DHCP is a networking protocol used to assign an IP tackle to your Apple machine. This is find out how to drive a brand new IP tackle on macOS.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) permits a community machine to request an IP tackle from a DHCP server on a community. DHCP makes beginning and configuring computer systems simpler because it’s normally automated and does not require any person intervention.
There are separate variations of the DHCP protocol for IP4 and IP6 (DHCPv6).
Normally, DHCP servers run both on your house community (in your router), in your ISP’s community, or on company servers in enterprise settings. DHCP may also be hosted within the cloud.
A part of the advantage of utilizing DHCP is your shopper machine does not need to know the tackle of the DHCP server – discovery is automated and clear (and is predicated on UDP truly). Shopper machines can maintain trying to find DHCP servers on a community till they discover one that may present an IP tackle.
You may as well run your individual standalone DHCP servers at residence, however until you are aware of the intricacies of the protocol and networking it could be extra hassle than it is price: misconfiguration of an area DHCP server may cause your community to behave erratically.
Most trendy residence routers, cable, and fiber-optic modems deal with DHCP for you.
The primary concept behind utilizing DHCP is that computer systems can dynamically and mechanically make an web connection with out every machine having to be manually configured with an IP tackle.
The time a DHCP server permits a single machine to be linked to 1 IP tackle is named the Lease Time. Default lease instances are normally twenty-four homes, however can differ. When the lease time expires, both a brand new IP tackle is assigned, or the identical IP tackle is used with the lease time reset.
Lease instances are used in order that if units disconnect from the community, their IP addresses may be recycled and assigned to different units on the community.
DHCP Historical past
DHCP’s predecessors have been RARP and BOOTP – each outlined within the early 1980’s. When the web started to change into commercialized within the early 1990’s it rapidly turned apparent that static IP administration for big numbers of IP units was impractical.
Based mostly on BOOTP, DHCP contains the noticeable variations of IP tackle pool allocation and reuse, and platform-specific configuration settings per linked machine.
The ultimate authentic model of DHCP was later up to date in 1997 with just a few further small modifications, and DHCPv6 was first outlined in 2003 (and later up to date in 2018).
DHCP startup on Macs
Whenever you begin your Mac, a background course of goes by means of the listing of its lively community interfaces within the order listed in System Settings->Community and pings your community for DHCP servers (by broadcasting the DHCPDISCOVER message) to request an IP tackle for every lively interface within the listing (until a particular interface is about to make use of guide IP addressing).
If any DHCP servers are listening and responding to this request (with a DHCPOFFER message), your Mac will ask certainly one of them for an IP tackle for every community interface. The responding DHCP server creates a brand new inner IP tackle in a desk – after which sends it to your Mac for its use.
macOS will take every acquired IP tackle and join an lively community interface to it. These addresses aren’t “actual” – they’re truly mapped internally at your router or ISP to an exterior tackle on the web.
A typical tackle your Mac may obtain from a DHCP server may look one thing like “192.168.0.1”.
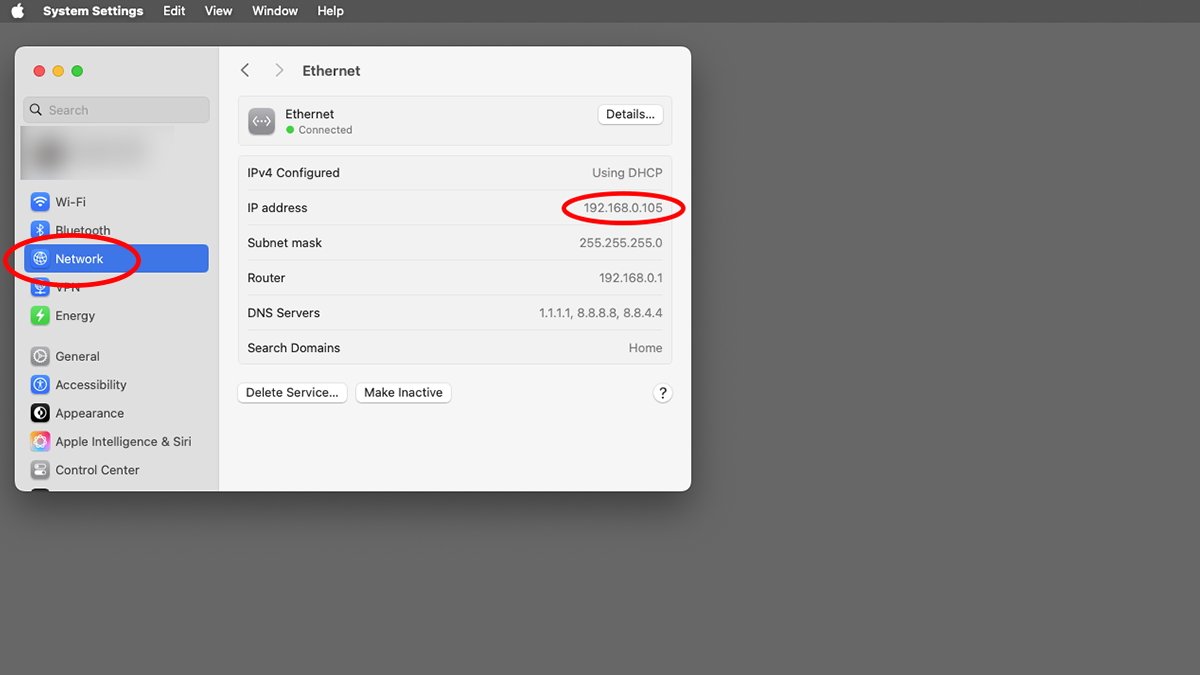
Should you go to System Settings->Community and click on on an lively community interface you may see an inventory of the community settings for that machine. For instance, Ethernet:
The machine pane shows whether or not the machine is lively, its IP tackle, the subnet masks used, and the native router tackle. Within the case of a house community, the router tackle will more than likely be your broadband modem, or an area router when you’ve got one configured.
