Your undertaking is late. Once more. The explanation why may shock you. It is doubtless not as a result of your crew is dangerous at estimating with story factors. And it is virtually definitely not as a result of your crew is lazy. In my expertise, the primary cause tasks are late is just because your product is larger than you assume it’s.
You might have thought of what the ultimate product will appear to be, however the full image is inconceivable to visualise initially.
4 Causes Merchandise Develop Past Preliminary Estimates
Let’s have a look at 4 the reason why merchandise (and their product backlogs) find yourself being larger than we predict.
1. Merchandise Evolve Over Time
The primary is that wants evolve. What your customers want at the moment is not going to be what they want later. The longer it takes to go from studying their must delivering them, the extra these wants will evolve.
2. Product Backlogs Have Emergent Necessities
Second, necessities emerge. Some options in a product can solely be found after you begin creating the product. As you do, you give early variations of the product to customers. They play with it. They experiment. They usually provide you with new concepts.
These emergent necessities are options nobody would have considered till they skilled the partial product or system. They make your product bigger than you thought as a result of they have been unanticipated.
3. All Groups Overlook Some Necessities Generally
Third, some necessities are missed. Irrespective of how arduous you strive, it’s most likely inconceivable to determine upfront all the pieces your customers will want. When interviewing customers, you’ll neglect to ask a query, you received’t observe by way of with one thing a consumer mentions, otherwise you’ll run out of time. You’ll overlook one thing.
4. Some Goals Are More durable-than-Anticipated to Obtain
Fourth, some aims will likely be more durable to realize than anticipated. Groups add options, features or capabilities to a product to realize outlined aims.
For instance, an airline could wish to enhance software program utilized by its customer support representatives in order that these reps can extra shortly re-route passengers affected by flight cancellations. The airline’s builders plan to realize that goal utilizing a brand new AI system to counsel passenger re-routing.
After implementing that new functionality, crew members measure the impression and study that it has solely gotten the group midway to the specified consequence.
In that case, there will likely be further work required to acquire the target. And, so, the product has change into bigger than initially thought.
The way to Account for Product Unknowns
First is to acknowledge that regardless of how nicely crew members do the job of understanding consumer wants, they won’t consider all the pieces.
Second, have a frank dialog with stakeholders (the product proprietor’s second crew) concerning the realities of product unknowns. Get them to acknowledge that they aren’t accomplished enthusiastic about what’s wanted, that wants will evolve, and that it’s inconceivable to consider all the pieces.
Third, keep away from making guarantees about when a product’s full scope may be delivered with out including some quantity of buffer to account for a way a lot bigger the total product could actually be. However how do we all know how a lot buffer so as to add?
The way to Calculate a Product Dimension Buffer
Right here’s one approach I’ve used for deciding how a lot larger a product will doubtless change into.
- Ask crew members what proportion of the last word resolution they assume they see (50 %? 80 %? 25 %?).
- The undertaking buffer is 1 divided by the % identified.
- Multiplying the dimensions of the present product backlog by the buffer provides you an estimate of the true measurement of the product.
For instance, if the crew says they assume that they see about half of the last word resolution, that implies that the unknown a part of the product backlog is identical measurement because the identified objects on the backlog. In that case, the total product is double the dimensions you assume it’s proper now.
The system for that is simply 1 divided by the % the crew thinks they know instances the present measurement of the product backlog.

