could additionally occur that such authority is overused, even when the infrastructure program has the perfect of intentions in exercising it. The authority may override the wishes or wants of the collaborating initiatives; for instance, it would drive collaborating packages to implement unfunded and even undesirable mandates.
Wherever doable, the authority of the widespread infrastructure program must be exercised in win-win preparations that attempt to present worth in each instructions, to each events. Win-win relationships can contain offering the supporting initiatives what they need (e.g., funding or sources), fixing points they could have by offering organizational experience, providing specialised coaching or assist that they want, and/or discovering methods to burnish their popularity.
The second approach to tackle cross-program dependencies is thru strategic approaches, similar to establishing a significant incentive that rewards cooperation to drive profitable joint end-to-end outcomes for customers. These approaches are weaker than structural approaches, however can be utilized to reinforce them and embody:
- establishing cross-fertilization/cross-functional groups (exchanging individuals to interrupt down obstacles and encourage cooperation)
- creating extra interdependencies (encouraging individuals to work collectively out of necessity).
The third approach to tackle cross-functional dependencies is thru much less formal motivational approaches. These approaches attempt to mitigate lack of belief and cooperation among the many completely different initiatives supporting the widespread infrastructure through the use of actions that assist keep or rebuild belief. Whereas weaker than both of the opposite two, these will also be used to reinforce structural and strategic approaches. Potential motivational approaches for addressing the habits may embody:
- Consciousness: Improve the notice of the issue and talk the significance of everybody making a distinction to resolve it.
- Proof of high quality: Present compelling proof that the services or products will work as marketed earlier than asking organizations to assist it or assist pay for it.
- Setting expectations: Encourage voluntary cooperation in settings during which persons are extra prone to be public-minded resulting from historical past and custom (e.g., Peace Corps or Conflict Bonds).
The Outlook for Cross-Practical Dependencies
On this submit, I’ve investigated one recurring program habits associated to the introduction of DevSecOps: cross-functional dependencies. DevSecOps is a robust strategy that raises new issues round cross-functional dependencies. The complexities of DevSecOps can require packages to make infrastructure modifications that may have important downstream results for different packages and initiatives. By growing mutually useful options, the authority of the widespread infrastructure program can encourage cooperation and higher habits.