The machine information additionally shows which DNS servers you are utilizing, and the way your web connection is configured. Within the case of DHCP, it is going to be displayed on the high.
Should you’re on a community that does not use DHCP however makes use of static IP addresses for every machine as a substitute, this line will learn “Manually” as a substitute of “DHCP”.
As soon as your Mac has requested and obtained a DHCP tackle from a server, these values will all be stuffed in mechanically.
Requesting a brand new DHCP IP tackle
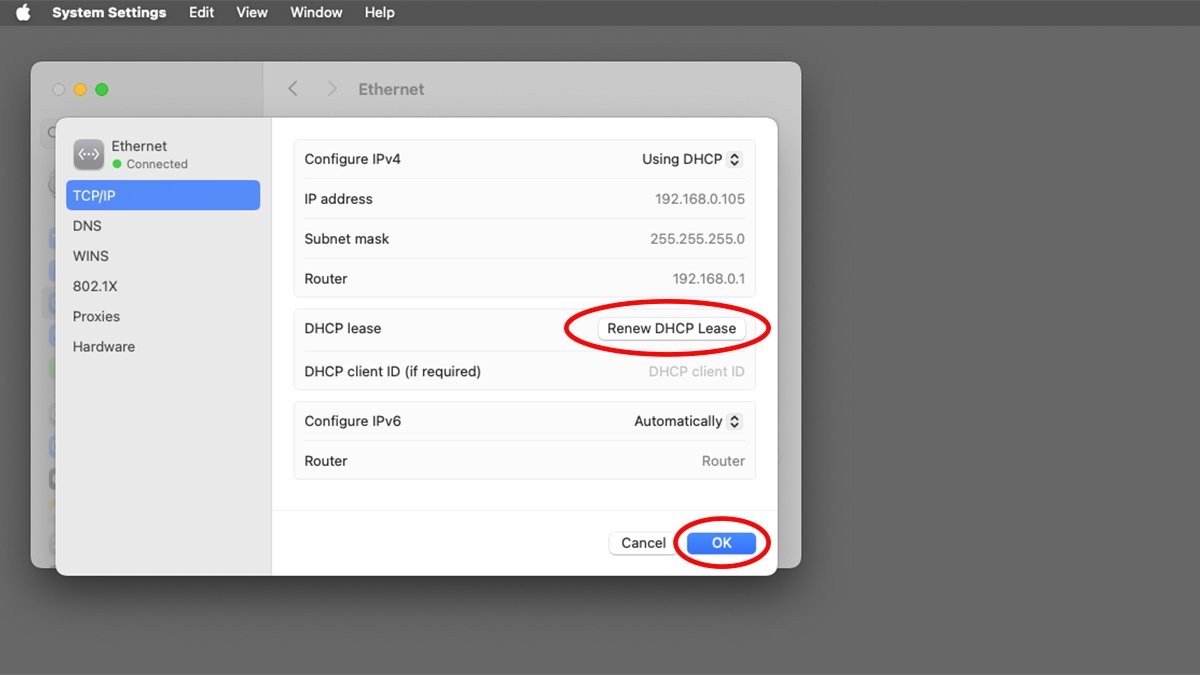
If for some purpose you wish to request a brand new IP tackle out of your community’s DHCP server, click on the Particulars… button on the high of the machine information pane. You will see a sheet itemizing community and {hardware} specifics for that machine.
One of many gadgets within the sheet’s listing is TCP/IP. Should you click on TCP/IP, you may primarily see the identical information as within the machine pane, however you may additionally discover a Renew DHCP Lease button:
Clicking this button will ship a request to the DHCP server to reset the DHCP Lease Time – or, in some circumstances request a brand new IP tackle. After clicking the button you may want to attend just a few seconds for the request/response from the server. When the brand new lease/tackle is acquired, macOS will replace the data within the machine interface pane mechanically.
Should you’re utilizing a VPN app (and it is linked) you might also must disconnect and reconnect it when you receive a brand new IP lease in your Mac.
However why?
Chances are you’ll be questioning why you’d wish to manually renew your DHCP lease. The reply is: normally you do not. The one time it is advisable to do that is whenever you’re experiencing networking conflicts or issues – for instance, in case your machine went to sleep and another machine in your native community is now utilizing the IP tackle you have been beforehand utilizing.
Or in some circumstances if intermediate native routers or switches have modified in your community and your Mac did not learn about it – or as talked about above within the case of VPN modifications (some routers can comprise DHCP relay brokers which discuss to DHCP servers).
Within the occasion your Mac says its community interface is linked however you do not have connectivity, you may attempt clicking Renew DHCP Lease to see if it solves the issue.
DHCP makes our lives vastly simpler by putting off guide IP tackle configuration which might rapidly change into a burden on massive networks. DHCP is straightforward and automated and more often than not you will not even want to consider it.