Adopting a microservice structure opens up many alternatives for companies, from flexibility in improvement to scalability and reliability. Nevertheless, this strategy just isn’t solely related to advantages, but in addition with various vital challenges.
From technical nuances to organizational modifications, it’s vital to know the potential complexities for the transition to achieve success. Under, our group has ready an inventory of key challenges corporations face when utilizing microservices.
How Microservices are Already Making Life Simpler For Customers and Corporations
Think about ordering meals by way of a cell utility. You select your meal, pay for the order, monitor the supply on a map, and get a notification when the deliveryman arrives.

All the pieces appears like a single service, however actually, there’s a entire set of separate, impartial techniques behind it: one in every of them processes orders, one other works with the menu, a 3rd with cost, a fourth with logistics, and a fifth is liable for push notifications. It is a microservice in motion.
Every of those items works autonomously. If, for instance, the notification system fails quickly, you’ll nonetheless have the ability to order and pay for meals. And if the corporate decides to introduce a brand new cost system or replace logistics, you are able to do this with out touching the remainder of the performance.
This strategy makes the service extra versatile, dependable, and user-friendly. What’s much more vital is that it’s worthwhile for enterprise: modifications may be carried out shortly, and the dangers of the whole system breaking down are minimized.
What’s Microservice Structure?
Microservice structure is a means of organizing a digital product by which an utility consists of many small, impartial parts. Every of them solves a strictly outlined process and might work independently of the others. That is the other of the standard strategy, when the whole utility is assembled “in a single piece” — like a monolith.
In a standard monolithic system, all features are interconnected, and the slightest change can have an effect on the whole system. That is handy on the product launch stage, however turns into an issue when the challenge grows: any replace takes time, the danger of failures will increase, and scaling turns into harder.
Why Microservices: Key Advantages
Corporations begin occupied with transferring to a microservices system after they face development, growing complexity of enterprise logic, or the necessity to make frequent modifications.
For instance, if you’re growing a web-based retailer and need to shortly add new cost strategies, automate supply, and join third-party companies, a microservice strategy provides you with the flexibleness you want. It permits you to scale solely these elements of the product that basically want it, avoiding overconsumption of assets.
Improvement groups can work in parallel on completely different parts with out interfering with one another, and launch new options in levels with out the danger of “dropping” the whole service.
For companies, microservices structure is about adaptability, velocity of change, and technological sustainability. It’s not only a query of “find out how to construct an app”, however a strategic resolution that impacts the effectivity of digital product improvement.
Main Challenges of Microservices Implementation
Whereas a number of companies provide nice alternatives for flexibility and scalability, there are a selection of sensible and organizational challenges in transferring to this structure. The next are the important thing challenges corporations face when implementing a microservice strategy.
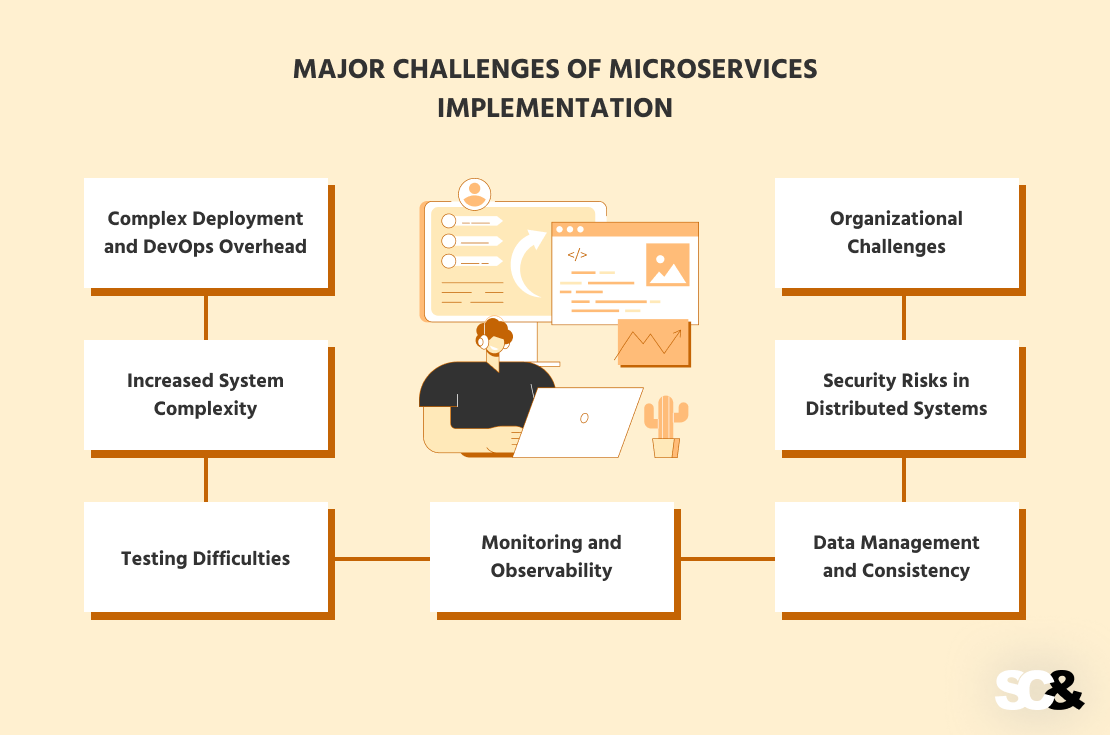
1. Complicated Deployment and DevOps Overhead
Every microservice is a separate part that must be custom-made, deployed, and up to date. This requires superior infrastructure: automated CI/CD processes, container administration (e.g., by way of Kubernetes), model management, and compatibility between companies. All this will increase the technical burden and requires well-built DevOps processes.