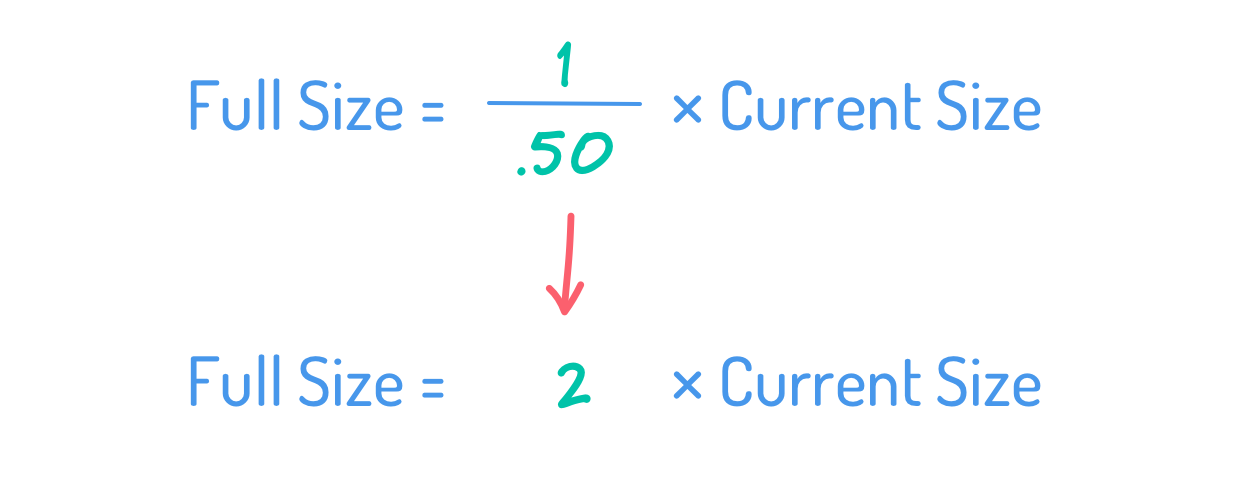
I simply gave the instance of a crew pondering they at the moment see half of the last word resolution. Substituting 50%, or 0.5, into the system, you may see that the total measurement of that product is double the present measurement.
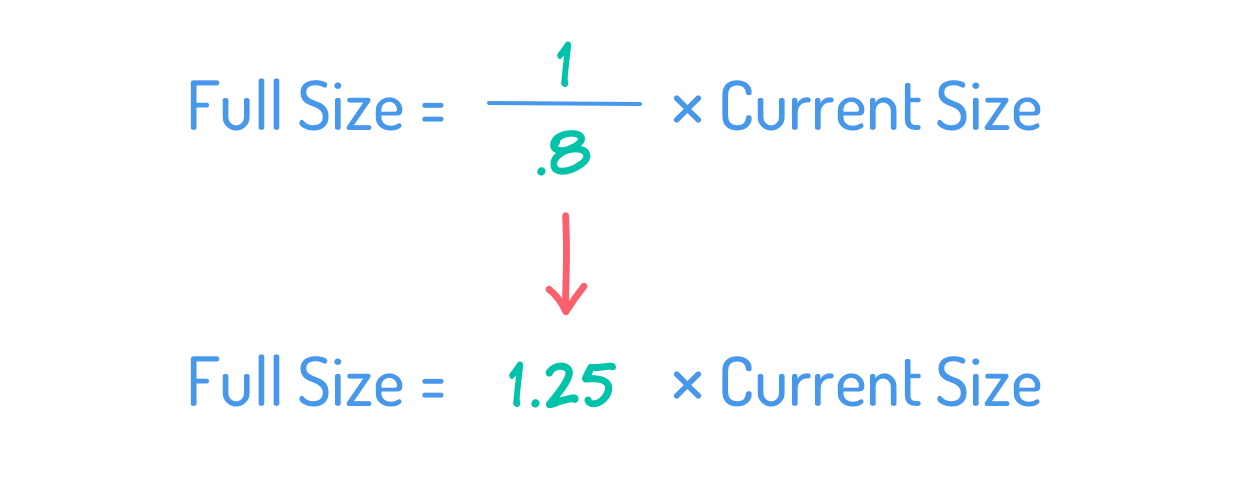
yet one more instance, suppose the crew has a collection of conversations with customers and stakeholders. Based mostly on that additional information, crew members consider they see about 80% of what customers will finally want on this product. Once we substitute 80% into the system, we see that the total measurement of the backlog is 25% better than the present measurement.
A tough calculation like this may give you an approximation of how a lot bigger your product is than the crew thinks it’s presently. This bigger measurement can be utilized in forming extra correct long-term forecasts when essential.

