
Sixty malicious Ruby gems containing credential-stealing code have been downloaded over 275,000 occasions since March 2023, concentrating on developer accounts.
The malicious Ruby gems have been found by Socket, which experiences they focused primarily South Korean customers of automation instruments for Instagram, TikTok, Twitter/X, Telegram, Naver, WordPress, and Kakao.
RubyGems is the official bundle supervisor for the Ruby programming language, enabling the distribution, set up, and administration of Ruby libraries, often known as gems, very like npm for JavaScript or PyPI for Python.
The malicious gems on this marketing campaign have been printed onto RubyGems.org underneath varied aliases over time. The offending publishers are zon, nowon, kwonsoonje, and soonje, spreading the exercise over a number of accounts to make the exercise tougher to hint and block.
The complete checklist of the malicious packages could be present in Socket’s report, however beneath are some notable circumstances of deceptively named or typosquatted packages:
- WordPress-style automators: wp_posting_duo, wp_posting_zon
- Telegram-style bots: tg_send_duo, tg_send_zon
- web optimization/backlink instruments: backlink_zon, back_duo
- Weblog platform mimics: nblog_duo, nblog_zon, tblog_duopack, tblog_zon
- Naver Café interplay instruments: cafe_basics[_duo], cafe_buy[_duo], cafe_bey, *_blog_comment, *_cafe_comment
All 60 gems highlighted within the Socket report current a graphical consumer interface (GUI) that seems legit, in addition to the marketed performance.
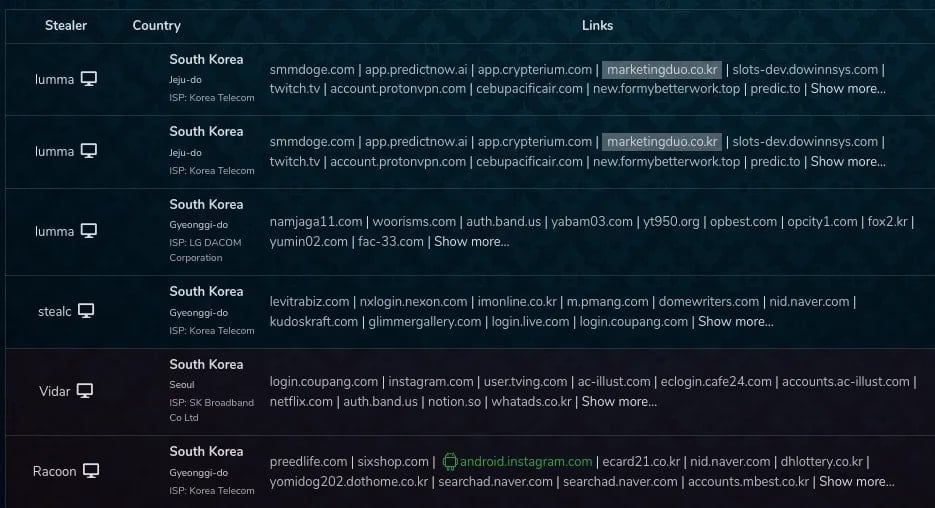
In apply, nonetheless, they act as phishing instruments that exfiltrate the credentials customers enter on the login kind to the attackers on a hardcoded command-and-control (C2) deal with (programzon[.]com, appspace[.]kr, marketingduo[.]co[.]kr).

Supply: Socket
The harvested knowledge contains usernames and passwords in plaintext, gadget MAC addresses for fingerprinting, and the bundle identify for marketing campaign efficiency monitoring.
In some circumstances, the instruments reply with a faux success or failure message, though no actual login or API name to the precise service is made.
Socket has discovered credential logs on Russian-speaking darknet markets that seem to derive from these gems, primarily based on interactions with marketingduo[.]co[.]kr, a doubtful advertising software web site tied to the attacker.
Supply: Socket
The researchers say that no less than 16 of the 60 malicious Ruby gems stay accessible, though they’ve reported all of them to the RubyGems workforce upon discovery.
Provide chain assaults on RubyGems aren’t unprecedented, they usually have been occurring for a number of years now.
In June, Socket reported one other case of malicious Ruby gems that typosquatted Fastlane, a legit open-source plugin that serves as an automation software for cell app builders, concentrating on Telegram bot builders particularly.
Builders ought to scrutinize libraries they supply from open-source repositories for indicators of suspicious code like obfuscated elements, take into account the writer’s status and launch historical past, and lock dependencies to ‘identified to be secure’ variations.