2. Elevated System Complexity
Microservices create a distributed structure the place many parts talk with one another by way of a community. This creates new challenges: find out how to manage steady information switch between companies, how to make sure fault tolerance, and find out how to synchronize information, particularly below excessive hundreds.
3. Testing Difficulties
Testing of microservices just isn’t solely testing the code of every particular person service, but in addition the entire bundle of them. This brings up the various varieties of testing that have to be accomplished for a complete performance examine: integration exams, contract exams, and the necessity to mock the conduct of different companies. All this will increase the time and assets required for QA processes.
4. Monitoring and Observability
To manage the operation of dozens (and generally a whole lot) of microservices, you want techniques for monitoring, logging, request tracing, and alerting. It is very important monitor the place precisely a failure occurred and the way it affected different companies. Instruments like Prometheus, Grafana, and Jaeger are actively used right here.
5. Knowledge Administration and Consistency
Not like a monolithic utility, the place all information may be saved in a single database, microservices usually use completely different databases. This makes it tough to take care of information integrity and requires particular approaches similar to eventual consistency, distributed transactions, or Saga-type templates.
6. Safety Dangers in Distributed Methods
Every microservice should be protected, each on the stage of interplay with different companies and within the exterior API. Because of this, authorization and authentication mechanisms are carried out (e.g., JWT, OAuth), and entry is organized by way of API gateways. With out centralized management, the danger of errors in safety configuration will increase.
7. Organizational Challenges
The microservice strategy requires group restructuring: transferring from vertical departments to cross-functional groups, every liable for its service. This calls for new rules of interplay, a transparent zone of accountability, and synchronization between departments in order that the structure doesn’t develop chaotically.
Frequent Errors When Adopting Microservices
The transition to microservice structure can present companies with tangible advantages, however provided that carried out accurately. Sadly, many corporations make related errors that result in increased challenge prices, slower improvement, and lack of management. Under are three of the most typical ones.
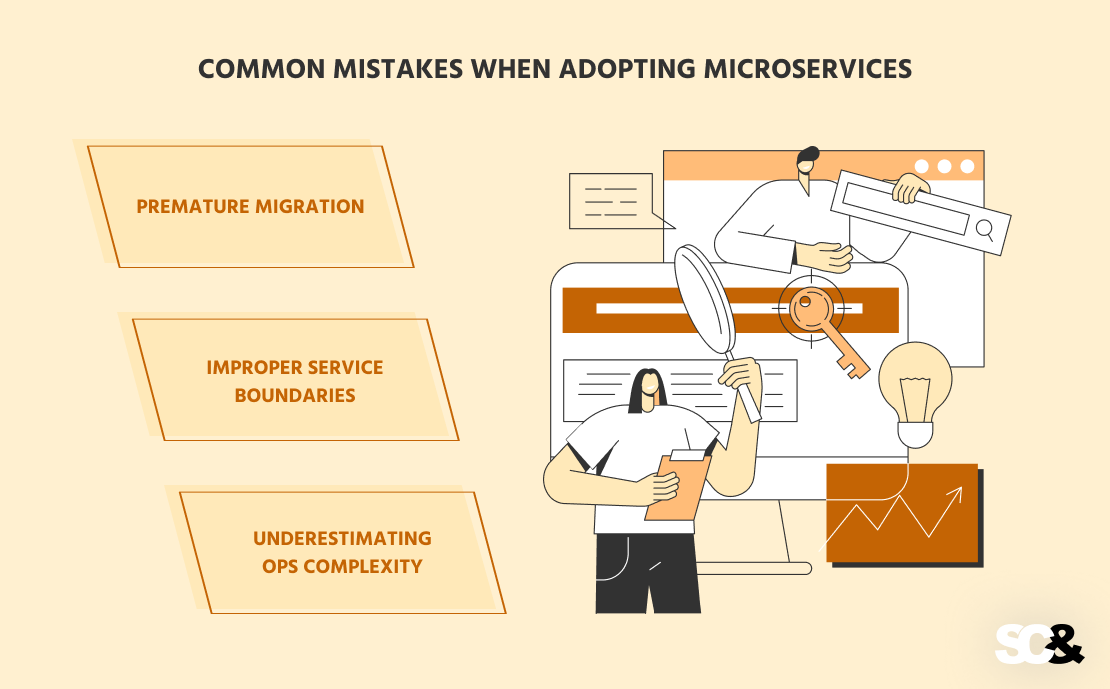
Untimely Migration
One of the crucial widespread errors is making an attempt to maneuver to microservices too early, when the product has not but reached the precise stage of maturity. Implementing a microservice structure requires severe preparation and is justified solely when scalability, flexibility, and excessive velocity of change are actually needed. In any other case, microservices complicate the system with none actual profit.
Improper Service Boundaries
A mistake on the service design stage can result in chaos within the structure. If companies are separated “by comfort” relatively than by enterprise logic, duplication, over-dependency, and inefficient communication between elements of the system happen. It’s important that every microservice displays a selected enterprise operate and is as autonomous as doable.
Underestimating Ops Complexity
Many individuals suppose that microservices are merely “splitting a monolith into elements”. However in follow, this implies constructing a fancy infrastructure: CI/CD, monitoring, safety, and fault tolerance. With out mature DevOps processes and expertise in constructing distributed techniques, the migration can result in instability and technical debt.
When To not Use Microservices
Microservice expertise is a robust instrument, however its implementation just isn’t justified in all instances. In keeping with an O’Reilly research, solely 13% of corporations reported full success after adopting microservices. The bulk (about 50%) charge the outcome as “largely profitable,” whereas practically 1 / 4 report restricted or no success. This underscores the purpose: microservices solely ship outcomes when they’re utilized consciously and with the challenge context in thoughts.
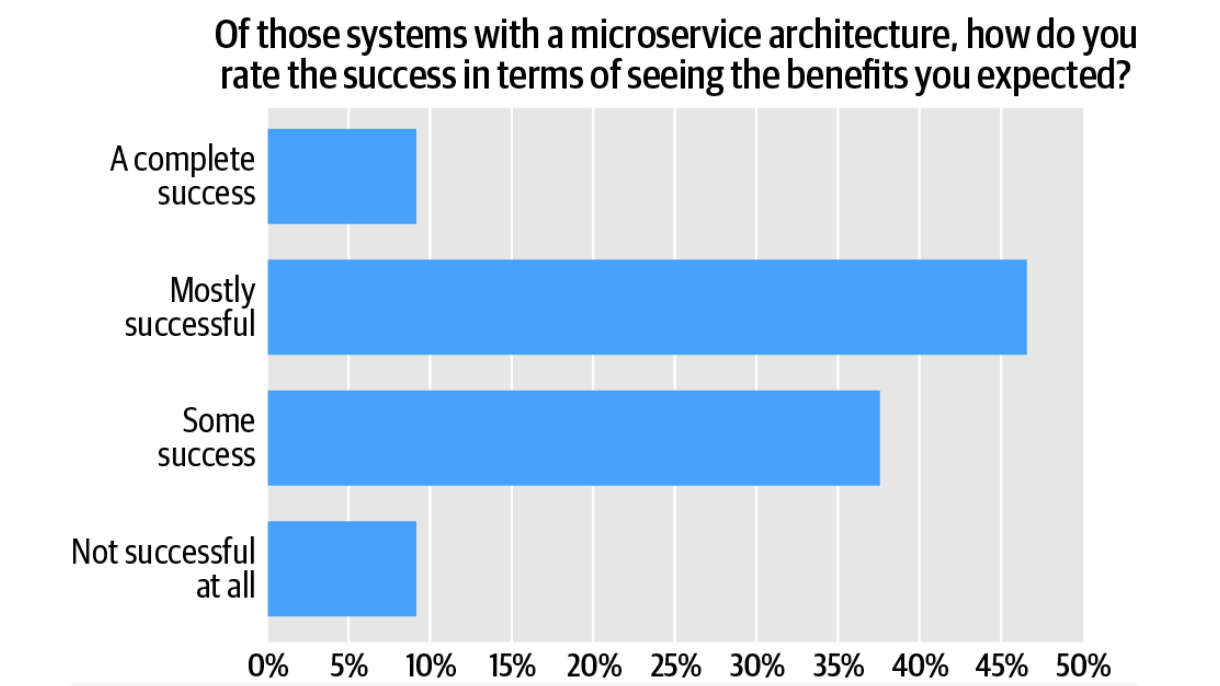
Analysis of the success of microservices implementation in line with O’Reilly information
Implementing microservices can significantly complicate the work, particularly if the group is small or the product is at an early stage, such because the MVP section. At this stage, velocity of launch, simplicity of structure, and minimal help prices are important. Splitting into dozens of companies that require separate configuration, testing, and monitoring will solely decelerate the method and won’t present tangible enterprise advantages.
Microservices are additionally inappropriate for initiatives without having for scaling. If the product is very specialised, with restricted performance and steady load, a traditional monolithic structure will likely be easier, extra dependable, and cost-effective. Microservices require mature DevOps processes, automation, monitoring instruments, and shut coordination between groups.
If these situations should not met, and architectural complexity just isn’t compensated by the size of the enterprise, it’s higher to give attention to simplicity and effectivity relatively than traits.
Greatest Practices to Overcome These Challenges
To implement microservice structure as successfully as doable and keep away from widespread errors, it is very important use confirmed approaches, each on the technical and organizational ranges. Under are the important thing practices that assist corporations efficiently address the challenges of the microservice strategy.
Using Considerate Design Patterns
Patterns similar to API Gateway, Circuit Breaker, and Service Mesh make it simpler to handle massive numbers of companies.
- Gateway API serves as a single level of entry for all consumer requests and offers safety, routing, and information aggregation.
- Circuit Breaker helps keep away from cascading failures — if one service is unavailable, requests are quickly redirected or blocked.
- Service Mesh lets you handle interactions between companies in a centralized means, together with safety, monitoring, and site visitors management.
Shifting to Occasion-driven Structure and Message Brokers
Occasion-driven structure permits companies to work together by way of occasions relatively than straight. This reduces dependencies between parts and simplifies scaling.
Utilizing techniques similar to Kafka or RabbitMQ helps to switch information reliably and asynchronously, particularly helpful below excessive hundreds and when massive quantities of information have to be processed.
Establishing Clear SLAs Between Providers
Every microservice ought to have clear boundaries of accountability and well-defined SLAs (service stage agreements). This helps to align expectations between groups, scale back conflicts, and guarantee predictability throughout the system.
Gradual Migration Technique
An entire and abrupt transition from a monolith to microservices is among the riskiest paths. It’s a lot safer to make use of a step-by-step migration: first allocate important features, switch them to separate companies, stabilize them, and solely then proceed. This strategy reduces dangers and permits the group to adapt to the brand new format of labor with out dropping high quality and velocity.
Actual-World Use Case: Migrating to Microservices in Enterprise Software program
One instance of a profitable migration to a microservice structure is the SCAND challenge for a big company consumer. Initially, the system was carried out as a monolith, which made scaling tough and slowed down the discharge of recent options.
The SCAND group audited the structure and proposed a phased transition technique. Key enterprise modules (authentication, doc processing, notifications) had been recognized, every of which grew to become an impartial microservice.
This allowed the consumer to speed up the implementation of modifications, enhance fault tolerance, and adapt the product to load development, with out risking the steady operation of the system.
Conclusion: Is Microservices Structure Proper for Your Undertaking?
Microservice structure is a wonderful alternative for scalable, technologically subtle options with energetic improvement. It offers flexibility, group independence, ease of upgrades, and a excessive stage of resilience. Nevertheless, within the case of small merchandise or MVPs, microservices may be redundant, growing complexity and help prices.
If you happen to’re unsure about whether or not this strategy is correct in your challenge, it’s vital to weigh technical and enterprise components: development targets, group maturity, velocity of improvement, and anticipated workloads. Contact us for assist auditing your system.


